Neuroanatomy S1 E7: Basal Ganglia #neuroanatomy #ubcmedicine
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the intricate role of the basal ganglia in regulating human behavior. It describes how the basal ganglia's circuits integrate motor, cognitive, and emotional processes to produce coordinated actions. The video explains the connections between different brain regions, highlighting how the direct and indirect pathways facilitate or suppress movements. It also emphasizes the role of practice, reward, and emotional expression in shaping behavior. The video illustrates how the basal ganglia manage everything from motor performance to emotional responses, ultimately influencing our actions and reactions in a fluid, efficient manner.
Takeaways
- 😀 The basal ganglia are deep nuclei in the brain that integrate all cortical activity into one behavioral output, influencing behavior and movement.
- 😀 There are different circuits in the basal ganglia that regulate motor behavior, cognition, and emotions.
- 😀 Posture, body language, and tone of voice are influenced by the basal ganglia, allowing us to understand someone's emotional state.
- 😀 The motor circuit of the basal ganglia helps streamline learned movements, making them appear effortless and fluid.
- 😀 The basal ganglia process sensory and motor input to decide whether to execute a movement and suppress competing movements.
- 😀 The cognitive loop is crucial for learning and refining motor actions through repeated practice and training.
- 😀 Dopaminergic connections in the nucleus accumbens provide rewarding feelings after successfully completing a task.
- 😀 The limbic circuit integrates emotional aspects with motor behavior, affecting how we display emotions through body language and facial expressions.
- 😀 The substantia nigra and subthalamic nucleus play important roles in the basal ganglia's motor regulation, with the former releasing dopamine for movement and reward.
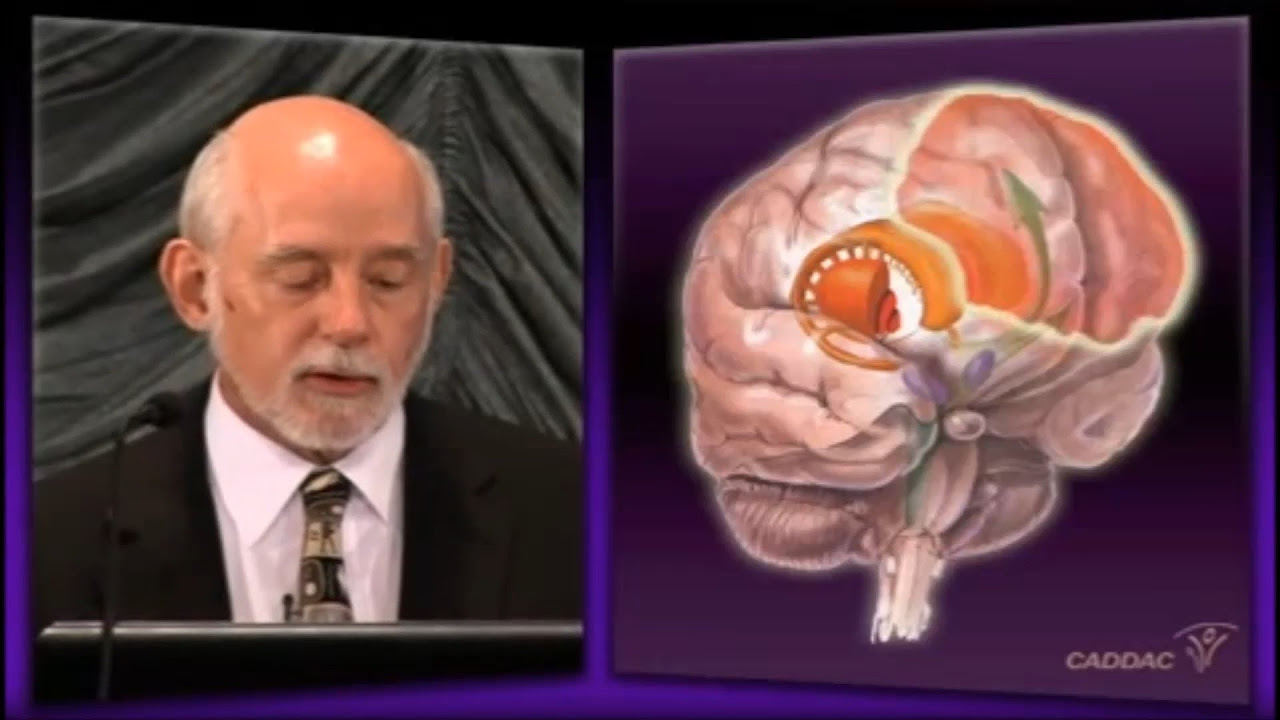
- 😀 A solid understanding of the anatomy of the basal ganglia and its nuclei, such as the caudate nucleus and globus pallidus, is essential for interpreting brain images in neuroimaging.
- 😀 The basal ganglia funnel cortical activity and integrate motivation, goals, and mood to result in a coordinated behavioral output.
Q & A
What is the role of the basal ganglia in behavior?
-The basal ganglia integrate cortical activity into one behavioral output, coordinating various aspects of behavior, including motor control, learning, cognition, and emotional regulation.
How do the basal ganglia influence motor output?
-The basal ganglia process input from motor and sensory areas of the cortex, facilitating goal-oriented movements through the direct pathway while suppressing competing movements through the indirect pathway, resulting in smooth and efficient motor output.
What are the three main circuits within the basal ganglia, and what do they regulate?
-The three main circuits are: the motor circuit, which integrates motor output; the cognitive or associative circuit, which plays a role in learning and higher cortical functions; and the limbic circuit, which regulates emotional aspects of behavior.
What is the significance of the cognitive or associative loop?
-The cognitive loop is important for motor learning and refining movements. It helps experiment with different strategies, gradually reducing activity as movements become well-learned and automated.
How does the limbic circuit contribute to behavior?
-The limbic circuit adds an emotional component to behavior, influencing motor expression, gestures, and facial expressions. It integrates emotional states with our movements and cognitive processes.
What role does the nucleus accumbens play in the cognitive loop?
-The nucleus accumbens, through its dopaminergic connections, provides rewarding feedback for successful tasks, which helps to reinforce and streamline cognitive processes during learning.
How does the basal ganglia regulate motor performance in well-rehearsed tasks?
-In well-rehearsed tasks, the motor loop becomes active, helping to coordinate movements with minimal cognitive effort. The basal ganglia streamline these movements, allowing for fluid and efficient performance.
What are the primary functions of the substantia nigra in basal ganglia circuitry?
-The substantia nigra, located in the midbrain, releases dopamine that influences motor output, facilitates cortical activity, and contributes to feelings of reward through its dopaminergic projections.
Where is the subthalamic nucleus located, and what is its function?
-The subthalamic nucleus is located inferiorly and laterally to the thalamus. It functions as a pacemaker for the basal ganglia circuitry, defining the rhythm of output through inhibitory influences.
What anatomical structures are involved in the basal ganglia circuits?
-Key structures involved in basal ganglia circuits include the caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, substantia nigra, subthalamic nucleus, and the thalamus. These nuclei are interconnected and help regulate motor, cognitive, and emotional functions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)