Pair of Linear Equations in two variables| Part-1| Class 10| Introduction |Mathematics NCERT / CBSE
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of linear equations in two variables is introduced as part of Class 10 mathematics. The session explains the general form of linear equations in one variable and then extends to two variables, emphasizing that the highest power of variables must be one. The chapter focuses on solving pairs of linear equations using graphical and algebraic methods, such as substitution, elimination, and cross-multiplication. The video also highlights the conditions under which solutions are unique, infinite, or nonexistent, making the topic accessible and engaging for students. The session concludes with an introduction to exercise 3.1.
Takeaways
- 😀 Linear equations involve equations with variables raised to the first power, where the highest degree of the variable is 1.
- 😀 A linear equation with one variable has the general form ax + b = 0, where 'a' is not equal to zero.
- 😀 If the power of a variable is greater than 1 (e.g., x² or x³), the equation is no longer linear and is classified as a quadratic or cubic equation, respectively.
- 😀 The general form of a linear equation in two variables (x and y) is ax + by + c = 0, where a, b, and c are real constants.
- 😀 In the case of a linear equation in two variables, 'a' and 'b' must never be zero simultaneously for it to be classified as a linear equation.
- 😀 A pair of linear equations involves two equations with two variables, typically written as: a₁x + b₁y + c₁ = 0 and a₂x + b₂y + c₂ = 0.
- 😀 Graphically, a linear equation in two variables represents a straight line, and the solution to the equation corresponds to the points on the line.
- 😀 The solution to a pair of linear equations can be found using methods such as graphical plotting or algebraic techniques, including substitution, elimination, and cross multiplication.
- 😀 There are three possible outcomes when solving a pair of linear equations: unique solution (intersecting lines), infinitely many solutions (coincident lines), or no solution (parallel lines).
- 😀 When the ratios of the coefficients (a₁/a₂, b₁/b₂, c₁/c₂) are equal, the equations represent coincident lines with infinitely many solutions. If they are unequal, the lines are parallel and have no solution.
Q & A
What is a linear equation in one variable?
-A linear equation in one variable is an equation where the highest power of the variable is 1, and it has the form ax + b = 0, where 'a' is the coefficient of the variable and 'b' is a constant. The key condition is that 'a' should never be zero.
What does it mean when an equation is described as 'linear'?
-An equation is called 'linear' if the highest power of its variable(s) is 1. This means that the variable(s) appear only to the first power and are not squared, cubed, or raised to any higher power.
What are the general forms of a linear equation in one variable and two variables?
-The general form of a linear equation in one variable is ax + b = 0, where 'a' is not equal to zero. The general form of a linear equation in two variables is ax + by + c = 0, where 'a' and 'b' are real coefficients, and 'x' and 'y' are the variables.
What happens if the highest power of a variable in an equation is greater than 1?
-If the highest power of a variable is greater than 1, the equation is no longer considered a linear equation. Instead, it becomes a quadratic equation (if the highest power is 2), cubic equation (if the highest power is 3), or another polynomial equation.
How can you graphically interpret a linear equation in two variables?
-When you plot a linear equation in two variables on a graph, it will form a straight line. Each point on the line is a solution to the equation.
What is the definition of a 'pair of linear equations'?
-A pair of linear equations in two variables consists of two linear equations that involve the same set of variables (e.g., x and y). These equations can be solved simultaneously to find the values of x and y that satisfy both equations.
What are the methods for solving a pair of linear equations in two variables?
-There are two main methods for solving a pair of linear equations: the graphical method (where the equations are plotted on a graph to find the intersection point) and the algebraic method (which includes the substitution, elimination, and cross-multiplication methods).
What does the graphical method for solving linear equations involve?
-The graphical method involves plotting each linear equation on a graph. The solution to the system of equations is the point where the two lines intersect. If the lines are parallel, there is no solution, and if the lines coincide, there are infinitely many solutions.
What is the substitution method for solving linear equations?
-The substitution method involves solving one of the equations for one variable (e.g., x or y) and substituting that expression into the other equation. This process simplifies the system, making it easier to solve for the other variable.
What happens if the ratio of coefficients of the variables in two linear equations is equal?
-If the ratio of coefficients (a1/a2 = b1/b2) is equal, but the constant terms (c1/c2) are not equal, the two lines represented by the equations will be parallel, and there will be no solution. This case is considered 'inconsistent'.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

memahami konsep persamaan linear satu variabel

Pengertian Sistem Persamaan Linear Tiga Variabel

Grade 8 Math Q1 Ep10: Linear Equation

Konsep Dasar Sistem Persamaan Linear Dua Variabel (SPLDV) | Matematika Wajib Kelas 10
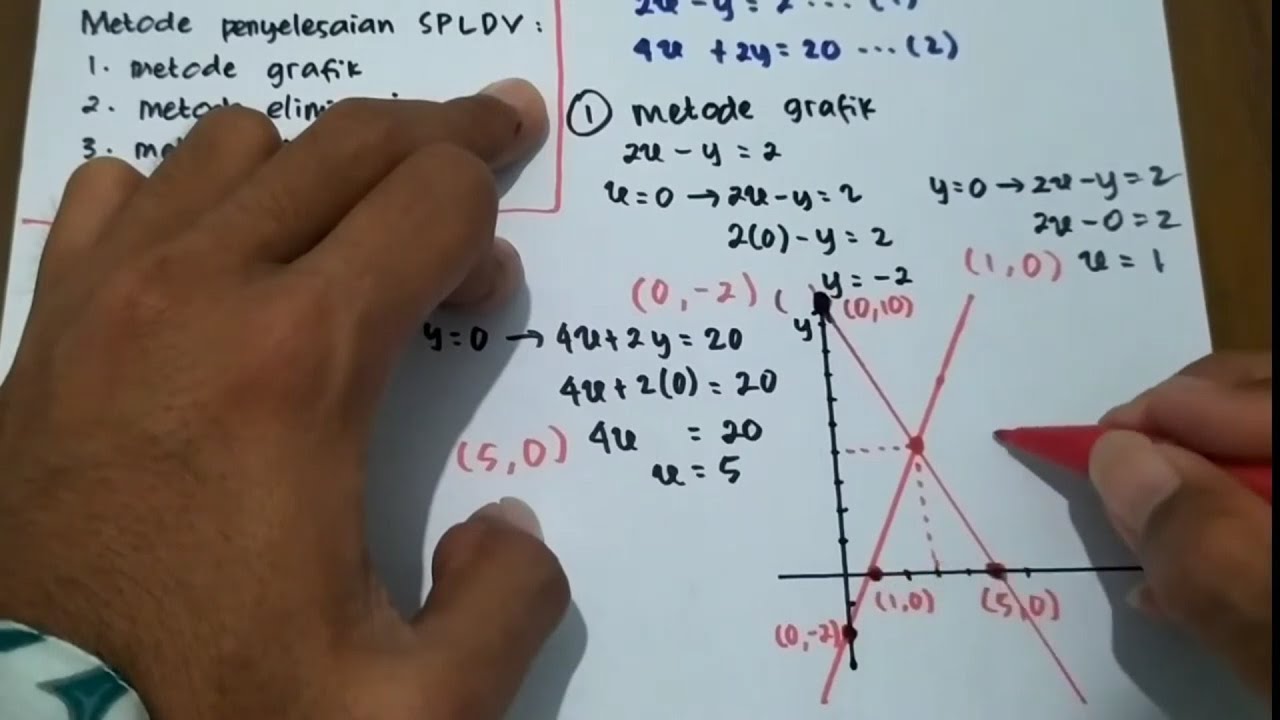
Sistem persamaan linear dua variabel kelas 10 - metode grafik

PERSAMAAN LINEAR DUA VARIABEL (PLDV) KELAS 9
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)