ESPELHOS ESFÉRICOS | AULA 01 | ELEMENTOS GEOMÉTRICOS
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the key principles of optics, specifically focusing on concave and convex mirrors. It discusses the concept of focal points, how light rays behave when they reflect off these mirrors, and the relationship between the center of curvature and the focal point. The teacher emphasizes the mathematical formulas used to calculate the distances involved, such as the distance between the vertex and the center, as well as the focus being half of that distance. Throughout, the instructor encourages active participation and reinforces key concepts with practical examples and exercises.
Takeaways
- 😀 Concave mirrors focus light inward, while convex mirrors spread light outward.
- 😀 The focal point of a concave mirror is halfway between the vertex and the center of curvature.
- 😀 The focal length is always half of the radius of curvature in a concave mirror.
- 😀 The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
- 😀 A concave mirror's reflective surface is on the inside, while a convex mirror's is on the outside.
- 😀 The focus is at the midpoint of the distance between the vertex and the center of curvature.
- 😀 If the distance from the center to the focus is 10 cm, the total radius will be 20 cm.
- 😀 The center of curvature and the focus should have the same distance from the vertex in a concave mirror.
- 😀 When discussing mirrors, the term 'principal axis' refers to the line passing through both the center and the vertex.
- 😀 The focus of a concave mirror can be visualized as halfway between the center of curvature and the vertex, which helps in determining measurements for rays and angles.
- 😀 Students are encouraged to practice the concepts by interacting with the lesson and solving example problems along with the instructor.
Q & A
What is the distance from the focus to the center of curvature in the mirror geometry discussed?
-The distance from the focus to the center of curvature is always half of the distance from the vertex to the center of curvature. For example, if the distance from the vertex to the center is 50 cm, the distance from the focus to the center would be 25 cm.
What distinguishes a concave mirror from a convex mirror?
-A concave mirror has its reflective surface on the inside, while a convex mirror has its reflective surface on the outside. This difference affects how light rays are reflected.
How does the angle of incidence relate to the angle of reflection in this mirror system?
-According to the law of reflection, the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection. This is a fundamental property of all mirrors.
What is the principal axis of a mirror, and where does it pass through?
-The principal axis is the straight line that passes through both the center of curvature and the vertex of the mirror. This axis is crucial for understanding the behavior of light rays and reflections.
Why is the focus always located at the midpoint between the center and the vertex in a concave mirror?
-The focus is always at the midpoint because the distance from the vertex to the center of curvature is divided into two equal parts, with the focus being halfway between them.
What is the focal distance in terms of the radius of curvature?
-The focal distance is always half the radius of curvature. For instance, if the radius is 20 cm, the focal distance will be 10 cm.
What happens when light rays strike the concave mirror's surface?
-When light rays strike the concave mirror's reflecting surface (the inner side), they reflect in a way that converges at the focal point, forming a real image.
How can one calculate the total radius of curvature if the focal distance is known?
-The total radius of curvature is twice the focal distance. So if the focal distance is 10 cm, the radius of curvature will be 20 cm.
How is the law of reflection used to solve problems with mirrors?
-The law of reflection is used to relate the angles of incidence and reflection. This principle helps determine the path of light rays and the position of images in various mirror problems.
What should students do if they are having trouble understanding the material discussed in the lesson?
-Students should review the available resources, such as the PDF and exercises provided, and feel free to contact the instructor via the chat for further clarification if needed.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

CAHAYA DAN ALAT OPTIK (PART 3) : CERMIN CEMBUNG DAN LENSA CEKUNG IPA KELAS 8 SMP

Espelhos Planos, Côncavos e Convexos (Como as Imagens se Formam?)
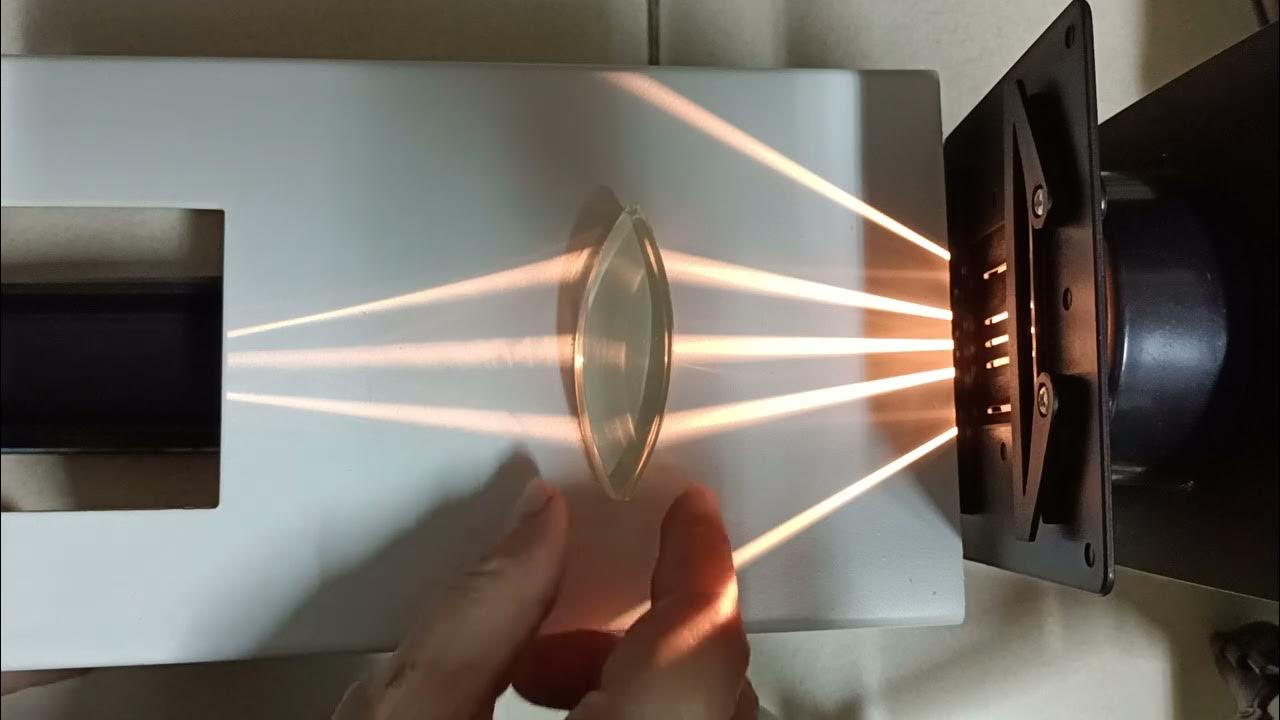

Pembiasan Cahaya Lensa Cembung dan Lensa Cekung

SPHERICAL MIRRORS
Cermin (4) - Cermin Cembung, Sifat Bayangan Cermin Cembung, Rumus Cermin Cembung - Fisika SMP

Grade 10 SCIENCE | Quarter 2 Module 7 | Refraction in Lenses • Ray Diagrams • Lens Equation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)