21.3 Nuclear Radiation
Summary
TLDRThis video script covers the fundamental concepts of nuclear radiation, including the types of radiation (alpha, beta, and gamma), their effects on human cells, and methods for measuring radiation exposure. It explains the tools used for detection, such as film badges and Geiger counters, and explores various applications like carbon-14 dating, medical imaging (PET scans), and agricultural enhancements. The script also discusses the nuclear reactions of fission and fusion, highlighting their uses and implications, including the management of radioactive waste produced by fission. Overall, it provides a comprehensive overview of nuclear radiation and its impact on both science and society.
Takeaways
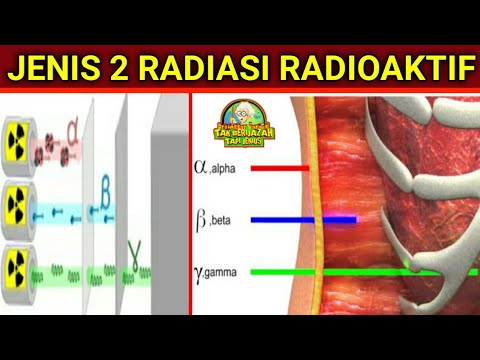
- 😀 Alpha radiation travels only a few millimeters in air and can be stopped with paper.
- 😀 Beta radiation, being lighter and faster, can travel a few meters and requires lead or glass to stop.
- 😀 Gamma radiation, with no mass or charge, is very difficult to stop and requires thick lead for mitigation.
- 😀 Radiation can damage human cells by disrupting DNA, leading to cancer and other health issues.
- 😀 Radiation exposure is measured in **rem** (radiation equivalent for man), with the average person exposed to 0.1 rem annually.
- 😀 Cosmic rays and altitude can increase radiation exposure, with frequent fliers and those at higher altitudes being more exposed.
- 😀 Film badges are used for long-term radiation exposure measurement by recording how much the photosensitive film darkens.
- 😀 Geiger counters provide real-time radiation readings through audible clicks, detecting ionizing radiation in the environment.
- 😀 Carbon-14 dating uses the proportion of carbon-14 to carbon-12 in organic material to determine age.
- 😀 PET scans use radioactive tracers, like iodine, to detect cancer and other issues by emitting gamma rays for imaging.
- 😀 Radioactive tracers are also used in agriculture to study fertilizer absorption by plants and prolong food shelf life by killing bacteria.
- 😀 Fission is the splitting of heavy atomic nuclei, like uranium-235, releasing energy, and is used in nuclear power plants and bombs.
- 😀 Fusion is the combining of lighter atomic nuclei, like deuterium, to form heavier nuclei, releasing even more energy, and powers stars.
- 😀 Nuclear waste from fission remains radioactive for thousands of years and requires safe storage in concrete bunkers or underground facilities.
Q & A
What are the main differences between alpha, beta, and gamma radiation?
-Alpha radiation has a short range, traveling only a few millimeters in air and can be stopped by paper. Beta radiation travels farther, up to a few meters, and requires lead or glass to stop it. Gamma radiation, having no mass or charge, is the most difficult to stop and requires lead for mitigation, though some radiation will still penetrate.
How does radiation affect human cells?
-Radiation can damage human cells by knocking out chunks of DNA, which can lead to mutations, cancer, and other health problems.
What is the unit used to measure radiation exposure, and what does it represent?
-Radiation exposure is often measured in *rem*, which represents the radiation equivalent for man. It measures the ionizing radiation affecting human tissue, with an example of a typical dose being around 0.1 rem per year.
How does altitude affect radiation exposure?
-People who live at higher altitudes or frequently fly, like pilots, are exposed to higher levels of cosmic radiation due to the thinner atmosphere, which offers less protection from radiation.
What are the two main devices used to detect radiation?
-The two main devices used to detect radiation are film badges and Geiger counters. Film badges measure radiation exposure over time by darkening in response to radiation, while Geiger counters provide real-time detection by emitting beeps every time radiation is detected.
How does carbon-14 dating work?
-Carbon-14 dating is based on the known proportion of carbon-14 in the Earth's atmosphere. Living organisms absorb carbon-14, which decays over time. By measuring the ratio of carbon-14 to carbon-12 in organic tissue, scientists can determine the age of the sample.
What is a PET scan, and how does it use radiation?
-A PET (positron emission tomography) scan uses radioactive tracers that emit positrons. When these positrons interact with electrons, they annihilate and release a specific type of radiation, which is detected to locate issues like tumors or brain activity.
How does radioactive tracing benefit agriculture?
-Radioactive tracers are used in fertilizers to track their movement and absorption by plants. This helps determine the efficiency of the fertilizer. Additionally, gamma radiation can be used to kill bacteria, prolonging the shelf life of agricultural products.
What is the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion?
-Nuclear fission is the splitting of a heavy nucleus into smaller parts, releasing energy, and is used in nuclear reactors. Nuclear fusion is the combining of smaller nuclei to form a larger one, releasing even more energy, and powers stars like the Sun.
What are the challenges associated with nuclear waste disposal?
-Nuclear fission produces radioactive waste that can remain hazardous for thousands of years. Proper disposal is critical to prevent radiation exposure. Waste is often stored in large concrete bunkers or underground facilities to isolate it and ensure public safety.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)