Evapotranspirasi
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of evapotranspiration, which is a combination of evaporation and transpiration. Evaporation refers to the process of water turning into vapor due to solar energy, while transpiration is the release of water vapor by plants during photosynthesis. The video discusses how evapotranspiration is influenced by environmental factors like sunlight, humidity, and temperature, as well as plant-specific factors like species and health. It also covers the four types of evapotranspiration: reference, potential, crop, and actual evapotranspiration, and methods for estimating it, including evaporation pans, climate data analysis, and remote sensing techniques.
Takeaways
- 😀 Evapotranspiration is the combined process of evaporation and transpiration.
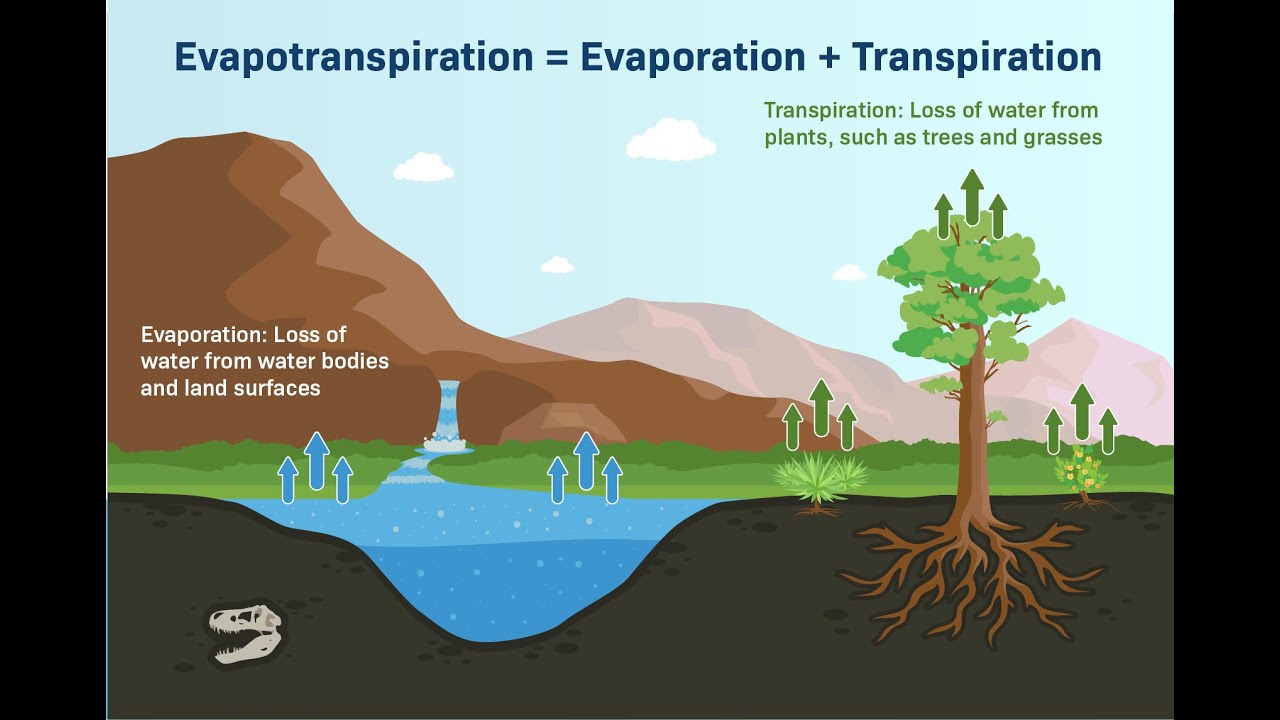
- 😀 Evaporation is the process of water turning into vapor or gas from surfaces like soil, rivers, lakes, and ponds due to sunlight.
- 😀 Transpiration is the process where plants release water vapor or gas through stomata during photosynthesis.
- 😀 Evaporation occurs due to the movement of water molecules with enough energy to transform into a gas.
- 😀 Transpiration happens when plants open their stomata to take in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
- 😀 Two main factors affect evapotranspiration: environmental factors and plant factors.
- 😀 Environmental factors influencing evapotranspiration include sunlight, air humidity, air temperature, air pressure, and wind speed.
- 😀 Plant factors that affect evapotranspiration include the plant species, the size of the plant, and the plant's condition.
- 😀 Four types of evapotranspiration: 1) Reference evapotranspiration (occurs on grass-covered land), 2) Potential evapotranspiration (occurs with abundant water), 3) Crop evapotranspiration (occurs with optimal water and plant conditions), and 4) Actual evapotranspiration (occurs when water is limited).
- 😀 Evapotranspiration can be estimated using three methods: 1) Evaporation pans and lysimeters, 2) Climate data analysis (e.g., the Penman-Monteith method), and 3) Remote sensing data (e.g., satellite imagery) using energy balance methods.
Q & A
What is evapotranspiration?
-Evapotranspiration is the combination of two processes: evaporation and transpiration. Evaporation refers to the transformation of water into vapor or gas from surfaces like soil, rivers, lakes, and ponds due to sunlight. Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapor through their stomata during photosynthesis.
How does evaporation occur?
-Evaporation occurs due to the movement of water molecules that gain enough energy to change into gas. This happens when heat, typically from the sun, causes the water molecules on the surface of the Earth to escape into the atmosphere as water vapor.
What role do plants play in evapotranspiration?
-Plants contribute to evapotranspiration through transpiration, where they release water vapor from their stomata. This process is closely linked to photosynthesis, as plants open their stomata to absorb carbon dioxide for the process of photosynthesis.
What are the main environmental factors that influence evapotranspiration?
-The key environmental factors affecting evapotranspiration include sunlight, air humidity, air temperature, atmospheric pressure, and wind speed.
How do plant factors affect evapotranspiration?
-Plant factors, such as plant type, size, and condition, also influence evapotranspiration. Healthy, larger plants tend to transpire more, and different species have varying levels of water usage and transpiration rates.
What are the four types of evapotranspiration?
-The four types of evapotranspiration are: 1) Reference or standard evapotranspiration, which occurs on a grass-covered surface; 2) Potential evapotranspiration, which happens when water is abundant and plants are healthy; 3) Crop evapotranspiration, where water is optimally available for plant growth; and 4) Actual evapotranspiration, which occurs when water is limited.
What is the difference between potential and actual evapotranspiration?
-Potential evapotranspiration occurs when there is an abundance of water available for plants, while actual evapotranspiration happens when the available water is limited, affecting the rate at which plants release water vapor.
What methods are used to estimate evapotranspiration?
-Evapotranspiration can be estimated using three main methods: 1) Evaporation pans and lysimeters, 2) Climatic data analysis, such as using the Penman-Monteith method, and 3) Remote sensing data or satellite imagery, using energy balance methods.
What is the significance of measuring evapotranspiration?
-Measuring evapotranspiration is crucial for understanding water cycles, irrigation requirements, and agricultural productivity. It helps in managing water resources efficiently and predicting crop yields.
Why does evapotranspiration vary with different environmental factors?
-Evapotranspiration varies based on factors like temperature, sunlight, humidity, and wind speed. These factors influence both the rate of evaporation from water bodies and the rate at which plants release water through transpiration.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Hidrologia 1 Evapotranspiração 6 Medição de evapotranspiração

Hidrologi - Evaporasi dan Evapotranspirasi

How much to irrigate | Netafim

Proses Air Berputar di Bumi:Siklus Hidrologi Itu Apa?| Kelompok 1 Kelas X.4 | SMAN 19 Kab. Tangerang

Mengukur dan menghitung Evapotranspirasi
Understanding Evaporation and Evapotranspiration: Key Concepts in Hydrology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)