Kurt Lewin´s Force Field Theory of Change | Organizational Change | MeanThat
Summary
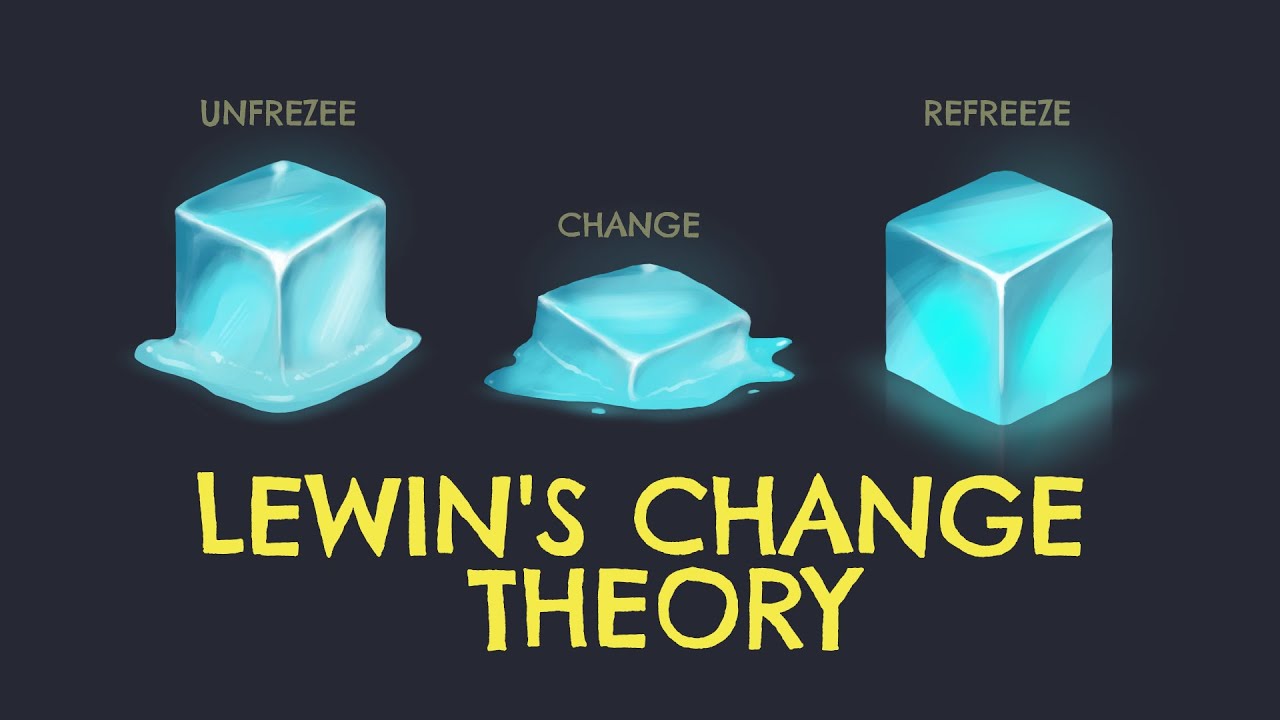
TLDRThe Force Field Theory of Change, developed by Kurt Lewin, explains how opposing forces within an organization influence change. The theory identifies two sets of forces: forces for change, which drive improvement and performance, and resistances to change, which maintain the current state. These forces interact over time to determine the pace and success of change. Lewin's model includes three stages: unfreeze, where the organization is prepared for change; change, where improvements are made; and refreeze, where the new state is solidified to prevent regression. Organizations can increase change forces, reduce resistances, or do both to facilitate transformation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Force Field Theory of Change is a famous organizational change model that describes two opposing forces within an organization: forces for change and resistances to change.
- 😀 The theory uses a graph to represent change, with time on the horizontal axis and performance level on the vertical axis, showing how performance changes over time.
- 😀 The goal of organizational change is to increase performance and efficiency within a set period, typically a year, as described in the example scenario.
- 😀 The two key forces in the model are: forces for change, which push for improvement, and resistances to change, which try to maintain the status quo.
- 😀 Forces for change motivate an organization to improve, aiming for higher performance and efficiency.
- 😀 Resistances to change are factors like organizational inertia that slow down or prevent change from occurring.
- 😀 There are three options for managing the forces in the change process: increasing forces for change, reducing resistances to change, or doing both simultaneously.
- 😀 The Force Field Theory also includes three stages for implementing change: unfreeze, change, and refreeze.
- 😀 The unfreeze stage involves breaking the organization's current state of inertia, making it receptive to change.
- 😀 The change stage is where the desired improvements or changes are actually made within the organization.
- 😀 The refreeze stage is crucial for stabilizing the organization in its new state to ensure long-term success and prevent regression.
Q & A
What is the primary concept behind Lewin's Force Field Theory of Change?
-Lewin's Force Field Theory of Change suggests that change within an organization is influenced by two opposing sets of forces: forces for change, which drive the organization to improve, and resistances to change, which hinder the process of improvement.
How is the relationship between forces for change and resistances to change depicted in the theory?
-In the theory, forces for change are represented as motivating factors that push the organization toward improvement, while resistances to change are represented as barriers or inertia that prevent the organization from moving forward.
What are the three main options for facilitating change according to the Force Field Theory?
-The three options for facilitating change are: (1) increasing the forces for change, (2) reducing the resistances to change, or (3) doing both simultaneously—enhancing the forces for change while reducing resistances.
What is the significance of the horizontal and vertical axes in the Force Field Theory graph?
-The horizontal axis represents time, and the vertical axis represents the level of performance or efficiency. The higher the point on the vertical axis, the better the performance or efficiency of the organization.
What does the concept of 'unfreezing' refer to in Lewin's model?
-Unfreezing refers to the first stage of the change process, where the organization must break free from its current state or inertia in order to begin the change. This stage involves addressing resistance to change and preparing the organization for transformation.
What happens during the 'change' stage in Lewin's Force Field Theory?
-During the 'change' stage, the desired improvements or changes are implemented in the organization. This involves making tangible adjustments to processes, structures, or behaviors to increase performance.
Why is the 'refreeze' stage important in Lewin's Force Field Theory?
-The 'refreeze' stage is crucial because it ensures that the changes made during the 'change' stage are sustained. Without refreezing, there is a risk that the organization could return to its previous state due to ongoing resistances to change.
Can the forces for change and resistances to change exist simultaneously in an organization?
-Yes, the forces for change and resistances to change coexist at all times. The challenge is to manage the balance between these forces to ensure successful organizational change.
What role do resistances to change play in Lewin's Force Field Theory?
-Resistances to change represent the factors that prevent or slow down the change process. They include organizational inertia, cultural resistance, and other factors that make the organization hesitant or reluctant to adopt new methods.
How does the Force Field Theory suggest an organization should approach change to increase the chances of success?
-The theory suggests that organizations should either increase the forces for change, reduce resistances, or ideally, do both to ensure the change process is successful. Additionally, the organization must go through the unfreeze, change, and refreeze stages to stabilize and sustain the change.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Lewin’s Change Theory - UnFreeze, Change, ReFreeze Method

What is Organizational Development? - Human Resources Career Series

GCSE Physics - Momentum Part 2 of 2 - Changes in Momentum #60

Definición del materialismo dialéctico karl marx

Work and Kinetic Energy - Physics

What is Organizational Behavior? Definition & Examples [2025]
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)