1. Pengantar Jaringan Saraf Tiruan
Summary
TLDRThis video lecture provides an introduction to artificial neural networks (ANNs), exploring the concept, models, and architectures of JST (Jaringan Syaraf Tiruan). It explains how ANNs are inspired by the human brain, focusing on neural connections and the learning process. The evolution of neural networks is traced from early developments to more recent advancements, including deep learning algorithms. The lecture covers the components of a neural network, including neurons, synapses, weights, and activation functions, and discusses various training methods, such as supervised and unsupervised learning. It also introduces different neural network architectures, from simple to complex models.
Takeaways
- 😀 Neural networks (Jaringan Syaraf Tiruan or JST) aim to mimic the human brain by using interconnected neurons to process data and learn patterns.
- 😀 The human brain consists of around 10^11 neurons, which serve as a foundation for artificial neural networks, though these models are much simpler.
- 😀 The development of neural networks began in the 1940s, with various milestones, such as the introduction of the perceptron, the emergence of backpropagation, and advancements like deep learning and generative adversarial networks (GANs).
- 😀 The growth of 'big data' and the internet has necessitated the development of more complex neural network architectures that can handle large datasets.
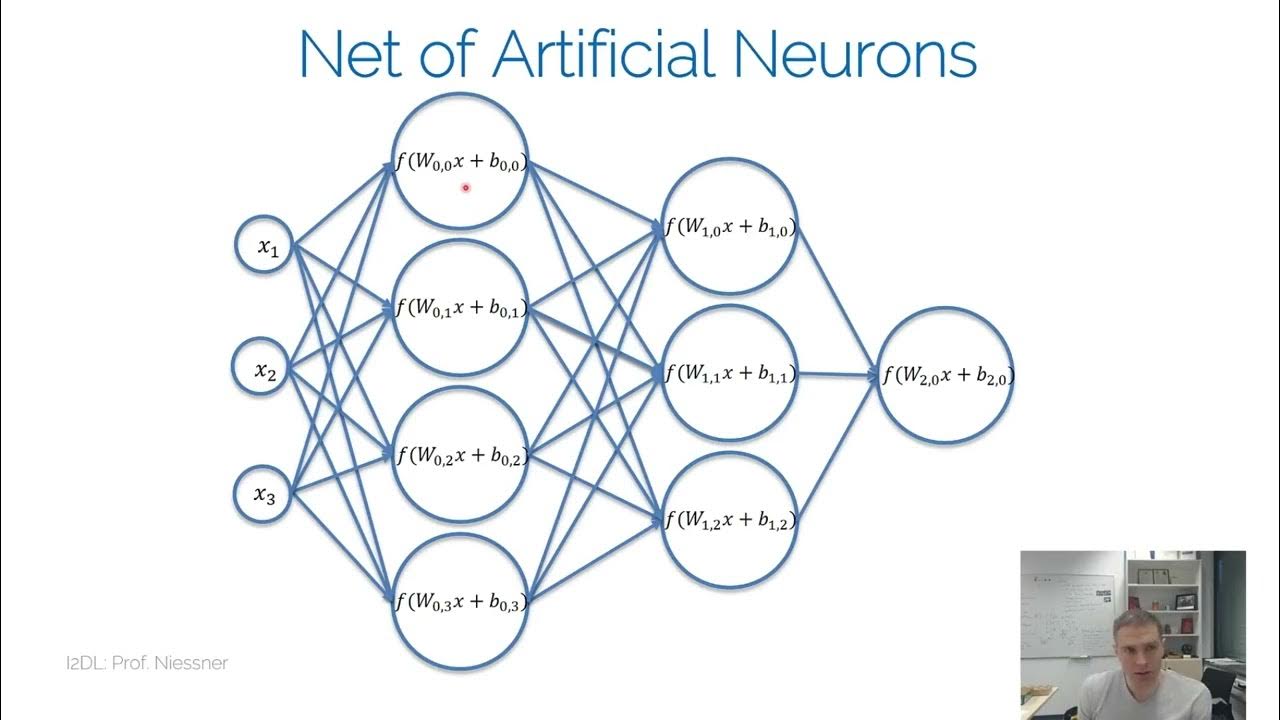
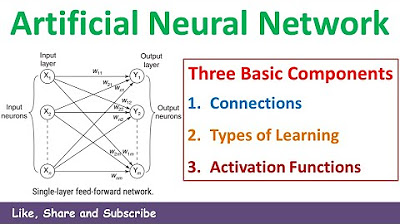
- 😀 Neural networks consist of neurons connected through synapses. These neurons process data through weights, biases, and activation functions to generate outputs.
- 😀 The architecture of a neural network typically includes an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. These layers help the network learn from input data.
- 😀 The learning process of neural networks includes supervised learning (where both input and output are provided) and unsupervised learning (where only inputs are given).
- 😀 A single-layer network consists of an input and output layer, but more complex tasks require multi-layer networks that include hidden layers for better performance.
- 😀 Activation functions play a crucial role in determining the output of neurons and can vary depending on the problem and network architecture.
- 😀 Neural network training involves calculating errors based on the difference between predicted and actual outputs, then adjusting weights to reduce this error and improve model accuracy.
Q & A
What is the basic concept of a neural network (JST)?
-A neural network is a computational model inspired by the human brain, designed to mimic the brain's ability to learn and process information. It consists of interconnected neurons and is used for tasks such as pattern recognition and data processing.
How do neural networks relate to the human brain?
-Neural networks are modeled after the human brain's neural structure. The human brain has around 10^11 neurons that are interconnected and capable of learning. Neural networks try to replicate this process in a simplified form to allow machines to learn from data.
What is the historical development of neural networks?
-Neural networks were first introduced in the 1940s with the perceptron model. After various phases of development, including a period of stagnation known as the 'AI Winter,' the field advanced with methods like backpropagation, deep learning, and the introduction of models such as GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks).
Why are neural networks important in the context of big data?
-Neural networks, especially deep learning architectures, are essential in handling big data. With the increasing volume and complexity of digital data, simpler neural network models are insufficient, and advanced models are needed for tasks like image recognition, speech processing, and more.
What are the main components of a neural network?
-A neural network typically consists of three main components: input layers, hidden layers, and output layers. Neurons in these layers are interconnected, with each connection having a weight and bias that affect the processing of data.
How does the training process of neural networks work?
-The training process involves adjusting the weights of the network based on the error between the predicted output and the desired output. This is typically done using methods like supervised learning, where the model is trained on labeled data, and unsupervised learning, where the model tries to identify patterns in unlabeled data.
What is the role of activation functions in neural networks?
-Activation functions determine whether a neuron should be activated or not, based on the processed input. These functions are crucial for introducing non-linearity to the network, allowing it to solve complex problems. Examples include sigmoid, ReLU, and tanh functions.
What is the difference between supervised and unsupervised learning in neural networks?
-In supervised learning, the model is trained on labeled data, meaning the input and desired output are provided. In unsupervised learning, the model is given data without labeled outputs and must identify patterns or groupings on its own.
What are the different types of neural network architectures?
-The main types of neural network architectures are single-layer neural networks, which consist of only input and output layers, and multi-layer neural networks, which include input, hidden, and output layers. Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) are another type that involves feedback loops.
What is the significance of multi-layer neural networks?
-Multi-layer neural networks are essential for solving complex problems that involve large and high-dimensional datasets. They consist of multiple layers of neurons that can process intricate patterns and produce more accurate outputs than simpler, single-layer networks.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Jaringan Syaraf Tiruan [1] : Konsep Dasar JST

The Next Generation Of Brain Mimicking AI

ANN vs CNN vs RNN | Difference Between ANN CNN and RNN | Types of Neural Networks Explained
I2DL NN
2. Three Basic Components or Entities of Artificial Neural Network Introduction | Soft Computing

Introduction to Neural Networks with Example in HINDI | Artificial Intelligence
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)