V11.1 Statis Tak Tentu - Force Method untuk Truss System
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Agus Setiawan explores how to analyze statically indeterminate truss structures using the Force Method. He explains how to identify such structures, remove redundant bars, and apply compensatory forces. The method involves calculating internal forces and deformations using equilibrium equations and material properties like modulus of elasticity. The video emphasizes the importance of careful calculations and thorough verification of equilibrium at each joint. With clear, step-by-step instructions, the Force Method remains an effective tool for engineers dealing with complex truss analysis.
Takeaways
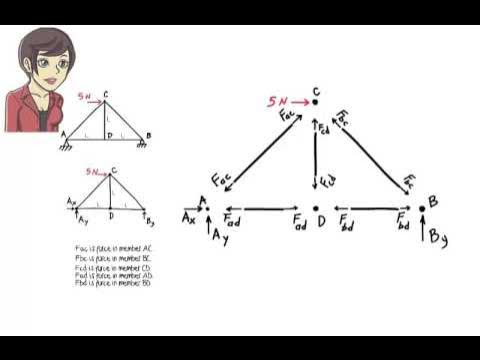
- 😀 A statically indeterminate truss structure occurs when the equation B + R > 2J is satisfied, where B is the number of truss members, R is the number of reactions, and J is the number of joints.
- 😀 The Force Method (Metode Gaya) is used to analyze statically indeterminate trusses by removing redundant members and applying compensating forces.
- 😀 Identifying redundant members is crucial; these are the extra members that make the structure statically indeterminate, and must be removed to simplify the system.
- 😀 A virtual structure is created after removing the redundant member, with compensating forces applied to keep the system balanced.
- 😀 Displacement calculations for the virtual structure use the formula Δ = (N × L) / (A × E), where N is the internal force, L is the length, A is the cross-sectional area, and E is the Young’s modulus.
- 😀 The calculation of internal forces involves using equilibrium equations for each joint and applying the Force Method principles to find unknown forces in the truss members.
- 😀 The compensation for the removed member is a force equal to the one that was originally carried by the member, which ensures the virtual structure behaves as if the member were still present.
- 😀 Compatibility of displacements between the actual and virtual structures is checked by using the Force Method's compatibility equations, ensuring the system’s integrity.
- 😀 The method helps in calculating internal forces in each truss member, including the determination of forces like the axial force in member AB or BC using vertical and horizontal equilibrium.
- 😀 After computing the forces, the results are verified by substituting back into the equilibrium equations to ensure balance and consistency in the calculations.
- 😀 The process is systematic and involves multiple calculations and checks, but the Force Method remains effective for analyzing complex statically indeterminate trusses.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video script?
-The video focuses on explaining the analysis of a statically indeterminate truss structure using the Force Method (Metode Gaya). It covers how to identify an indeterminate structure, remove redundant members, and calculate internal forces and displacements in the structure.
What does it mean for a structure to be statically indeterminate?
-A structure is considered statically indeterminate when the number of bars (B) and reactions (R) exceeds twice the number of joints (J), i.e., B + R > 2J. This condition leads to a system that cannot be solved using basic equilibrium equations alone and requires additional methods like the Force Method.
How is the Force Method applied to analyze a truss structure?
-The Force Method involves removing a redundant member from the truss, applying a virtual load to the removed member, and then calculating the displacements (Delta) caused by this virtual load. The internal forces are calculated using equilibrium equations, and the results are combined to find the final forces in the original structure.
Why is it necessary to remove a redundant member in the Force Method?
-A redundant member is removed to simplify the structure, reducing the number of unknown forces and making it possible to solve the system using virtual forces. The removed member is then replaced with a virtual force to calculate the displacement, which allows for the analysis of the original structure.
What role does virtual work play in the analysis of indeterminate structures?
-Virtual work is used in the Force Method to calculate the displacement at the location of the removed redundant member. By applying a virtual load and calculating the displacement, the method helps in determining the internal forces and ensuring compatibility between the virtual and real structures.
What is the significance of the compatibility condition in the Force Method?
-The compatibility condition ensures that the displacement caused by the virtual load matches the displacement in the real structure. This step is crucial for calculating the final internal forces in the original structure, as it ensures the system's consistency.
How are internal forces calculated using the Force Method?
-Internal forces are calculated by applying equilibrium equations, such as Sigma of vertical forces = 0 and Sigma of horizontal forces = 0, to determine the forces in the truss members. The displacements from the virtual load help in determining the final forces in the real structure.
What does the equation B + R > 2J signify in the context of a truss structure?
-The equation B + R > 2J helps to identify if a truss structure is statically indeterminate. Here, B represents the number of bars, R represents the number of reactions, and J represents the number of joints. If this equation is satisfied, the structure is considered indeterminate and requires methods like the Force Method for analysis.
What does it mean when the calculated internal force in a truss member is zero?
-When the internal force in a truss member is zero, it indicates that the member does not carry any load or contribute to the overall stability of the structure. This is often a result of the equilibrium analysis where the forces balance out.
How is the final internal force in the original structure determined after using the Force Method?
-After calculating the internal forces and displacements using the Force Method, the final internal forces in the original structure are determined by substituting the results from the virtual structure back into the original system. The calculated values are then used to check the equilibrium and compatibility, finalizing the force distribution.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
SA04: Truss Analysis: Method of Joints

S21A- STATIKA PORTAL 3 SENDI- REAKSI PERLETAKAN

ANALISA STRUKTUR 2 KONSEP DASAR MATRIKS FLEKSIBILITAS#flexibilitymatrix#Flexibility#matrix

S-10 Pengenalan Truss

Structural Theory 1 Chapter 1 Structural Elements & Types of Structure Part 1 (with Subtitles)

3. Metode Direct Design Method
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)