PLTU Pusat Listrik Tenaga Uap
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the operation of Steam Power Plants (PLTU), which convert the kinetic energy of steam into electricity. It outlines key components such as boilers, turbines, condensers, and generators, explaining the Rankine cycle and its efficiency. The benefits of PLTU include low energy costs, reliability, and abundant coal reserves in Indonesia. However, PLTU also has environmental drawbacks, including harmful emissions, pollution, and potential long-term damage from coal mining. The video highlights both the advantages and disadvantages of PLTU in generating electricity, especially in the context of Indonesia.
Takeaways
- 😀 PLTU (Coal-Fired Power Plant) converts kinetic energy from steam into electrical energy, making it a major source of electricity worldwide.
- 😀 Around 86% of global electricity is generated from coal-fired power plants due to their high efficiency and economical electricity production.
- 😀 Indonesia has abundant coal reserves, which contribute to the viability of PLTUs in the country.
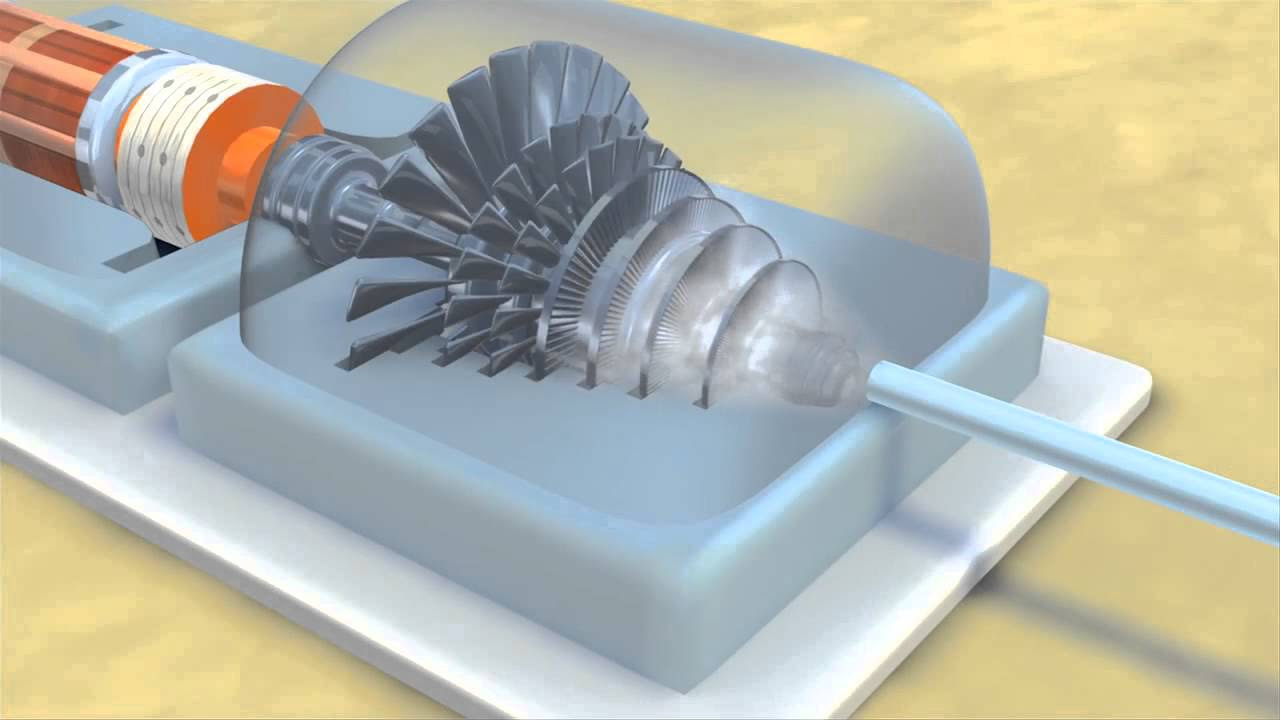
- 😀 A PLTU consists of key components: boiler, steam turbine, condenser, and generator, each playing a crucial role in energy conversion.
- 😀 The boiler heats water to produce high-pressure steam, which drives the turbine to generate mechanical energy.
- 😀 The steam turbine converts thermal energy from steam into mechanical energy, which is transferred to the generator to produce electricity.
- 😀 The condenser cools the steam exiting the turbine, turning it back into water, which is then returned to the boiler for reuse, creating a closed-loop system.
- 😀 PLTU operates based on an ideal Rankine cycle, regulating pressure and temperature to convert water into steam and vice versa.
- 😀 Demineralized water (demin) is used in PLTU to ensure effective energy transfer with minimal scaling or corrosion.
- 😀 Key benefits of PLTU include low coal costs, reliable continuous power supply, abundant coal reserves, and a high load factor (up to 80%).
- 😀 However, PLTUs have environmental drawbacks, including harmful emissions (e.g., sulfur dioxide), greenhouse gases, toxic ash waste, and water pollution.
- 😀 Coal mining for PLTU operation is costly, potentially harmful to the environment, and requires significant investment in infrastructure.
Q & A
What is a PLTU (Steam Power Plant)?
-A PLTU is a power plant that uses the kinetic energy of steam to generate electricity. It is one of the most common sources of electricity worldwide, contributing to 86% of the global electricity generation due to its high efficiency.
Why is PLTU commonly used to generate electricity?
-PLTU is widely used because it is highly efficient, making electricity generation economically viable. Additionally, Indonesia has abundant coal reserves, which further supports the use of PLTU in the region.
What are the main components of a PLTU?
-The main components of a PLTU are the boiler, steam turbine, condenser, and generator. The boiler heats water to create high-pressure steam, which drives the turbine. The turbine is connected to a generator that produces electricity, while the condenser cools the steam back into water.
What is the function of the boiler in a PLTU?
-The boiler's function is to convert water into high-pressure steam by heating it. This steam is then used to drive the turbine, generating mechanical energy that is eventually transformed into electrical energy.
How does the steam turbine in a PLTU work?
-The steam turbine converts the thermal energy of high-pressure steam into mechanical energy. As the steam flows over the turbine blades, it causes the turbine to spin, and this rotation is linked to a generator that produces electricity.
What is the role of the condenser in a PLTU?
-The condenser's role is to cool the steam that has passed through the turbine, converting it back into water. This process allows the water to be reused in the boiler, forming a closed-loop cycle.
What is the Rankine Cycle and how is it related to PLTU?
-The Rankine Cycle is an ideal thermodynamic cycle that describes the process of converting heat into mechanical energy. In PLTU, this cycle involves heating water to create steam, driving a turbine, and then condensing the steam back into water to repeat the process.
What are the advantages of PLTU?
-The advantages of PLTU include low cost due to the cheap price of coal, high predictability, and reliability since it can operate continuously 24/7. Additionally, Indonesia has abundant coal reserves, and infrastructure for coal mining and transport is well-established.
What are the environmental drawbacks of PLTU?
-PLTU has several environmental drawbacks, including the emission of harmful substances such as sulfur dioxide, which can cause respiratory diseases. It also produces greenhouse gases and fly ash, which are toxic and can degrade air quality and pollute water sources.
How does coal extraction for PLTU impact the environment?
-Coal extraction can cause environmental damage by altering the landscape and topography. Unused mining sites can disrupt natural habitats and contribute to long-term ecological changes, making the process harmful to the environment.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)