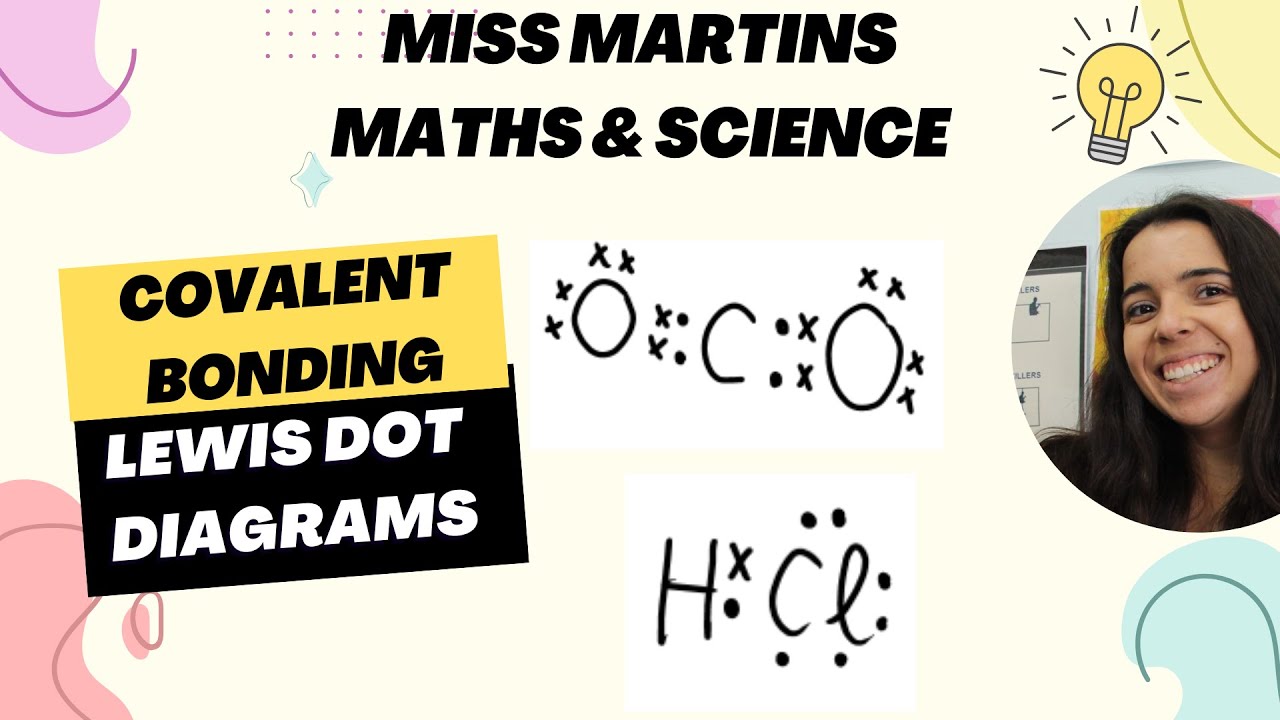Grade 11 Lewis Diagrams Chemical Bonding
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the focus is on Lewis dot diagrams and chemical bonding, specifically covalent bonds. The video explains the importance of understanding how to draw Lewis dot diagrams for covalent compounds and the octet rule, which atoms follow to achieve a stable electron configuration. It covers how atoms share valence electrons to form bonds, including single, double, and triple bonds. Examples include molecules like H2, HCl, O2, and N2. The video also discusses how to use the periodic table to determine the number of valence electrons, essential for creating accurate Lewis dot diagrams.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lewis dot diagrams are essential for representing covalent bonds and molecules.
- 😀 Covalent bonds form when two non-metal atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
- 😀 The **Octet Rule** states that atoms strive to have eight electrons in their outermost shell, except for hydrogen, which needs two.
- 😀 Valence electrons, which are the outermost electrons in an atom, are the key to determining how atoms bond.
- 😀 The periodic table helps identify the number of valence electrons for each element, crucial for drawing Lewis dot diagrams.
- 😀 When drawing Lewis dot diagrams, only the valence electrons are shown as dots or crosses around the element symbol.
- 😀 Atoms with unfilled valence electron shells bond by sharing electrons to achieve a full outer shell and lower potential energy.
- 😀 Bonding pairs are shared electrons that form bonds, while lone pairs are non-bonding electrons.
- 😀 Different types of covalent bonds include single bonds (one shared pair of electrons), double bonds (two pairs), and triple bonds (three pairs).
- 😀 The hydrogen molecule (H₂) involves two hydrogen atoms sharing a single pair of electrons to complete their stable configuration.
- 😀 In molecules like HCl (hydrogen chloride), hydrogen shares its single electron with chlorine, which needs one more to reach an octet structure.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The video focuses on Lewis dot diagrams and chemical bonding, particularly how to represent covalent bonds through Lewis dot diagrams.
What is a covalent bond?
-A covalent bond is the sharing of electrons between two non-metal atoms to form a molecule. The shared electrons help both atoms achieve a more stable electron configuration.
Why do atoms form covalent bonds?
-Atoms form covalent bonds to achieve a stable electron configuration, often resembling that of a noble gas, which results in a lower potential energy and greater stability.
What does the octet rule state?
-The octet rule states that atoms tend to combine in such a way that they have eight electrons in their outermost energy level, resembling the electron configuration of noble gases. Hydrogen is an exception, needing only two electrons.
What are valence electrons and why are they important for drawing Lewis dot diagrams?
-Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. They are crucial for drawing Lewis dot diagrams because they determine how atoms will bond by sharing these electrons with other atoms.
How do you determine the number of valence electrons for an element?
-The number of valence electrons for an element can be determined by its group number on the periodic table. For example, Group 1 elements have one valence electron, Group 2 have two, and so on.
How are Lewis dot diagrams for elements drawn?
-Lewis dot diagrams for elements are drawn by placing dots (or crosses) around the element's symbol to represent the valence electrons. Each side of the symbol (top, right, bottom, left) gets one dot until all valence electrons are represented.
What is the difference between bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons in a Lewis dot diagram?
-Bonding pairs are electrons that are shared between two atoms to form a covalent bond, while lone pairs are electrons that are not shared and remain on the individual atom.
What is a single bond, double bond, and triple bond in the context of covalent bonding?
-A single bond involves the sharing of one pair of electrons between two atoms, a double bond involves the sharing of two pairs of electrons, and a triple bond involves the sharing of three pairs of electrons.
How do you draw a Lewis dot diagram for a molecule like H2 (hydrogen gas)?
-To draw a Lewis dot diagram for H2, you would show each hydrogen atom with one valence electron. The two hydrogens share their electrons to form a single bond, with the shared electrons placed in the middle.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)