1.- Enrutamiento Estático 3 Routers
Summary
TLDRThe video script details a step-by-step process of setting up a static routing network with multiple routers and machines. It covers the physical connection using UTP cables, configuring IP addresses, and setting up gateways for different subnets. The script also explains the process of enabling serial connections, adjusting routing tables, and verifying network connectivity between devices. The focus is on the technical aspects of network configuration and static routing.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script describes a process of setting up a static routing network with two routes.
- 🛠️ It begins by creating a network with a switch and three machines connected via UTP cables through their Ethernet ports.
- 🔌 The script mentions the need to press 'control' to maintain the connection and to turn off the router before adding a module.
- 💡 After powering on the router, the script discusses the configuration of the network, including assigning a network number and setting a static IP address for the machines.
- 📝 The script specifies the use of a Class C network with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- 🔄 It details the process of changing the IP address for different networks and setting the gateway.
- 🔗 The script explains the importance of checking connections between machines and the router to ensure they are properly established.
- 🔄 It also covers the process of copying and setting up a second network with a different IP scheme.
- 🚀 The script includes instructions for setting up static routing between different networks, specifying the network, subnet mask, and next hop.
- 🔍 It emphasizes the need to verify communication between networks and to make adjustments to routing rules as necessary.
- 🔄 Lastly, the script mentions adding a third network and adjusting the static routing rules to accommodate the new network setup.
Q & A
What is the primary objective of the video script?
-The primary objective of the video script is to demonstrate the process of setting up a static routing network with multiple routers and machines.
How many machines and routers are involved in the initial network setup described in the script?
-In the initial network setup, there are three machines and one switch involved.
What type of cable is used to connect the machines to the switch in the script?
-The machines are connected to the switch using UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cables through their Ethernet ports.
Why does the router show all connections in red at the beginning of the script?
-The router shows all connections in red because all its connections are initially turned off or disconnected.
What is the purpose of placing a module in the router's physical interface as described in the script?
-The module is placed in the router's physical interface to expand its connectivity, allowing for more devices to be connected to the network.
What is the IP address range used for the first network setup in the script?
-The IP address range used for the first network setup is 192.168.10.x, with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
How does the script describe changing the IP addresses for different networks?
-The script describes changing the last digit of the IP address, such as changing from 10 to 20, and adjusting the gateway accordingly.
What is the purpose of configuring static IP addresses for the machines in the script?
-Configuring static IP addresses ensures that each machine has a fixed IP address and can be easily managed and accessed within the network.
What is the significance of the serial interface mentioned in the script when connecting routers?
-The serial interface is used to connect routers for inter-router communication, allowing them to exchange routing information and facilitate data transfer between different networks.
How does the script describe the process of enabling communication between different networks?
-The script describes the process of enabling communication by configuring static routing, specifying the destination network, subnet mask, and the next hop router's IP address.
What is the final step described in the script for ensuring proper network communication?
-The final step described is to verify that there is communication between all devices and routers, checking for successful pings and ensuring that the connections are stable.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
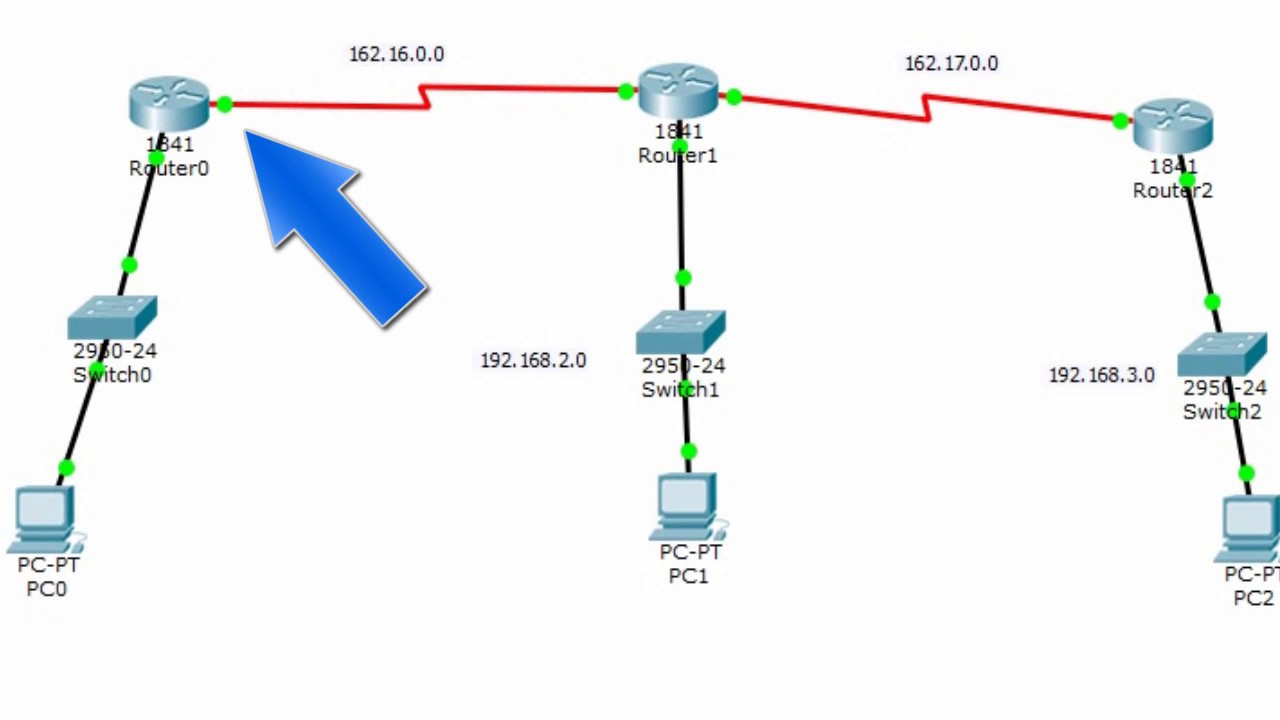
Enrutamiento estatico (3 router) Packet Tracer
PENJELASAN VLAN + HOTSPOT (MIKROTIK) | 12-12-2022

Penjelasan lengkap dan penyelesaian UKK TKJ 2025 paket 2

Konfigurasi Routing Dinamis di Cisco Packet Tracer #5 BGP (Border Gateway Protocol)

Implementasi Static Routing pada Jaringan VPN

Cara Konfigurasi Routing Statis Dengan 3 Router 3 Switch 9 PC di Cisco Packet Tracer
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)