Perhitungan kimia / Stoikiometri - Menghitung massa dan volume zat pada persamaan reaksi
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the Smart Chemistry channel covers essential stoichiometry concepts and chemical calculations, including how to calculate the mass and volume of unknown substances in a reaction. The video explains key topics such as balancing chemical equations, mole ratios, and the decomposition and combustion of compounds. It provides clear examples, such as determining the volume of N2O5 from N2 and O2 and calculating the mass of CO2 produced from burning ethane. The content aims to help viewers understand the steps for solving chemical problems effectively, emphasizing the importance of balanced equations and mole comparisons.
Takeaways
- 😀 Always balance the chemical equation before performing stoichiometric calculations.
- 😀 The coefficient ratio in a balanced equation is equivalent to the mole ratio and volume ratio, particularly when dealing with gases.
- 😀 Heating a substance leads to decomposition, whereas burning a substance reacts it with oxygen.
- 😀 Moles are central to stoichiometric calculations and are used to compare the amounts of substances in a reaction.
- 😀 To calculate the mass or volume of an unknown substance, use the coefficient comparison in the balanced equation.
- 😀 The formula for determining the volume of gas at STP is: volume = moles × 22.4 L.
- 😀 Remember that the mass of a substance is not directly comparable to its coefficient ratio; instead, you compare moles.
- 😀 Chemical reactions, like combustion or decomposition, follow clear, predictable stoichiometric relationships.
- 😀 In combustion reactions, hydrocarbons react with oxygen to produce CO2 and H2O, and the amount of CO2 produced can be calculated.
- 😀 To find the volume of a gas produced or consumed in a reaction, use the mole ratio and apply the ideal gas law at STP.
Q & A
What is the importance of balancing a chemical reaction equation before performing stoichiometric calculations?
-Balancing the chemical reaction equation is crucial because it ensures that the number of atoms of each element is conserved, allowing for accurate mole and volume ratios in subsequent calculations.
What is the difference between 'heated' and 'burned' in chemical reactions?
-When a substance is 'heated,' it undergoes decomposition, breaking down into simpler substances. In contrast, when a substance is 'burned,' it reacts with oxygen (O2), producing products such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
How does the concept of mole ratio relate to stoichiometric calculations?
-Mole ratio, derived from the balanced chemical equation, is used to convert between the amounts (moles) of different substances involved in the reaction. It allows for the determination of unknown substances based on known ones.
In the combustion of a hydrocarbon (CxHy), what are the typical products formed?
-The typical products of the combustion of a hydrocarbon are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), as the hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen (O2).
How do you calculate the volume of an unknown substance produced in a chemical reaction?
-To calculate the volume of an unknown substance, you use the coefficient comparison (or mole ratio) from the balanced equation, applying the known volume of a reactant and the volume ratios between reactants and products at constant pressure and temperature.
What does STP stand for, and why is it important in gas volume calculations?
-STP stands for Standard Temperature and Pressure, which is defined as 0°C (273.15 K) and 1 atm pressure. At STP, gases have a volume of 22.4 L per mole, which allows for easier calculation of gas volumes in chemical reactions.
How can you determine the mass of CO2 produced from burning ethane (C2H6)?
-To determine the mass of CO2 produced, first calculate the moles of ethane (C2H6) from its given mass, then use the mole ratio from the balanced equation to find the moles of CO2, and finally convert the moles of CO2 to mass using its molar mass.
Why is it important to use the coefficient comparison in stoichiometry, and how does it apply to gas volume calculations?
-The coefficient comparison, or mole ratio, is essential in stoichiometry because it allows you to convert between the amounts of different substances. In gas volume calculations, it helps determine the volumes of gases produced or consumed based on the volume of a given reactant or product, assuming constant pressure and temperature.
What is the significance of the 'mole = mass/Mr' formula in stoichiometry?
-The formula 'mole = mass/Mr' allows you to calculate the number of moles of a substance from its mass, where Mr is the molar mass (molecular weight) of the substance. This is a crucial step in stoichiometric calculations.
What happens to KClO3 when heated, and how is this relevant to stoichiometric calculations?
-When KClO3 is heated, it decomposes into KCl and O2. In stoichiometric calculations, you need to use the balanced equation for the decomposition to determine the amount of O2 produced, based on the amount of KClO3 reacted.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

9.1 Introduction to Stoichiometry

Gas Stoichiometry - Explained

QUANTITATIVE CHEMISTRY - GCSE Chemistry (AQA Topic C3)
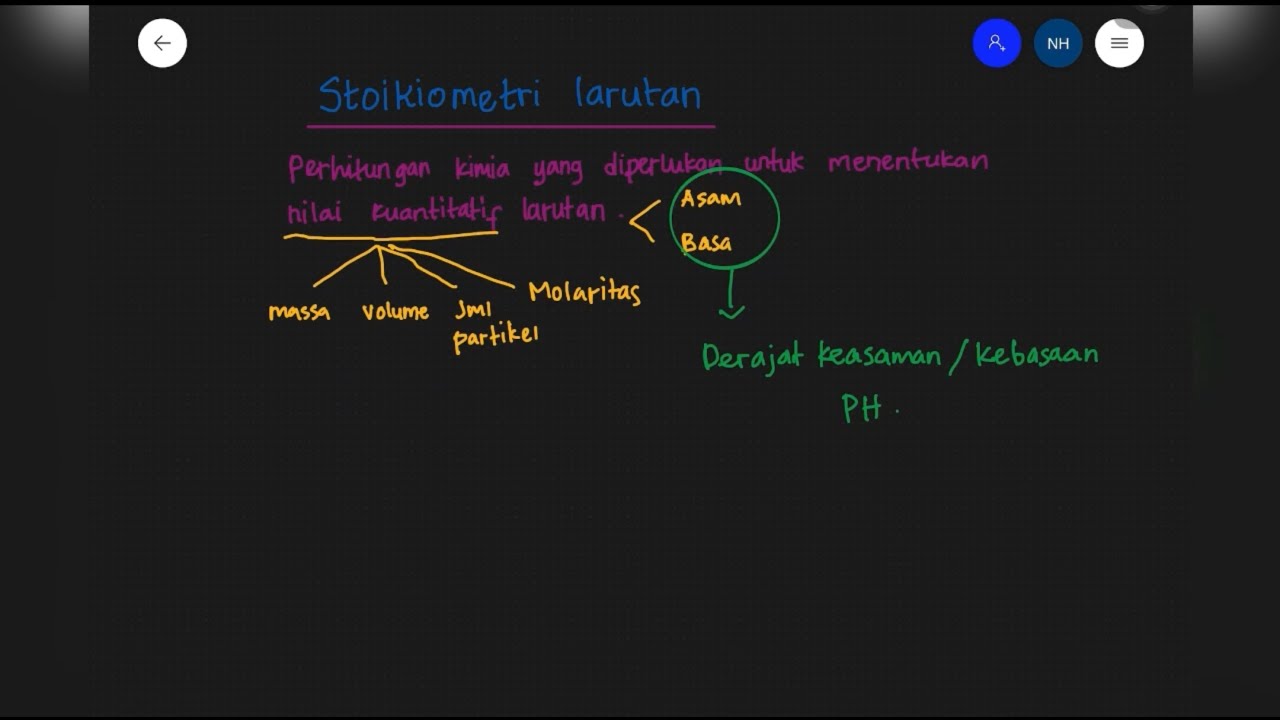
Stoikiometri Larutan || Larutan Asam dan Basa || Materi Kimia SMA Kelas XI || Hikmah nor
KONSEP MOL - KIMIA - MATERI UTBK SBMPTN DAN SIMAK UI - UTBK 2022 | SIMAK UI 2022

Konsep Mol - Stoikiometri - Perhitungan Kimia - Kimia Kelas 10
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)