SEL TUMBUHAN DAN FUNGSINYA
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the various organelles found in plant cells, highlighting their functions and structures. It begins by introducing the cell as the smallest unit of life and moves on to describe 11 key organelles, including the cell wall, membrane, nucleus, plastids, vacuoles, and mitochondria. Each organelle’s role is discussed, from protecting and shaping the cell to storing energy, producing proteins, and enabling photosynthesis. The video aims to provide a clear and comprehensive understanding of plant cell structure, making it an essential resource for learning about cell biology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cells are the smallest structural and functional units of living organisms, composed of various organelles.
- 😀 The cell wall is the outermost layer of plant cells, providing protection, shape, and controlling turgor pressure.
- 😀 The cell membrane, composed of lipids and proteins, regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell.
- 😀 The nucleus, the largest part of the plant cell, controls cell activities and stores genetic information.
- 😀 Cytoplasm is a fluid inside the cell that facilitates chemical reactions and acts as a medium for organelles.
- 😀 Plastids, including chloroplasts, are responsible for photosynthesis and carbohydrate production in plant cells.
- 😀 Vacuoles store nutrients, waste products, and pigments, and help maintain cell turgidity.
- 😀 Ribosomes, the smallest organelles, are the sites of protein synthesis in the cell.
- 😀 The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is involved in protein and lipid synthesis, and also aids in material transport within the cell.
- 😀 Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, generating energy through respiration, and also involved in the citric acid cycle.
Q & A
What is a cell and why is it considered the smallest unit of life?
-A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of a living organism. It is considered the smallest unit of life because it can carry out all necessary life processes, such as metabolism and reproduction, on its own.
What is an organelle and what role does it play in plant cells?
-An organelle is a specialized structure within a cell that performs specific functions. In plant cells, organelles such as the cell wall, mitochondria, and plastids work together to support various life processes like energy production and photosynthesis.
What is the function of the cell wall in plant cells?
-The cell wall is the outermost layer of the plant cell. It provides structural support, protection, and shape to the cell, helps maintain turgor pressure, and controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell.
What is the role of the plasma membrane in plant cells?
-The plasma membrane is a lipid-protein membrane that surrounds the cell. It regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell, protects the cell’s interior, and helps receive external signals from the environment.
How does the nucleus function in plant cells?
-The nucleus is the largest organelle in a plant cell and contains the genetic material. It regulates cell activities such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction, and stores genetic information in the form of DNA.
What is the importance of chloroplasts in plant cells?
-Chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll, a pigment that captures light energy, converting it into chemical energy to produce carbohydrates for the plant.
What are vacuoles and what functions do they serve in plant cells?
-Vacuoles are large, membrane-bound organelles that store substances like food, water, and waste products. They also help maintain cell rigidity by regulating turgor pressure and play a role in the storage of metabolic byproducts.
How do ribosomes contribute to protein synthesis in plant cells?
-Ribosomes are small structures that facilitate the synthesis of proteins by translating messenger RNA (mRNA) into amino acid chains. They can either be attached to the endoplasmic reticulum or float freely in the cytoplasm.
What are the two types of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) found in plant cells, and what are their functions?
-The two types of endoplasmic reticulum are the rough ER (granular) and the smooth ER (agranular). The rough ER is involved in protein synthesis and transport, while the smooth ER synthesizes lipids, hormones, and other molecules like glycogen.
What role do mitochondria play in plant cells?
-Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell. They are responsible for generating energy in the form of ATP through cellular respiration, a process that converts chemical energy from nutrients into usable energy.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

BIOLOGI Kelas 11 - Struktur dan Organel Sel | GIA Academy

CARA MUDAH MEMPELAJARI SEL HEWAN DAN SEL TUMBUHAN

Biology - Cell Structure (Cont.)

WCLN - Cell Organelles - Biology
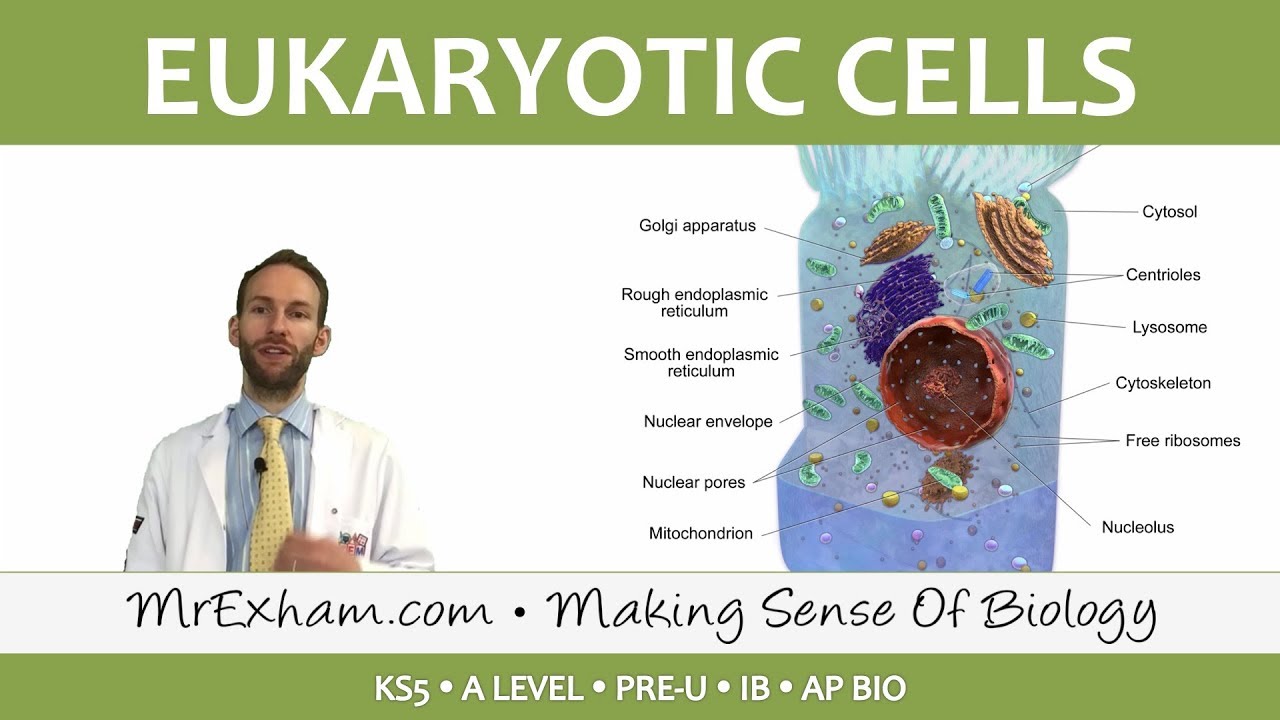
Eukaryotic Cell Structure - Organelles - Post 16 Biology (A Level, Pre-U, IB, AP Bio)
PARTS AND FUNCTIONS OF A CELL SCIENCE 7 QUARTER 2 MODULE 3
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)