Termodinamika - Fisika Kelas 11 (Kurikulum 2013 Revisi) - Quipper Video
Summary
TLDRIn this educational session on thermodynamics, the speaker introduces key concepts like energy transfer through heat and work, the role of systems and surroundings, and types of systems such as isolated, closed, and open systems. The video covers the principles of energy within, including kinetic energy in gases, and how temperature changes affect energy. The speaker also explains the first and second laws of thermodynamics, the Carnot cycle, and heat engines, aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of thermodynamics and its application in real-world systems.
Takeaways
- 😀 Thermodynamics is the study of energy transfer, specifically through heat and work between systems and their surroundings.
- 😀 Heat is the transfer of energy due to a temperature difference, always flowing from the hotter object to the cooler one.
- 😀 Work refers to energy transferred through mechanical processes, often involving physical movement or forces.
- 😀 A system is the object or substance being studied, while the environment refers to everything outside of it.
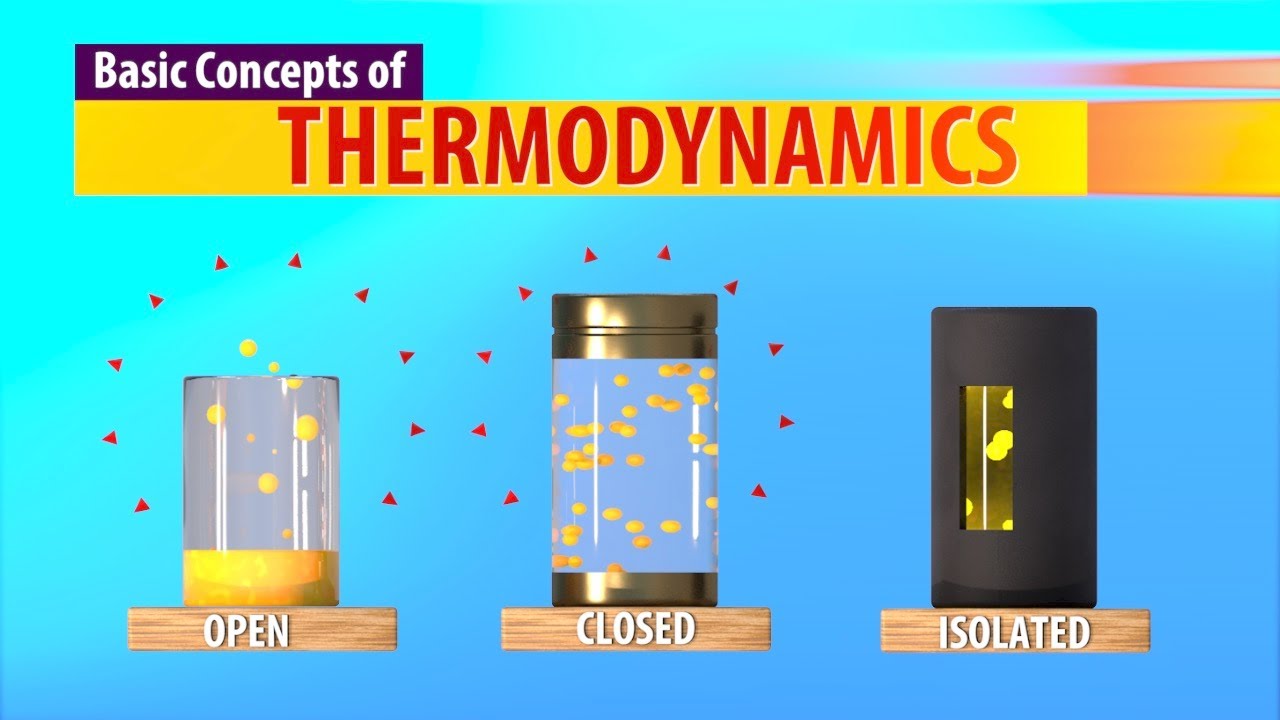
- 😀 There are three types of systems: isolated, closed, and open systems, each with different energy and matter exchange properties.
- 😀 An **isolated system** does not exchange energy or matter with its surroundings, like a thermos bottle.
- 😀 A **closed system** allows energy exchange but not matter, such as a closed kettle of water.
- 😀 An **open system** allows both energy and matter to be exchanged, like the ocean where evaporation occurs.
- 😀 Internal energy is the energy within a system, primarily from the kinetic energy of particles, and is influenced by temperature.
- 😀 The change in internal energy for a gas can be calculated using the formula: ΔU = 3/2 n R ΔT for monoatomic gases, where ΔU is the change in internal energy, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and ΔT is the temperature change.
- 😀 Understanding thermodynamics is essential for understanding how energy flows in various physical processes and how it can be applied in real-world machines and systems.
Q & A
What is thermodynamics?
-Thermodynamics is the science that studies the processes of energy transfer, specifically in the form of heat (calor) and work, that occur between a system and its surroundings.
What are the main forms of energy discussed in thermodynamics?
-The two main forms of energy discussed in thermodynamics are heat (calor) and work, which are transferred between the system and its surroundings.
What is the difference between heat and work in thermodynamics?
-Heat refers to the transfer of energy caused by a difference in temperature, whereas work refers to the energy transfer through mechanical means, such as the movement of an object.
What is meant by 'system' and 'environment' in thermodynamics?
-In thermodynamics, a system refers to the object or matter being studied, while the environment (or surroundings) refers to everything outside the system that can interact with it, such as its container.
What are the three types of systems in thermodynamics?
-The three types of systems are: 1) Isolated systems, where neither energy nor matter can be exchanged with the surroundings. 2) Closed systems, where energy can be exchanged, but matter cannot. 3) Open systems, where both energy and matter can be exchanged.
What is an isolated system? Can you give an example?
-An isolated system is one where no energy or matter is exchanged with the surroundings. An example is a thermos containing hot water, where the temperature of the water remains constant because no heat enters or leaves the container.
What is a closed system? Can you give an example?
-A closed system allows the exchange of energy, but not matter, with the surroundings. For example, a sealed kettle of water, where heat can be transferred to or from the environment, but no water leaves the kettle.
What is an open system? Can you give an example?
-An open system allows both the exchange of energy and matter with its surroundings. An example is the ocean, where water evaporates and energy is transferred from the sun.
How does temperature affect the internal energy of a gas?
-The internal energy of a gas is directly related to its temperature, as temperature influences the kinetic energy of the gas molecules. The higher the temperature, the greater the internal energy.
What is the formula for calculating the change in internal energy for a monoatomic gas?
-For a monoatomic gas, the change in internal energy is calculated using the formula ΔU = (3/2) nRΔT, where n is the number of moles of gas, R is the ideal gas constant, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Termodinamika Kelas XI IPA

Hukum Termodinamika, Bagian 1: Energi Dalam dan Hukum Pertama
Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics (Animation)

Thermodynamics Class 11 in 5 Minutes | Chemistry | Quick Revision | NEET, JEE & CBSE |

Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics [Year - 1]

BAB 10 TERMODINAMIKA_MAPEL FISIKA_SMA KELAS XI #fyp #fypage #fypyoutube #termodinamika #fisika
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)