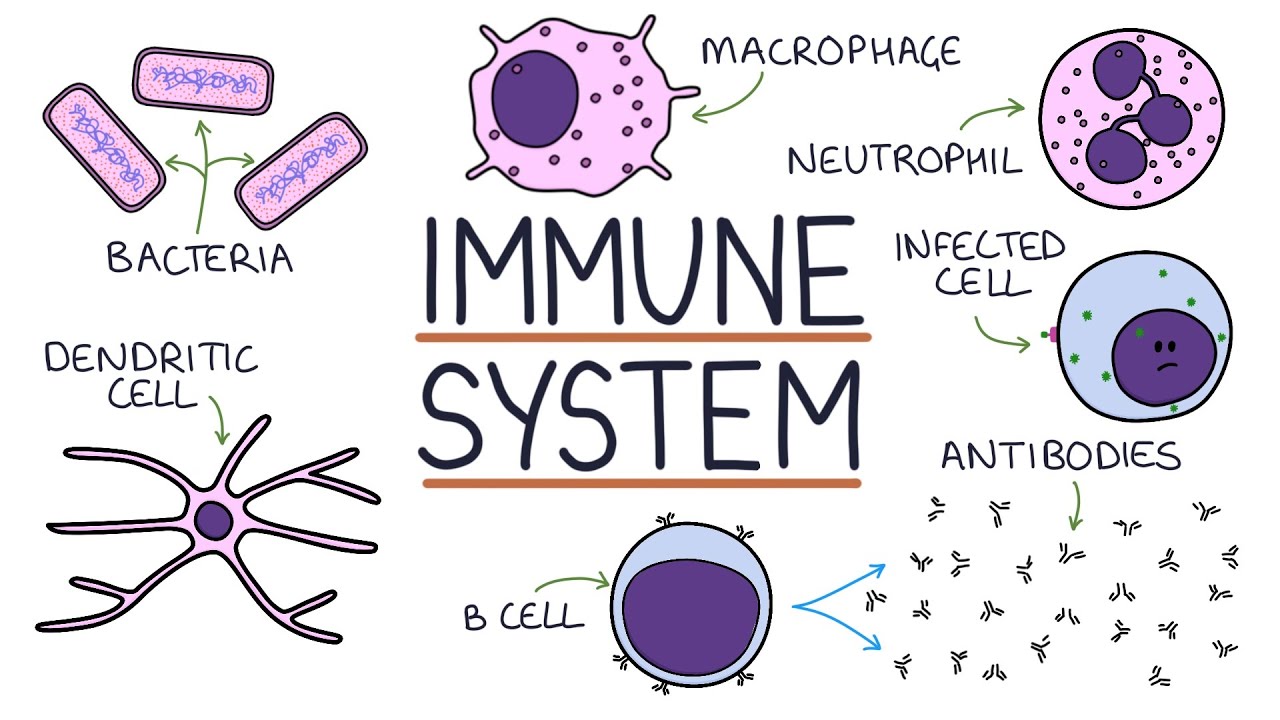
Imunosupresan (1): Aktivasi dan Diferensiasi Sel Limfosit T
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the intricate process of T lymphocyte activation and differentiation, which is essential for immune system function. The process begins when antigen-presenting cells (APCs) capture and present antigens to naive T cells through MHC molecules. Activation requires three key signals: antigen recognition, costimulatory signals, and intracellular signaling pathways. These signals lead to the proliferation and differentiation of T cells into specialized subsets, such as helper T cells (CD4+) and cytotoxic T cells (CD8+), which play crucial roles in immune responses. Additionally, memory T cells are formed to ensure rapid responses in future encounters with the same pathogens.
Takeaways
- 😀 The activation and differentiation of T lymphocytes is a complex process.
- 😀 T cells are categorized into two main types: CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.
- 😀 The activation of T cells begins when foreign antigens are recognized by Antigen-Presenting Cells (APCs) through phagocytosis.
- 😀 During T cell activation, the antigen is presented on MHC class II (for CD4+ T cells) and MHC class I (for CD8+ T cells).
- 😀 The modified APCs migrate to lymph nodes to present the antigen to naive T cells, leading to their activation.
- 😀 Activation of naive T cells requires three main signaling pathways: antigen recognition, costimulation, and adhesion with APCs.
- 😀 Costimulatory molecules, such as CD80/86 and CD28, play a crucial role in T cell activation by providing additional signals.
- 😀 If costimulation is absent, T cells remain inactive or become anergic.
- 😀 Cytokines like Interleukin-2 (IL-2) are produced during T cell activation, leading to further activation and proliferation of T cells.
- 😀 Activated T cells differentiate into various types: CD4+ helper T cells (Th1, Th2, Th17) and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs).
- 😀 Memory T cells, particularly CD4+ memory T cells, are formed to provide a quicker immune response if the same antigen reappears.
Q & A
What is the process of T lymphocyte activation?
-T lymphocyte activation begins when a foreign antigen is recognized by antigen-presenting cells (APCs) via phagocytosis. The APCs present the antigen on their surface using Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) molecules, which are recognized by T cells through their receptors.
What are the main types of MHC molecules involved in T cell activation?
-MHC class II molecules are involved in presenting antigens to CD4+ T cells, while MHC class I molecules present antigens to CD8+ T cells.
What role do costimulatory molecules play in T cell activation?
-Costimulatory molecules, such as CD80, CD86, and CD28, provide the second signal required for T cell activation. Without this signal, T cells may become inactivated or enter a state of anergy.
Why is IL-2 important for T cell activation?
-IL-2 is crucial because it binds to the IL-2 receptor (CD25) on T cells, promoting further T cell proliferation and differentiation during the immune response.
How do T cells differentiate after activation?
-After activation, CD4+ T cells differentiate into various helper T cell subtypes (Th1, Th2, Th17), while CD8+ T cells differentiate into cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), which can directly attack infected cells.
What is the significance of memory T cells?
-Memory T cells are long-lived cells that 'remember' specific antigens. If the same pathogen invades again, memory T cells can quickly respond by proliferating and differentiating into effector T cells to fight the infection.
What is the role of the NFAT transcription factor in T cell activation?
-NFAT (Nuclear Factor of Activated T-cells) is activated through intracellular signaling pathways, particularly calcium signaling. Once activated, NFAT moves to the nucleus to induce the expression of genes involved in T cell activation, including those for cytokines like IL-2.
What are the different types of helper T cells, and what are their functions?
-Helper T cells can differentiate into Th1, Th2, or Th17 subtypes. Th1 cells help in immune responses against intracellular pathogens, Th2 cells support responses against extracellular pathogens, and Th17 cells are involved in inflammatory responses and defense against fungi and bacteria.
What is the function of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs)?
-Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), derived from CD8+ T cells, directly kill infected or abnormal cells by recognizing specific antigens presented on MHC class I molecules on the surface of these cells.
What happens if a T cell does not receive costimulatory signals during activation?
-If a T cell does not receive the necessary costimulatory signals, it may become anergic (inactive) and unable to mount an effective immune response to the antigen.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)