Apa dan Bagaimana Penelitian Survei
Summary
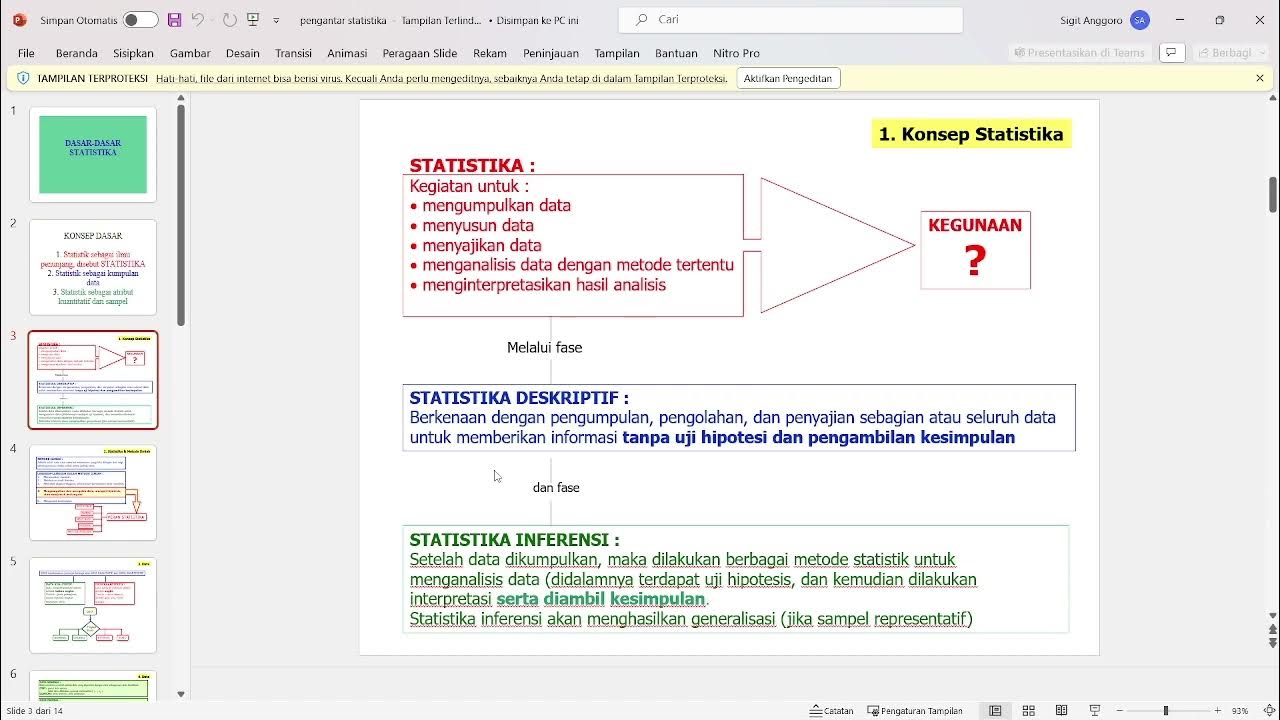
TLDRThis video discusses the survey method in scientific research, explaining its role as a descriptive research method that uses sampling to draw conclusions about large populations. It covers the importance of accurate sampling, the concept of margin of error, and how surveys are typically conducted using structured or mixed questionnaires. The video also highlights the application of surveys in various fields such as politics, economics, and employment, with examples from global and national institutions. Additionally, it discusses data analysis using statistical methods to derive meaningful conclusions from survey data.
Takeaways
- 😀 Surveys are a descriptive research method used to gather data about the current conditions of a population, often on a large scale.
- 😀 A survey involves collecting data from a sample of a large population, and the results can be generalized to the entire population.
- 😀 Surveys are commonly used in fields like politics (e.g., polling), economics, and social sciences to gather insights about public opinion, economic conditions, and more.
- 😀 A census is a type of survey conducted on the entire population, unlike regular surveys which use a sample.
- 😀 Sampling is crucial in survey research; selecting a representative sample is essential to ensure the generalizability of the findings to the larger population.
- 😀 Margin of error is an important concept in surveys, indicating the potential deviation in survey results from the actual population parameters.
- 😀 The margin of error (e.g., 3%) allows researchers to quantify the reliability of their conclusions, with a smaller margin indicating higher accuracy.
- 😀 Data collection for surveys is often done using structured questionnaires, which may include closed or open-ended questions depending on the study's goals.
- 😀 Modern surveys can leverage technology, such as online forms (e.g., Google Forms), making data collection more efficient and accessible.
- 😀 Data analysis in surveys can range from simple descriptive statistics (e.g., percentages) to more complex statistical methods (e.g., regression analysis) depending on the research objectives.
- 😀 The key to successful survey implementation lies in selecting a proper sample, defining the margin of error, and using appropriate data collection and analysis techniques.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of using surveys in scientific research?
-Surveys are used in scientific research to describe the current state of large populations, often helping researchers to generalize findings from a sample population to a larger group.
How are surveys different from censuses in terms of data collection?
-Surveys collect data from a sample of the population, while censuses collect data from every individual in the population. A census aims to gather comprehensive information, such as the national population count, while surveys focus on a smaller sample to generalize findings.
What is a common tool used to collect data in surveys?
-A common tool used for data collection in surveys is a questionnaire, which can be structured with predefined answers or open-ended to allow respondents to provide their own input.
How does the concept of sample selection impact the accuracy of survey results?
-Proper sample selection is crucial in ensuring the accuracy of survey results. The sample must represent the larger population accurately, as the conclusions drawn from the sample are generalized to the whole population.
What is the significance of margin of error in surveys?
-The margin of error represents the potential inaccuracy in survey results. It quantifies the degree of uncertainty in how well the sample represents the larger population. For example, a 3% margin of error means there is a 97% confidence that the results reflect the true population condition.
What types of statistical methods can be used to analyze survey data?
-Survey data can be analyzed using simple descriptive statistics like percentages or more complex methods such as correlation or regression analysis, depending on the survey's objective and the type of data collected.
Why are surveys commonly used in political research?
-Surveys are widely used in political research to assess public opinion on various political issues, such as voter preferences for candidates, political parties, or government policies.
How has technology influenced survey data collection?
-Technology has made survey data collection more efficient by enabling tools like Google Forms or online questionnaires. These platforms allow for easy distribution, data gathering, and analysis, streamlining the overall process.
What is the difference between descriptive and analytical survey data analysis?
-Descriptive data analysis involves summarizing and presenting the survey data in a simple form, like percentages or averages, whereas analytical analysis involves using advanced statistical techniques like regression or correlation to explore relationships between variables.
How does a survey contribute to understanding large-scale issues, such as economics or employment?
-Surveys help to collect data from large groups, offering valuable insights into issues like economic conditions or employment trends. This data can be generalized to reflect broader national or global trends, assisting policymakers and organizations in decision-making.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

TYPES OF SURVEY RESEARCH- Survey Research Method in Psychology | CBSE | Class 11 NCERT Psychology

Jenis - Jenis Penelitian Kuantitatif [ Nomor 4 Sering Banget Dipakai ! ]

Understanding Statistical Inference - statistics help

Kuliah Statistika Industri | Teknik Sampling

Geo X. 50. Penelitian Geografi.
Statisitik ke 3-1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)