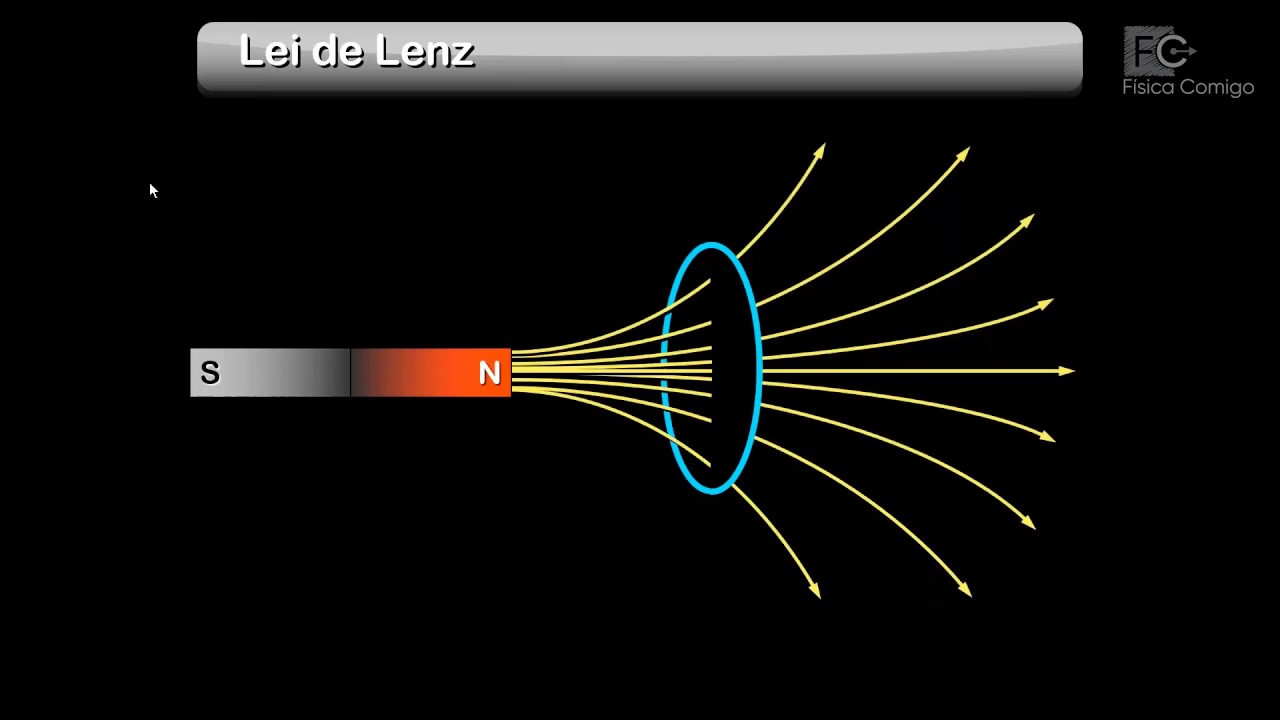
Eddy Currents Caused by Electromagnetic Induction
Summary
TLDRThis demonstration showcases the concept of eddy currents using two identical slugs, one magnetic and one non-magnetic, dropped through an aluminum pipe. The non-magnetic slug falls quickly, while the magnetic one falls slowly. This difference in speed is due to the induction of eddy currents in the aluminum pipe, caused by the changing magnetic field of the falling magnet. These induced currents generate their own magnetic field, which opposes the magnet’s motion, slowing its fall. This experiment illustrates the phenomenon of eddy currents and their interaction with magnetic fields.
Takeaways
- 😀 Eddy currents are induced in the aluminum pipe by the falling magnetic slug.
- 😀 The non-magnetic slug falls quickly through the pipe without generating any eddy currents.
- 😀 The magnetic slug falls slowly due to the opposing magnetic field created by eddy currents in the aluminum pipe.
- 😀 Eddy currents are loops of electric current generated in conductors when exposed to a changing magnetic field.
- 😀 The magnetic field created by eddy currents in the aluminum pipe opposes the motion of the magnetic slug, slowing it down.
- 😀 The aluminum pipe is paramagnetic, meaning it weakly responds to magnetic fields but does not attract the non-magnetic slug.
- 😀 The two slugs used in the experiment are identical in size and weight, except for the fact that one is magnetic.
- 😀 The behavior of the magnetic slug, falling slowly, demonstrates the effect of eddy currents in action.
- 😀 The experiment visually shows the difference in speed between the magnetic and non-magnetic slugs.
- 😀 The phenomenon of eddy currents demonstrates how electrical energy is converted into heat and magnetic forces as the magnetic field interacts with the conductor.
Q & A
What is the purpose of the experiment in the script?
-The experiment demonstrates the concept of eddy currents using two identical slugs, one magnetic and one non-magnetic, to observe how they behave when falling through an aluminum pipe.
Why does the magnetic slug fall slower than the non-magnetic one?
-The magnetic slug falls slower because it induces eddy currents in the aluminum pipe. These eddy currents create a magnetic field that opposes the falling slug, slowing it down.
What material is the pipe made of, and what is its magnetic property?
-The pipe is made of aluminum, which is paramagnetic. This means it has a very weak response to magnetic fields and does not attract magnets.
How does the magnetic slug interact with the aluminum pipe during the experiment?
-As the magnetic slug falls through the aluminum pipe, its changing magnetic field induces eddy currents in the pipe. The magnetic field produced by these eddy currents opposes the motion of the falling slug, slowing it down.
What are eddy currents, and how are they created in this experiment?
-Eddy currents are circulating currents that are induced in a conductor when it is exposed to a changing magnetic field. In this experiment, the falling magnetic slug creates a changing magnetic field in the aluminum pipe, which in turn induces eddy currents.
What happens when the non-magnetic slug falls through the pipe?
-The non-magnetic slug falls rapidly through the pipe because it does not interact with the aluminum in the same way as the magnetic slug. Without a magnetic field to induce eddy currents, there is no force to slow it down.
Why does the aluminum pipe not pick up the non-magnetic slug?
-Aluminum is a paramagnetic material, which means it has a very weak magnetic response. Therefore, it does not attract the non-magnetic slug.
What role do the eddy currents play in the experiment?
-The eddy currents generate a magnetic field that opposes the motion of the falling magnetic slug. This opposing force slows down the magnet's fall through the aluminum pipe.
Can aluminum pipes be used to demonstrate eddy currents with other objects?
-Yes, aluminum pipes can be used to demonstrate eddy currents with other objects that have magnetic properties. The key is that the object must create a changing magnetic field as it moves through the pipe.
What is the overall scientific principle being demonstrated in this experiment?
-The experiment demonstrates the principle of electromagnetic induction, specifically how a changing magnetic field induces eddy currents in conductors, which in turn creates a magnetic field that opposes the original motion of the magnetic object.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)