Engineering Physics | Unit 5 | Magnetism (Part 2)
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the fundamental concepts of magnetism, focusing on key terms such as magnetic flux, magnetic dipole moment, and magnetic field strength. It covers the relationships between magnetic induction and permeability, as well as the units and dimensions of magnetic properties. The video also delves into the effects of materials in magnetic fields, including their permeability and magnetization. A detailed explanation of various magnetic phenomena, including the behavior of magnetic dipoles and induction, is provided, making it a comprehensive guide for students and enthusiasts of physics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Introduction to the basic concepts of magnetism, including magnetic flux, dipole moment, and magnetic field strength.
- 😀 Magnetic flux is defined as the number of magnetic field lines passing through a given area.
- 😀 Magnetic dipole moment represents the strength and orientation of a magnet, indicating the magnitude and direction of its magnetic field.
- 😀 The magnetic field strength at any point is represented by the magnetic induction (B), which is influenced by the surrounding magnetic field.
- 😀 Magnetic flux density is a measure of the number of magnetic field lines per unit area and is crucial in understanding the magnetic behavior of materials.
- 😀 The relationship between magnetic induction and permeability is key to understanding how materials interact with magnetic fields.
- 😀 Relative permeability of a material indicates how easily the material can be magnetized by a magnetic field.
- 😀 The concepts of magnetization and the effect of external magnetic fields on materials are explained, focusing on their influence on material properties.
- 😀 The lecture discusses how materials are classified based on their magnetic properties, such as ferromagnetic, paramagnetic, and diamagnetic materials.
- 😀 The script also touches upon practical applications and measurements, like the calculation of magnetic forces and the role of materials in various devices and systems.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The primary focus of the video is an introduction to the topic of magnetism, covering basic terms and definitions related to magnetic fields and phenomena.
What is magnetic flux?
-Magnetic flux is the total number of magnetic field lines passing through a given area. It is a measure of the strength and extent of a magnetic field in that area.
What does the magnetic dipole moment represent?
-The magnetic dipole moment represents the strength and orientation of a magnet's magnetic field. It is associated with a system that behaves like a small magnet, characterized by a north and south pole separated by a small distance.
How is magnetic induction defined in the context of magnetism?
-Magnetic induction, or magnetic field intensity, refers to the magnetic field produced in a material. It is represented by the symbol 'B' and depends on the magnetic field strength and the material's magnetic properties.
What is the relationship between magnetic induction and permeability?
-Magnetic induction (B) is related to the magnetic field strength (H) and the permeability (μ) of the material. The relationship is expressed as B = μH, where μ is the material's permeability, indicating how easily the material can support the formation of a magnetic field.
What is the role of relative permeability in magnetism?
-Relative permeability is a measure of a material's ability to conduct magnetic flux compared to a vacuum. It is the ratio of the material's permeability to the permeability of free space.
How is magnetic field strength measured?
-Magnetic field strength is measured in amperes per meter (A/m) and represents the intensity of the magnetic field at a specific point.
What are the units for magnetic flux density?
-Magnetic flux density is measured in tesla (T), which is equivalent to one weber per square meter (Wb/m²).
What is the significance of the magnetic dipole moment in terms of the material's magnetic properties?
-The magnetic dipole moment plays a crucial role in defining the material's ability to generate a magnetic field. It represents the maximum force that can act on a magnetic dipole when placed in an external magnetic field.
What is magnetic permeability, and why is it important?
-Magnetic permeability is a measure of a material's ability to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. It is important because it determines how well a material can conduct magnetic flux, which directly affects the strength and efficiency of magnetic fields in various applications.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

MAGNETISM ,IMPORTANT TERMS & EQUATIONS IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
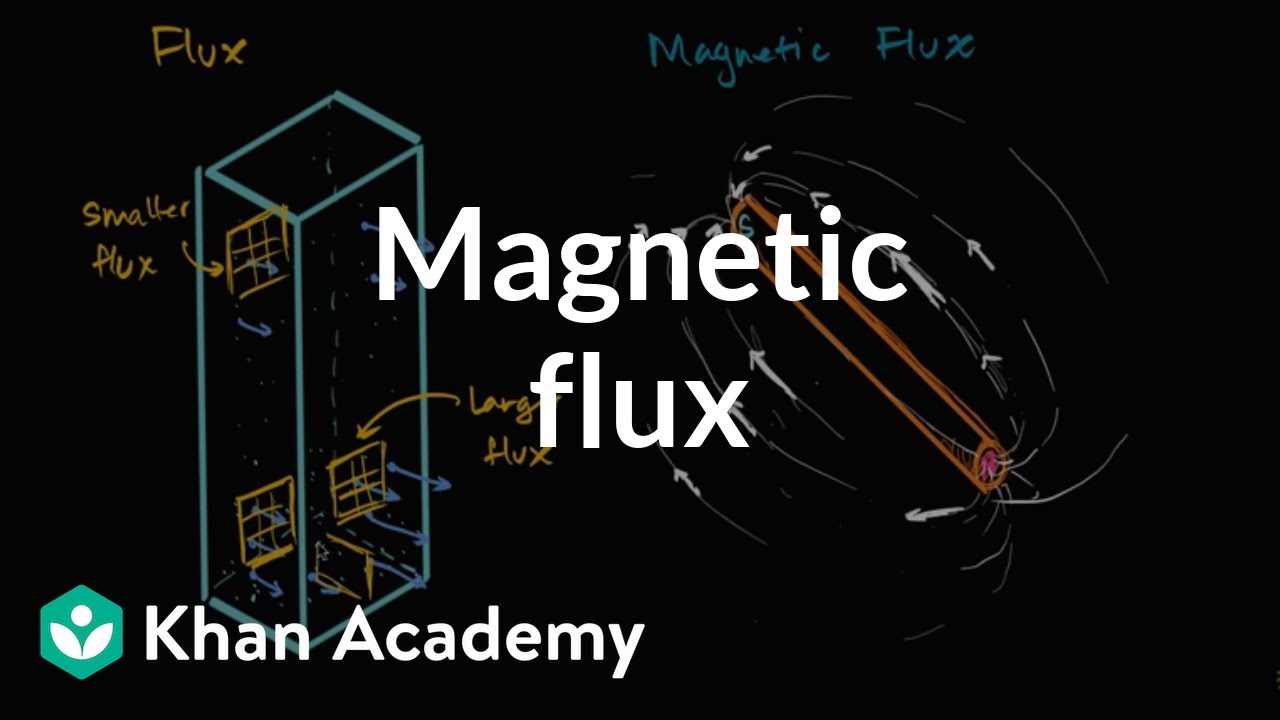
Flux and magnetic flux

Listrik Magnet 13.4 Elektrodinamika Induksi Elektromagnetik Hukum Faraday

Important Terms in Magnetic Circuit
Episode 34: Magnetism - The Mechanical Universe

Materi Kemagnetan Kelas 9 (Part-2) Kemagnetan Bumi, Migrasi Hewan dan Pemanfaatan Elektromagnet
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)