Cara mudah baca spektra IR | Bahas soal spektra IR | Kupas tuntas 5 soal spektra IR
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial explores the process of elucidating the structure of organic compounds using IR spectroscopy. The instructor provides clear, step-by-step examples, identifying key spectral features such as SP3 C-H stretching, CH2 and CH3 bending, and characteristic absorption peaks for functional groups like hydroxyl (-OH) and carbonyl (C=O). Through detailed analysis of compounds like pentane, hexane, butanol, and butanone, viewers learn how to correlate specific IR peaks with molecular structures, providing a practical guide to interpreting IR spectra for organic compound identification.
Takeaways
- 😀 Identification of organic compounds using IR spectroscopy is straightforward when key spectral features are analyzed.
- 😀 For pentane (C5H12), SP3 hybridized carbons and specific CH3 and CH2 stretching and bending vibrations are crucial for identification.
- 😀 The fingerprint region (1000-500 cm-1) is important for identifying longer carbon chains, as seen in hexane (C6H14).
- 😀 The broad OH stretch in butanol around 3300 cm-1 is a key feature for identifying alcohols in IR spectra.
- 😀 In IR spectroscopy, CH3, CH2, and CH bending vibrations typically appear in the 1300–1500 cm-1 range.
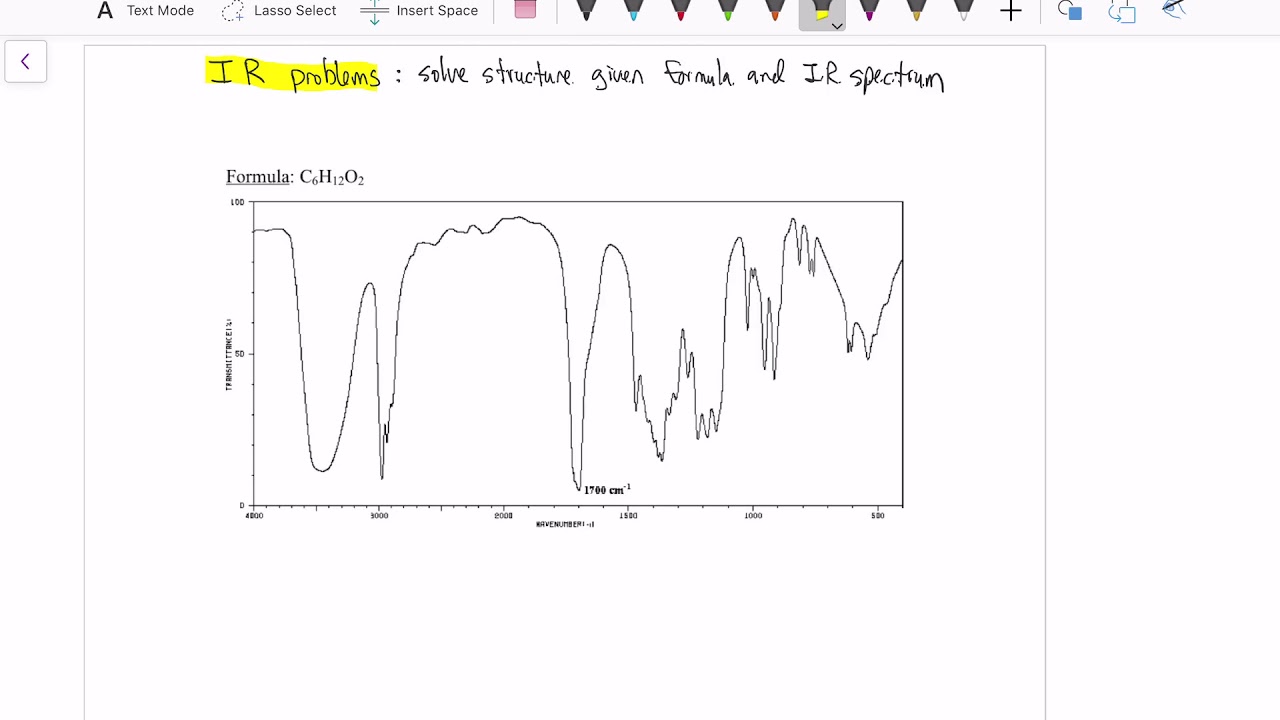
- 😀 The presence of the carbonyl (C=O) group in butanone is identified by a sharp peak around 1718 cm-1, indicative of a ketone.
- 😀 Overtones in the IR spectrum around 3400 cm-1, which are double the carbonyl stretch frequency, can be used to identify the presence of carbonyl compounds.
- 😀 Alcohols and ethers can be distinguished based on their characteristic C-O stretching vibrations, often around 1100 cm-1.
- 😀 The key for identifying functional groups in IR spectra is focusing on distinct peaks such as OH, CH3, CH2, and C=O stretches.
- 😀 Intensity differences in peaks (high or low) help differentiate between similar functional groups and molecular structures.
Q & A
What is the key feature of identifying pentane in IR spectroscopy?
-The key feature for identifying pentane in IR spectroscopy is the presence of SP3 C-H stretching around 2900–2800 cm^-1 and CH2 bending at 1462 cm^-1, along with CH3 bending at 1366 cm^-1.
What distinguishes hexane's IR spectrum from pentane's?
-The primary distinction between hexane and pentane in IR spectroscopy is the longer alkane chain in hexane, which gives rise to a fingerprint region absorption around 720 cm^-1, in addition to similar SP3 C-H stretching at 2900–2800 cm^-1.
How is the presence of an alcohol group identified in IR spectroscopy?
-The presence of an alcohol group in IR spectroscopy is identified by the broad and strong OH stretching band around 3300 cm^-1, caused by hydrogen bonding, along with typical SP3 C-H stretching between 2900–2800 cm^-1.
How can butanol be distinguished in an IR spectrum?
-Butanol can be distinguished by the broad OH stretching band around 3300 cm^-1, SP3 C-H stretching between 2900–2800 cm^-1, and CH2 bending at 1457 cm^-1 and CH3 bending at 1376 cm^-1.
What is the significance of the fingerprint region in IR spectroscopy?
-The fingerprint region, typically between 1000–1500 cm^-1, is crucial for differentiating molecules, especially larger ones, as it contains unique absorption bands specific to each molecule's structure.
What is the role of overtone peaks in IR spectroscopy, particularly in ketones?
-Overtone peaks in IR spectroscopy, such as those around twice the C=O stretching frequency (e.g., around 3400 cm^-1), represent the harmonic oscillation of the C=O bond and help confirm the presence of ketones, like butanone (butanon).
How are ketones identified in IR spectroscopy?
-Ketones are identified by a sharp C=O stretching band around 1718 cm^-1, which is typically intense and narrow, along with SP3 C-H stretching between 2900–2800 cm^-1 and C-O bending around 1206 cm^-1.
Why is the C=O stretching absorption band important for identifying ketones in IR spectroscopy?
-The C=O stretching absorption band around 1718 cm^-1 is characteristic of ketones, providing a clear identification due to its sharp, intense, and narrow appearance, which distinguishes it from other functional groups.
What distinguishes the IR spectra of alcohols and ethers?
-Alcohols have a broad OH stretching band around 3300 cm^-1, while ethers typically show a C-O stretching band around 1100 cm^-1, without the broad OH feature.
How can the presence of an ether group be identified in an IR spectrum?
-The ether group can be identified by a C-O stretching band around 1100 cm^-1, which is distinct from alcohols and ketones. The lack of OH stretching is a key indicator of an ether.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)