Bagaimanakah Tahapan Reaksi Gelap?
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains the Calvin Cycle, a key part of photosynthesis, also known as the dark reaction. It outlines how plants use carbon dioxide to produce sugar through a series of reactions, following the light reactions that generate ATP and NADPH. The video details each step of the cycle, including carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration of RuBP. The process requires ATP and NADPH, and it contrasts with human respiration, where oxygen is needed to break down sugars for energy. The video concludes with a challenge question and further exploration into C3, C4, and CAM pathways.
Takeaways
- 😀 The dark reaction in photosynthesis is also known as the Calvin cycle, where carbon dioxide is used by plants to produce glucose.
- 😀 The Calvin cycle does not require direct sunlight, which is why it is also called the dark reaction.
- 😀 The Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma of chloroplasts, after the light reaction has produced ATP and NADPH.
- 😀 ATP and NADPH, generated in the light reaction, provide energy for the Calvin cycle to fix carbon and produce sugars.
- 😀 The Calvin cycle produces G3P (Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate), a three-carbon sugar, not glucose directly, which contains six carbons.
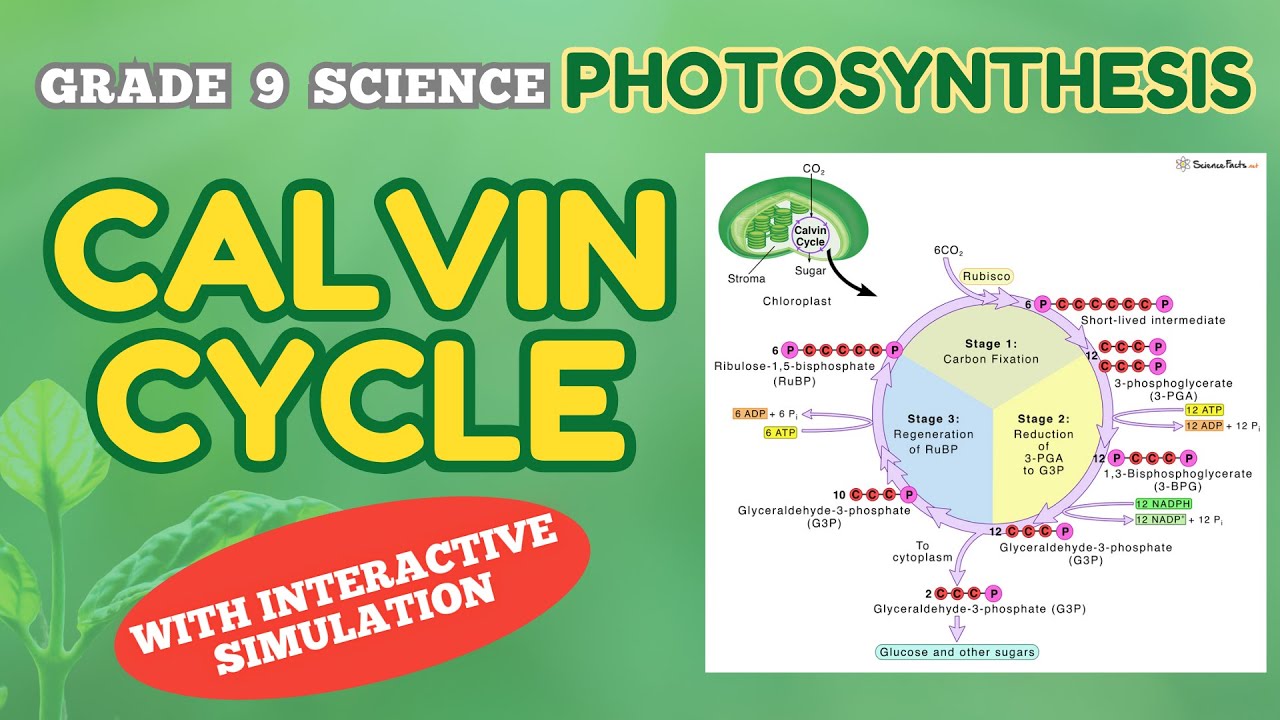
- 😀 In the first phase of the Calvin cycle, carbon dioxide is fixed by Rubisco, combining with RuBP (Ribulose bisphosphate).
- 😀 The Calvin cycle involves a series of reactions: fixation, reduction, and regeneration of RuBP.
- 😀 The second phase of the Calvin cycle reduces 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA) to G3P using ATP and NADPH.
- 😀 For each cycle, the Calvin cycle produces one molecule of G3P, but five molecules are recycled to regenerate RuBP.
- 😀 To form one G3P, the Calvin cycle requires nine ATP molecules and six NADPH molecules.
- 😀 Oxygen is required for human respiration to break down glucose and produce energy, while plants need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis to build organic materials like glucose.
Q & A
What is the Calvin Cycle, and why is it also called the dark reaction?
-The Calvin Cycle, also known as the dark reaction, is a part of photosynthesis where carbon dioxide is converted into glucose. It is called the dark reaction because it does not require sunlight directly to occur, unlike the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
Who discovered the Calvin Cycle, and why is it named after him?
-The Calvin Cycle is named after Melvin Calvin, the scientist who discovered the process. The cycle is named after him because he identified the reactions that convert carbon dioxide into sugars in plants.
How do ATP and NADPH play a role in the Calvin Cycle?
-ATP and NADPH, produced during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, provide the energy and electrons needed for the Calvin Cycle. ATP is used to convert intermediate compounds, while NADPH is used in the reduction phase to form G3P (Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate).
What is the first step of the Calvin Cycle, and what molecules are involved?
-The first step of the Calvin Cycle is fixation, where three molecules of CO2 combine with three molecules of ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme Rubisco, resulting in an unstable intermediate that breaks down into three molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate.
What happens during the reduction phase of the Calvin Cycle?
-During the reduction phase, each molecule of 3-phosphoglycerate receives a phosphate group from ATP and is reduced by NADPH to form G3P (Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate), a 3-carbon sugar. This phase requires a total of 6 ATP and 6 NADPH molecules for 6 molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate.
What is G3P, and how is it used in the Calvin Cycle?
-G3P (Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate) is a 3-carbon sugar produced during the reduction phase of the Calvin Cycle. It is the product of the cycle and can be used to form glucose and other organic compounds in the plant. However, only one molecule of G3P is released per cycle, while the others are recycled to regenerate RuBP.
How is RuBP regenerated in the Calvin Cycle?
-RuBP (Ribulose bisphosphate) is regenerated in the final step of the Calvin Cycle. Five molecules of G3P are rearranged through a series of reactions, utilizing 3 ATP molecules, to regenerate three molecules of RuBP, allowing the cycle to continue.
Why do plants need carbon dioxide, and how do they use it?
-Plants need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. CO2 is incorporated into organic compounds during the Calvin Cycle, where it is converted into sugars like G3P, which are used for energy, growth, and other functions.
What is the relationship between respiration in humans and photosynthesis in plants?
-In humans, respiration is a catabolic process that breaks down complex molecules like glucose using oxygen to release energy. In contrast, photosynthesis in plants is an anabolic process where simple molecules like CO2 and water are used to create complex sugars (glucose) using light energy.
How many ATP and NADPH molecules are needed to produce one molecule of G3P in the Calvin Cycle?
-To produce one molecule of G3P, the Calvin Cycle requires 9 ATP and 6 NADPH molecules. These molecules are used in the various steps of fixation, reduction, and regeneration of RuBP.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)