STRUKTUR DAN FUNGSI SEL PENGANTAR
Summary
TLDRThis educational video covers the topic of cells, their structure, and function in biology. It introduces the concept of cells as the smallest unit of life and elaborates on their role in living organisms. The script explains key cell functions such as respiration, excretion, and reproduction, touching on the importance of cell division, including mitosis and meiosis. The lesson also discusses the use of microscopes, including light and electron microscopes, for studying cells, and touches on the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The video encourages students to explore further with online resources.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cells are the smallest unit of living things, forming the basic structural and functional components of organisms.
- 😀 Cells are capable of performing life functions such as respiration, excretion, synthesis, reproduction, and response to stimuli.
- 😀 The smallest units of life include not only cells but also molecules such as carbohydrates, fats, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
- 😀 Genetic material like DNA plays a crucial role in heredity and the transmission of traits between generations.
- 😀 Cells undergo growth and reproduction, often involving division processes like mitosis and meiosis.
- 😀 The size of cells typically ranges from 0.2 mm to 200 micrometers, and microscopes are essential for visualizing them.
- 😀 There are two types of microscopes discussed: light microscopes (with a maximum magnification of 2000x) and electron microscopes (with a magnification of up to 500,000x).
- 😀 Light microscopes in schools have ocular and objective lenses, providing magnification up to 400x, while oil immersion can increase magnification to 1000x.
- 😀 Electron microscopes come in two types: Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM), which examine the surface of objects, and Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM), which focus on internal structures like cell organelles.
- 😀 In-vitro studies are conducted in laboratories, while in-vivo studies involve examining the processes in living organisms. Both approaches help in understanding cellular components and functions.
Q & A
What is the definition of a cell as mentioned in the script?
-A cell is described as the smallest unit of living things, which forms the basic structure and function of all organisms.
What is the significance of DNA in living organisms?
-DNA is the genetic material that contains the instructions for the inheritance of traits and plays a critical role in reproduction and cell function.
What are the basic characteristics of life that cells exhibit?
-The characteristics include respiration, excretion, transportation, synthesis, reproduction, and response to stimuli.
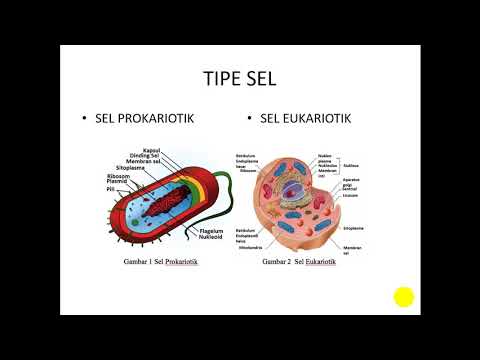
What is the distinction between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Prokaryotic cells are simpler cells without a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus and more complex structures.
What does the term 'cell division' refer to, and what are its types?
-Cell division refers to the process by which a cell reproduces. The two main types are mitosis (for growth and repair) and meiosis (for reproduction).
What are the two main types of microscopes mentioned in the script?
-The two main types of microscopes are light microscopes, which magnify up to 2000 times, and electron microscopes, which can magnify up to 500,000 times.
What is the function of the scanning electron microscope (SEM)?
-The SEM is used to examine the surface of objects, such as bacteria or cells, by scanning them with a focused electron beam.
What is the role of mitochondria in the cell?
-Mitochondria are cell organelles responsible for energy production through cellular respiration. They also contain structures called cristae.
What does 'in vitro' and 'in vivo' mean in biological studies?
-'In vitro' refers to studies conducted outside the living organism, typically in a laboratory setting, while 'in vivo' refers to studies conducted within a living organism.
How does the magnification of light microscopes compare to electron microscopes?
-Light microscopes offer a maximum magnification of 2000 times, while electron microscopes can provide magnifications up to 500,000 times, allowing for much more detailed observations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Cells: Structures and Functions | Biology

PENGENALAN SEL - IPA KELAS 8 SMP KURIKULUM MERDEKA
BIOLOGI KELAS 11 MATERI SEL : Tipe Sel, Organel Sel dan Transportasi Zat Antar Membran

Struktur dan Fungsi Karbohidrat | Biomolekul #2

Introduction to Biology | Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 Nepal | Biology Class 11 in Nepal | Sj Classes

Biologi Kelas XI - Sel - Pengertian dan Bagian-Bagian Sel
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)