Absorption Bands in Infrared Spectroscopy
Summary
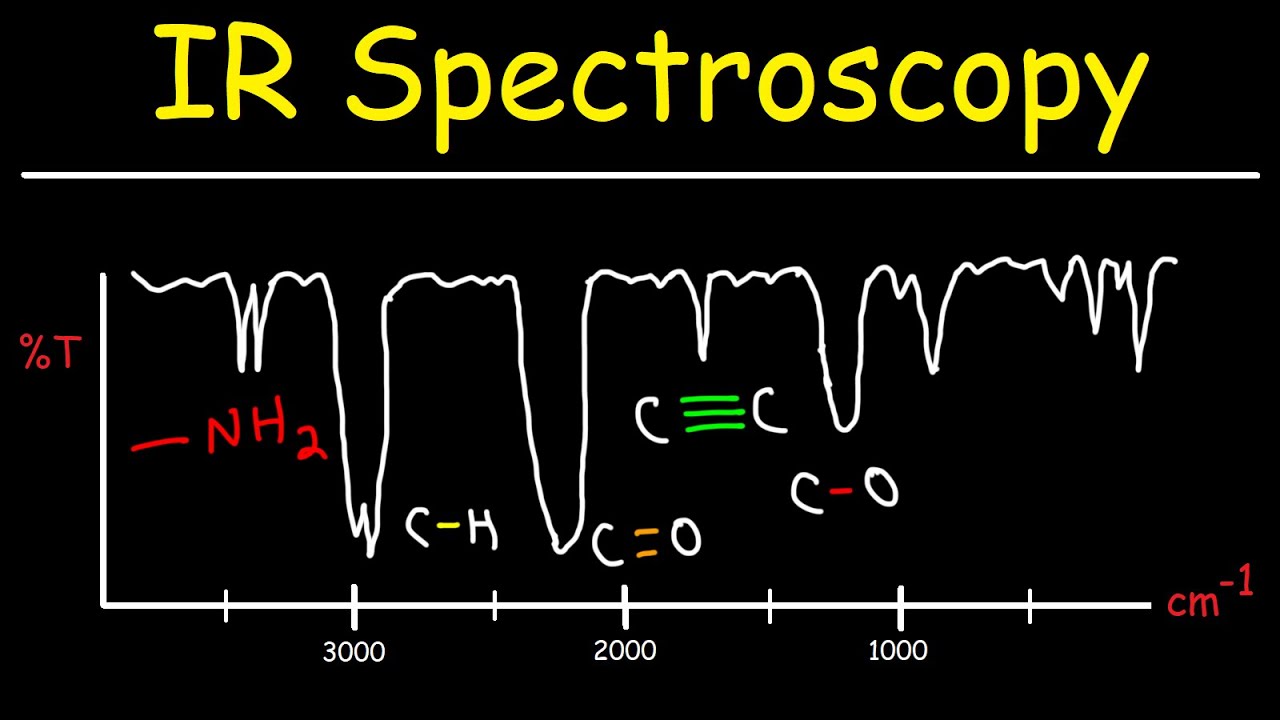
TLDRThis lecture explores the relationship between the intensity of absorption bands in IR spectra and the dipole moment of bonds. It explains that a greater dipole moment, influenced by the charge difference and bond length, leads to a more intense absorption band. Stronger bonds, such as C=O, have higher dipole moments, resulting in more intense signals compared to weaker ones like C=C. The lecture also highlights the polarities of bonds like CH, OH, and NH, with OH bonds being the most intense due to their high polarity. Understanding these concepts helps interpret IR spectra and predict absorption intensities.
Takeaways
- 😀 The intensity of absorption bands in IR spectroscopy varies, with some peaks being strong, broad, and others weak or medium intensity.
- 😀 Absorption band intensity is related to the dipole moment of the bond causing the absorption, which is influenced by the charge on the atoms and the bond length.
- 😀 The dipole moment (μ) is calculated using the equation μ = e × D, where 'e' is the charge on the atoms and 'D' is the bond length.
- 😀 A greater dipole moment results in a greater change in dipole when the bond stretches, leading to a stronger absorption band.
- 😀 The greater the change in dipole moment during bond stretching, the more intense the absorption band is in the IR spectrum.
- 😀 Bonds with a greater difference in electronegativity between the atoms, such as C=O, result in stronger absorption bands due to a higher dipole moment.
- 😀 The C=O bond has a stronger IR absorption band compared to the C=C bond because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon, creating a larger dipole moment.
- 😀 The CH bond is the least polar and therefore produces a weak absorption band in the IR spectrum.
- 😀 The OH bond is the most polar bond among CH, NH, and OH bonds, leading to the strongest absorption intensity in the IR spectrum.
- 😀 NH bonds have a medium intensity on the IR spectrum, falling between CH and OH bonds in terms of polarity and dipole moment.
- 😀 Understanding the relationship between dipole moment and absorption intensity helps interpret molecular interactions in IR spectroscopy and the corresponding absorption bands.
Q & A
What is the relationship between the intensity of an absorption band and the type of bond?
-The intensity of an absorption band is related to the dipole moment of the bond. A greater dipole moment leads to a more intense absorption band in the infrared (IR) spectrum.
Why do some absorption bands have higher intensities than others?
-The intensity of absorption bands depends on the dipole moment of the bond. Bonds with a greater dipole moment cause a larger change in dipole when they stretch, leading to more intense absorption bands.
What equation is used to understand the dipole moment of a bond?
-The dipole moment is given by the equation: Dipole moment = e × D, where 'e' is the charge on the atoms and 'D' is the bond length or the distance between the atoms.
How does the dipole moment change when a bond stretches?
-When a bond stretches, the bond length (D) increases, which in turn increases the dipole moment, since the dipole moment is directly proportional to both the charge on the atoms and the bond length.
What is the connection between the change in dipole moment and the intensity of the absorption band?
-The greater the change in dipole moment during bond stretching, the more intense the absorption band will be in the IR spectrum.
Why is the C=O bond more intense than the C=C bond in an IR spectrum?
-The C=O bond is more intense because the oxygen atom is more electronegative than carbon, leading to a greater dipole moment. This stronger dipole moment causes a more intense absorption band.
How does the electronegativity of atoms affect the intensity of absorption bands?
-The greater the electronegativity difference between the atoms in the bond, the more polar the bond becomes, which increases the dipole moment and the intensity of the absorption band.
What is the relative intensity of the O-H, N-H, and C-H bonds in the IR spectrum?
-In the IR spectrum, the O-H bond has the strongest intensity, the N-H bond has a medium intensity, and the C-H bond has the weakest intensity. This is due to the difference in dipole moments, with O-H being the most polar and C-H the least.
Why is the CH bond less intense compared to the OH bond in IR spectroscopy?
-The CH bond is less intense because carbon and hydrogen have similar electronegativities, resulting in a less polar bond and a smaller dipole moment. In contrast, the O-H bond is highly polar due to the large electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen.
What do we learn from the IR absorption bands of functional groups like C=O, O-H, and N-H?
-From the IR absorption bands of functional groups, we learn that the greater the dipole moment of a bond, the more intense the absorption band. This is reflected in the relative strengths of the absorption bands, with C=O being stronger than C=C, and O-H being stronger than C-H.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)