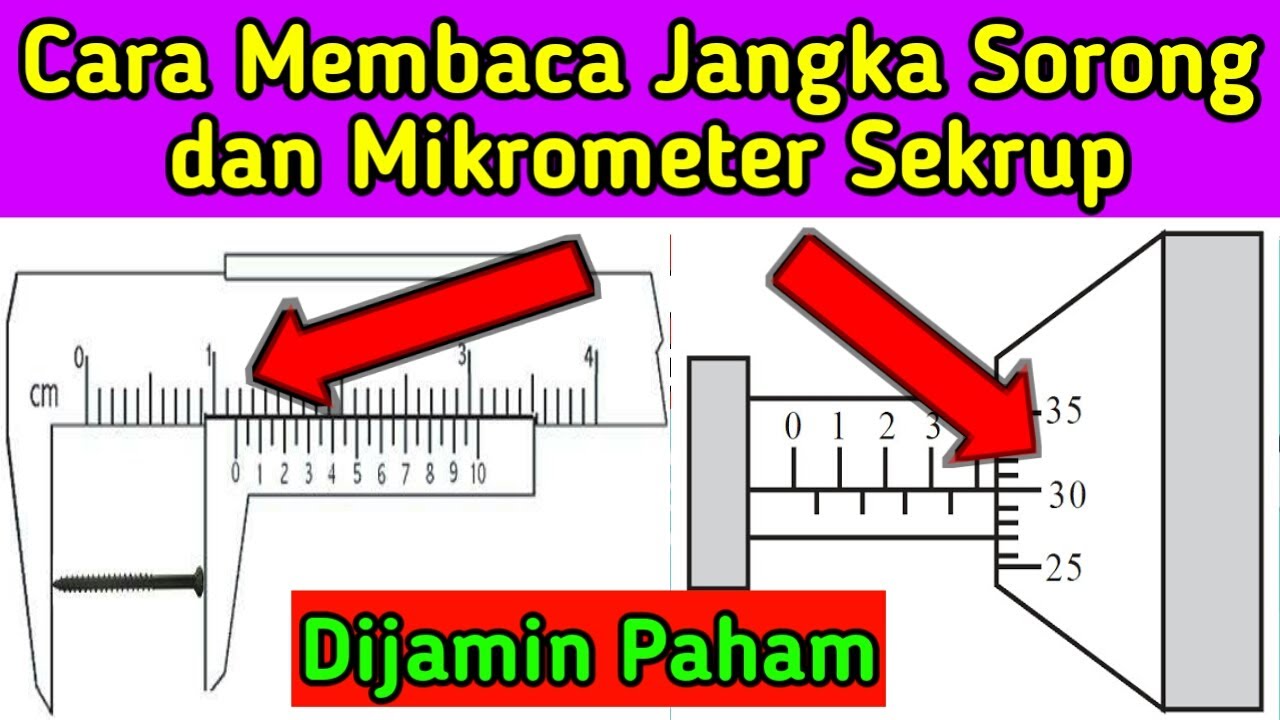
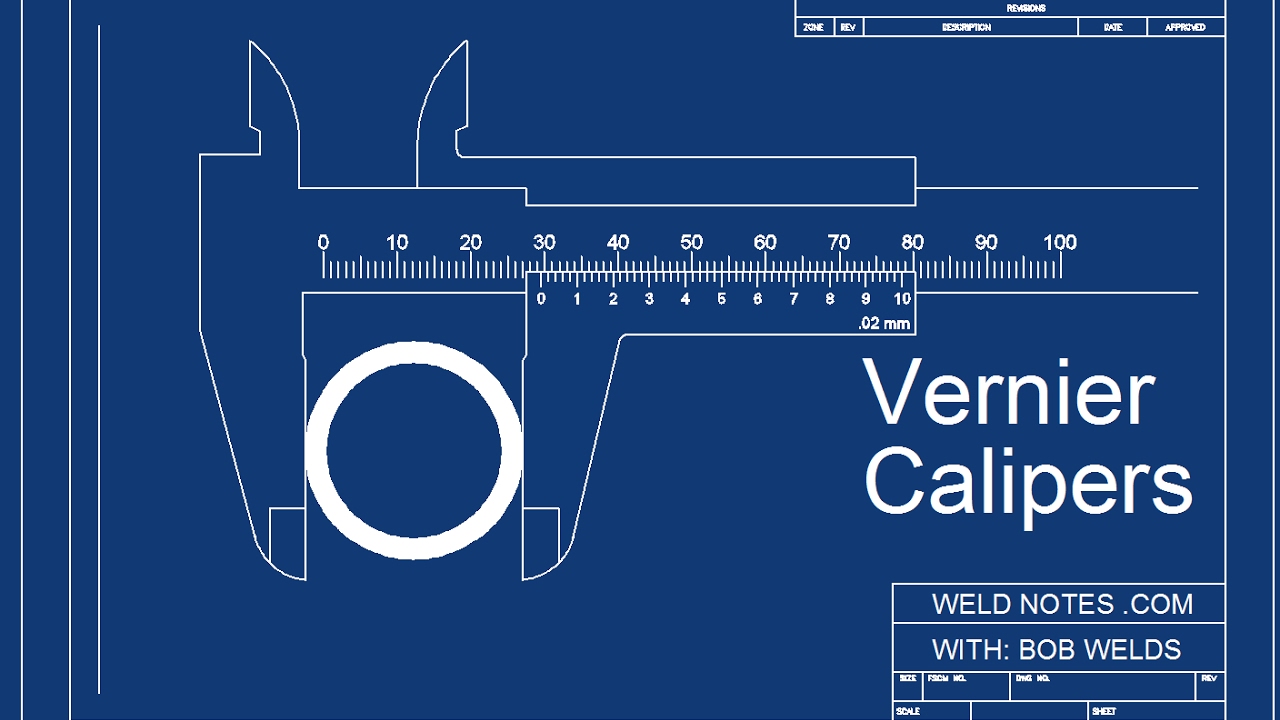
Vernier Callipers Experiment Introduction Edunovus Online Smart Practicals
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the working principle and usage of vernier calipers, a precise measuring instrument used to measure small objects more accurately than a regular meter scale. It covers the components of vernier calipers, including the main scale, vernier scale, and jaws for measuring external and internal diameters. The video also explains how to calculate measurements using these scales, demonstrating the process with examples. Additionally, it discusses zero errors and corrections that may occur due to manufacturing defects or wear in the device. The importance of the least count in determining accurate measurements is also highlighted.
Takeaways
- 😀 Verner Calipers are precise measuring instruments used in physics labs to measure small objects that cannot be measured accurately with a standard meter scale.
- 😀 The Verner Calipers were invented by French mathematician Pierre Verner in 1631 and consist of two main components: a fixed main scale and a movable vernier scale.
- 😀 The calipers have two jaws: external jaws for measuring the diameter of objects like spheres or cylinders, and internal jaws for measuring the diameter of hollow objects.
- 😀 A metal strip on the back of the calipers is used to measure the internal depth of cylindrical objects.
- 😀 The vernier scale works based on the Vernier principle, where one scale (main scale) is divided into smaller divisions that are measured by a second scale (vernier scale).
- 😀 The least count of the Verner Calipers is 0.1 mm, representing the smallest length that can be measured accurately.
- 😀 To calculate the length of an object using Verner Calipers, the total reading is the sum of the main scale reading and the vernier scale reading multiplied by the least count.
- 😀 In case of zero errors, if the zero of the vernier scale is to the right of the main scale, it's known as a positive zero error, requiring a negative correction.
- 😀 If the zero of the vernier scale is to the left of the main scale, it's called a negative zero error, and the correction is positive.
- 😀 The formula for total reading is: Main Scale Reading + (Vernier Coincidence × Least Count), and corrections are applied based on any observed zero error.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of vernier calipers?
-Vernier calipers are primarily used to measure the lengths of small objects accurately, which cannot be measured using a regular meter scale.
Who invented the vernier calipers, and when?
-The vernier calipers were invented by the French mathematician Pierre Vernier in 1631.
What is the structure of the vernier calipers?
-Vernier calipers consist of a long rectangular metal strip with a fixed jaw at one end, graduated in inches at the top and in centimeters at the bottom, which is called the main scale. A movable rectangular metal strip with a special graduation, called the vernier scale, slides over the main scale.
What are the two types of jaws in the vernier calipers used for?
-The external or lower jaws are used to measure the diameter of solid objects like spheres or cylinders, while the internal or upper jaws are used to measure the internal diameter of hollow cylinders.
How does the vernier caliper measure depth?
-A metal strip at the back of the vernier calipers is used to measure the internal depth of a cylinder.
What is the vernier principle?
-The vernier principle involves dividing a given length into smaller divisions of different lengths using two scales, the main scale and the vernier scale. This allows for precise measurements by comparing the two scales' divisions.
What is the least count or vernier constant of the vernier calipers?
-The least count or vernier constant of the vernier calipers is the smallest length that can be accurately measured. It is equal to the difference between one main scale division and one vernier scale division, typically 0.1 mm.
How do you calculate the total reading using the vernier calipers?
-The total reading is calculated by adding the main scale reading to the product of the least count and the vernier scale reading (vernier coincidence). The formula is: Total reading = Main scale reading + (Vernier coincidence × Least count).
What is zero error in the context of vernier calipers?
-Zero error occurs when the zero of the vernier scale does not coincide with the zero of the main scale. This can either result in an excess or a deficiency in the measurement, requiring a correction to obtain accurate readings.
How do you correct for positive and negative zero errors?
-In the case of a positive zero error, the reading should be corrected by subtracting the extra length measured by the instrument. For a negative zero error, the correction involves adding the extra length to the reading.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)