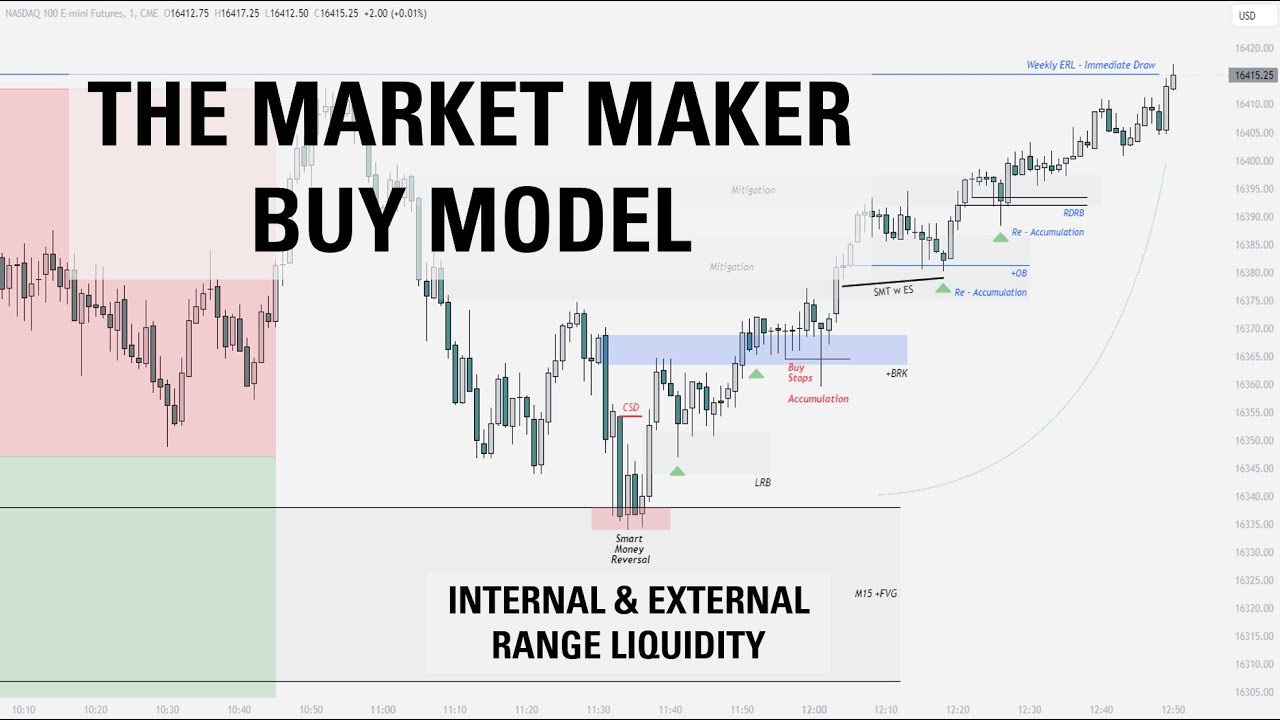
Your Market Maker Model Guide (MMXM Secrets)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker provides a comprehensive breakdown of the Market Maker Model, emphasizing the importance of understanding market context through different time frames and fair value gaps (FVGs). They explain how traders can navigate the market by identifying high-probability areas of price action using FVGs and adjust their entries based on context. The speaker highlights the importance of avoiding tight stop losses and focusing on higher time frames for better accuracy. With practical tips and a step-by-step approach, the video empowers traders to capitalize on high-probability setups and improve their decision-making skills.
Takeaways
- 😀 The importance of context in trading: Understanding the context of higher time frames is crucial for identifying high-probability trade setups.
- 😀 Time frames are hierarchical: To refine your entry point, zoom into lower time frames once a high or low context level is identified on a higher time frame.
- 😀 Lags in price action are key: Recognizing pauses or lag zones in price movement is essential for making informed trade decisions.
- 😀 Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are critical tools: FVGs help traders pinpoint reliable entry points, especially on higher time frames like the 1-hour or 15-minute.
- 😀 Don’t get distracted by small fluctuations: Smaller FVGs on low time frames like the 1-minute can lead to low-probability setups, so focus on larger, more reliable gaps.
- 😀 Stop loss management: Setting a reasonable stop loss is important to avoid getting stopped out prematurely due to normal market fluctuations.
- 😀 The Market Maker Model: Understanding how market makers manipulate liquidity is key for identifying where the market will likely continue or reverse.
- 😀 Market movements are fractal: Similar price action patterns can be observed across different time frames, making it easier to recognize high-probability setups.
- 😀 The entry pattern is simple: Once the context is defined and the right liquidity levels are identified, the entry pattern becomes straightforward and easy to execute.
- 😀 Be cautious with tight stop losses: Avoid suffocating your stop loss; this could lead to getting stopped out unnecessarily, as the hard work has already been done in identifying the context.
- 😀 Continuous learning is essential: By studying live examples, like the ones shared in the video, you can improve your understanding of market maker models and become more effective at predicting market movements.
Q & A
What is the importance of context in market maker models?
-Context is essential for identifying high-probability price movements. By understanding the broader market context (e.g., using higher time frames like 4-hour, daily, and weekly charts), traders can more accurately predict future price action, distinguishing between premium and discount arrays.
How does a trader identify the right time frame for trading?
-Traders should start with higher time frames (like 4-hour or daily) to establish context. Once the market context is understood, they can zoom in to lower time frames (e.g., 1-hour, 5-minute, or 1-minute) for precise entries based on fair value gaps (FVGs).
What role do fair value gaps (FVGs) play in market analysis?
-FVGs are key indicators that help identify areas where price action is likely to continue or reverse. These gaps are used to predict where market maker models will form, guiding traders to profitable entry points and ensuring they trade in high-probability areas.
Why is it critical to avoid suffocating your stop loss?
-Suffocating a stop loss, by making it too tight, increases the likelihood of getting stopped out before the price moves in the expected direction. This can lead to unnecessary losses. It's important to give the trade room to breathe and avoid excessive emotional reactions.
What should a trader focus on when analyzing market maker models?
-A trader should focus on understanding where and when market maker models form by identifying the context (premium vs. discount arrays) and observing fair value gaps (FVGs). Entry patterns and stop-loss placement are secondary to establishing the right context.
What happens when a lag doesn’t hold in market maker models?
-When a lag doesn’t hold, it may be because new context has emerged. This requires zooming out to a higher time frame to understand the broader market context. Lower probability lags are more likely to occur when higher time frame context is ignored.
How does the fractal nature of market maker models work?
-Market maker models operate in a fractal manner, meaning the same principles apply across different time frames. A market maker model on a weekly chart, for example, can have corresponding smaller models on daily, 4-hour, and lower time frames, all working together to provide entry opportunities.
What is the relationship between different time frame fair value gaps?
-Fair value gaps (FVGs) on higher time frames (e.g., weekly or daily) are stronger than those on lower time frames (e.g., 5-minute). Traders should prioritize gaps on higher time frames when deciding on potential trade setups, as they represent stronger market forces.
What is the importance of emotional discipline in trading based on market maker models?
-Emotional discipline is vital in trading, as traders may be tempted to overcomplicate entry decisions or set stop losses too tightly due to fear or greed. A systematic approach helps traders stay objective, focusing on context and high-probability setups instead of emotional impulses.
How can a trader apply the market maker model in real-time trading?
-In real-time trading, traders can apply the market maker model by analyzing the market context, looking for fair value gaps, and waiting for the right entry patterns. For example, a trader can forecast price movement using the weekly or daily context, and execute trades on lower time frames like 1-minute or 5-minute, following the identified gaps and price action.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)