PEMBELAJARAN SENI MUSIK |notasi balok, birama dan nilai ketuk
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Bening introduces the basics of musical notation, focusing on the universal system of the staff, clefs, and note values. She covers essential elements such as the staff, ledger lines, and the importance of clefs like the treble clef, along with understanding time signatures and note durations. The video aims to demystify music notation by explaining how notes are placed on the staff and how different clefs indicate specific notes. Viewers also learn how to interpret time signatures and measure subdivisions, with practical examples and exercises.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video begins with a warm greeting and thanks for the support received from subscribers, encouraging new viewers to subscribe and activate notifications.
- 😀 The focus of the video is on teaching music notation, specifically the universal musical notation system called 'notasi balok' or staff notation.
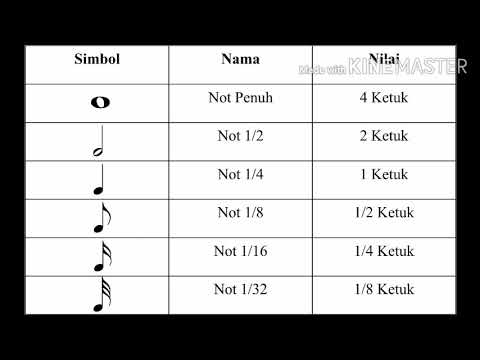
- 😀 The script reviews the basic parts of musical notation, including the note head, stem, and flag.
- 😀 'Notasi balok' (staff notation) is explained as a system that uses symbols, specifically notes, to represent music.
- 😀 The video introduces the concept of the 'staff' (paranada), which consists of five horizontal lines and four spaces, where notes are written to represent pitches.
- 😀 The use of ledger lines is explained for notes that go above or below the staff, with more ledger lines being used for higher or lower pitches.
- 😀 The importance of clefs (kunci) in music notation is highlighted, with a particular focus on the treble clef (kunci G) and its role in indicating the location of specific notes.
- 😀 The video explains the meaning of a time signature (tanda birama), how it divides the staff into sections, and how it affects the rhythm and structure of a musical piece.
- 😀 A discussion of common time signatures, like 2/4 and 3/4, illustrates how the number on top indicates the number of beats per measure, while the number on the bottom shows the type of note receiving one beat.
- 😀 Finally, the video emphasizes the practical application of music notation by explaining how notes are placed in measures to match the beats indicated by the time signature, and encourages students to practice understanding these musical concepts.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video script?
-The primary focus of the video script is to explain the concept of 'notasi balok' (staff notation) in music, including its components, symbols, clefs, time signatures, and their usage in reading and writing music.
What is 'notasi balok' or staff notation?
-'Notasi balok' refers to musical notation that uses symbols or pictures, commonly known as musical notes or 'titi nada,' to represent pitches and rhythms in music. It consists of three main parts: the note head, stem, and flag.
What is a 'staf' or staff in musical notation?
-A 'staf' or staff consists of five horizontal lines and four spaces where musical notes are written. The placement of notes on the staff corresponds to their pitch, with higher notes written above and lower notes below.
How do 'ledger lines' work in musical notation?
-Ledger lines are small horizontal lines used to extend the staff when notes go beyond its range. These lines help notate pitches that are higher or lower than the staff can accommodate.
What is the function of a clef in musical notation?
-A clef is a symbol used to indicate the specific pitch of notes on the staff. Common clefs include the treble clef, bass clef, and alto clef. The treble clef, for example, indicates that the second line of the staff represents the note 'G'.
What is the purpose of a time signature in music?
-A time signature, placed at the beginning of a musical piece, determines the number of beats in each measure (or 'ruas birama') and the type of note that gets the beat. For example, in 2/4 time, each measure contains two beats, and each beat is represented by a quarter note.
How is a time signature 2/4 interpreted in musical notation?
-In a 2/4 time signature, there are two beats per measure, with each beat represented by a quarter note. This means you would use quarter notes (which have a value of one beat) to fill the measure.
Why is the quarter note used in the 2/4 time signature?
-The quarter note is used in the 2/4 time signature because each quarter note is worth one beat, and two quarter notes fit perfectly into each measure, which has two beats in total.
What is the role of 'ruas birama' or measure in musical notation?
-A 'ruas birama' or measure is a segment of music between two vertical bar lines that contains a set number of beats. The length of the measure is defined by the time signature.
How do different types of notes correspond to their values in a time signature?
-In the example of the 2/4 time signature, a quarter note represents one beat. Other notes, like the half note, have longer durations. A half note is worth two beats, which fits into the time signature by taking up one full measure.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)