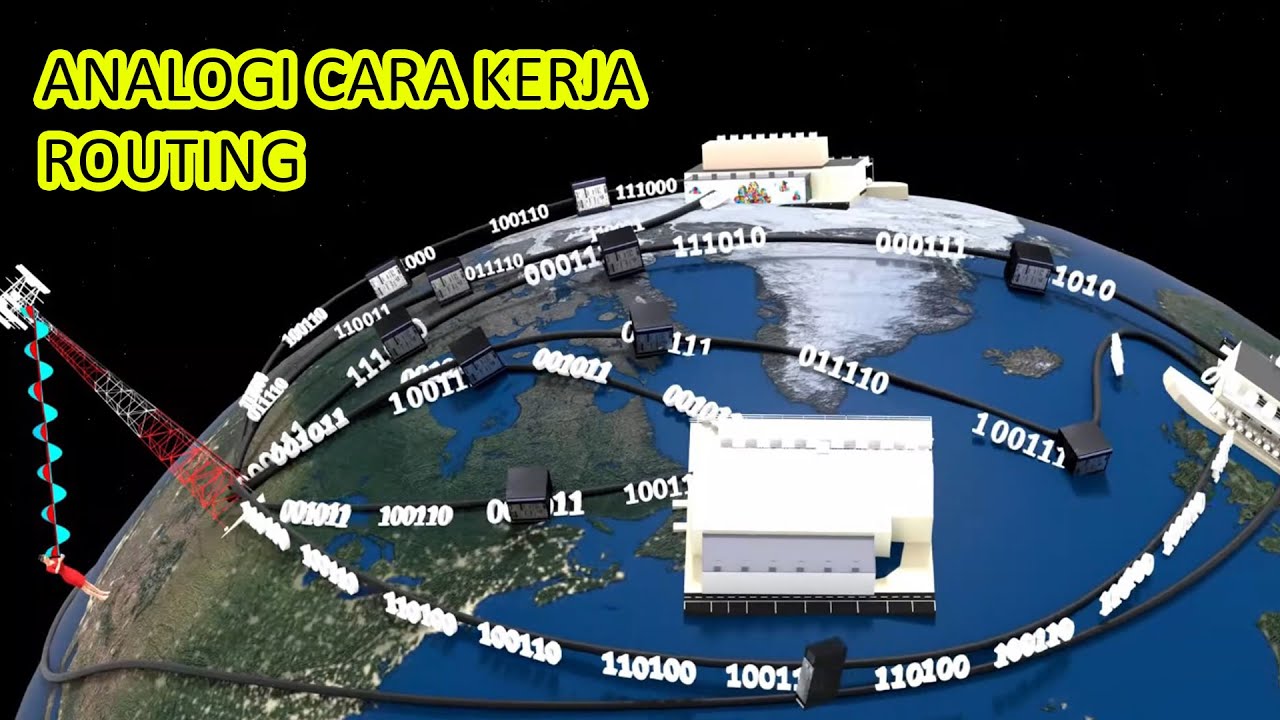
Pertemuan 13 - Routing Fundamental
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses the fundamentals of routing, focusing on both static and dynamic routing. It explains how static routing requires manual intervention by network administrators, best suited for small-scale networks with limited routes. On the other hand, dynamic routing uses protocols to automatically adjust to topology changes and is more suitable for large-scale networks. The video further explores routing protocols like BGP and IGP, differentiating between vector design and state-circle protocols. Emphasis is placed on the importance of selecting the appropriate routing protocol based on network needs and scale.
Takeaways
- 😀 Routing is a mechanism for sending data packets across networks, operating at Layer 3 of the OSI model.
- 😀 Static routing requires manual configuration by a network administrator to define routes and update the routing table.
- 😀 Static routing is best suited for small-scale networks with a single route or limited exit paths.
- 😀 A disadvantage of static routing is the need to manually adjust the routing table when the network topology changes.
- 😀 Static routing is more resource-efficient as it consumes fewer router resources, but it can become complex and difficult to manage as the network grows.
- 😀 Dynamic routing uses routing protocols to automatically determine routes based on network conditions and topology changes.
- 😀 Dynamic routing is suitable for networks with multiple routers and complex routing paths, as it can adapt to changes without manual intervention.
- 😀 Routing protocols help routers communicate and exchange routing information, with two main types: Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) and Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP).
- 😀 IGP protocols like RIP and OSPF calculate the best route based on either distance or bandwidth to ensure the fastest path.
- 😀 The major distinction between vector-based and link-state routing protocols is that vector protocols calculate the closest path based on distance, while link-state protocols consider bandwidth and speed to find the optimal route.
- 😀 Routing protocols are essential for large networks where multiple routes or ISPs are used, ensuring redundancy and continuous network connectivity even if one route or ISP fails.
Q & A
What is the purpose of routing in networking?
-Routing is a mechanism for sending data packets from one network to another. It operates at layer 3 of the OSI model and determines the best path for data transmission between networks.
What is static routing, and when is it typically used?
-Static routing involves manually configuring the routing table of a network device. It is used in small networks with simple topology or when there is only one route for data to follow. It requires the network administrator to intervene whenever there are changes in the network topology.
What are the advantages of static routing?
-Static routing saves resources on routers as it doesn't consume much power or require complex configurations. It is also considered safer because the administrator knows the exact routing paths.
What are the disadvantages of static routing?
-The main disadvantage is that it becomes complicated when the network grows or if there are frequent changes in topology. Manual intervention is required to update the routing table, which can be time-consuming.
How does dynamic routing differ from static routing?
-Dynamic routing automatically adjusts to changes in the network by using routing protocols. Unlike static routing, no manual configuration is required when the network topology changes. It is more suitable for larger networks with multiple routers and paths.
What are the key characteristics of dynamic routing?
-Dynamic routing protocols enable routers to share information and adapt to network changes without manual intervention. This approach is ideal for large, complex networks where paths may change frequently.
What are the potential drawbacks of dynamic routing?
-Dynamic routing can place a heavy load on routers as they must constantly update routing tables and communicate with other routers. This can impact router performance, especially in large-scale networks.
What are routing protocols, and why are they important?
-Routing protocols are standards that govern the communication between routers to share information and determine the best routes for data. They are important because they allow devices to exchange routing information and ensure data is efficiently transmitted across networks.
What is the difference between exterior gateway protocols (EGP) and interior gateway protocols (IGP)?
-EGPs are used to exchange routing information between different autonomous systems, such as on the internet, while IGPs are used within a single autonomous system to route traffic between routers.
What are some examples of IGP routing protocols mentioned in the transcript?
-Examples of IGP routing protocols mentioned include RIP (Routing Information Protocol) and OSPF (Open Shortest Path First). These protocols are used within a single network to manage routing information.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)