METABOLISME HEWAN
Summary
TLDRThis presentation discusses animal metabolism, focusing on key processes such as anabolism and catabolism. It explains how metabolism involves the conversion of food into energy, and the synthesis of proteins, lipids, and other essential molecules. The session covers both aerobic and anaerobic respiration, including the stages like glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport. It also delves into processes like photosynthesis, chemosynthesis, and protein synthesis. The discussion highlights the importance of these biochemical pathways for sustaining life and energy production in animals.
Takeaways
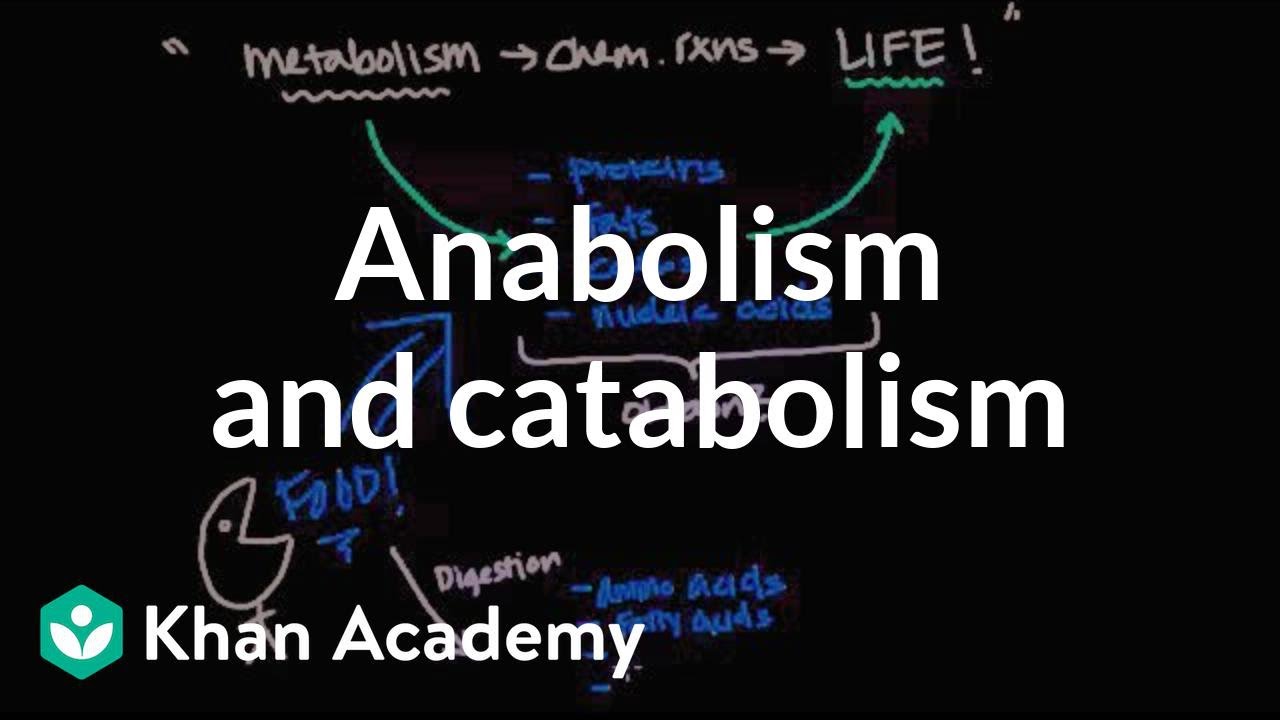
- 😀 Metabolism is the process of forming compounds in cells, accompanied by energy changes, including both anabolic and catabolic reactions.
- 😀 Anabolism involves synthesizing complex compounds from simpler ones, requiring energy, such as light energy for photosynthesis and chemical energy for chemosynthesis.
- 😀 Catabolism refers to the breakdown of complex compounds into simpler ones, releasing energy that can be used by organisms for their activities.
- 😀 The main purposes of metabolism are to convert food into energy, convert food into raw materials for protein synthesis, and eliminate metabolic waste.
- 😀 The digestive system of animals, like cows, breaks down food into components like proteins, carbohydrates, and fats that are absorbed for use in metabolism.
- 😀 Kemosynthesis is a process in which energy from chemical reactions (not light) is used by bacteria to assimilate carbon, typically in environments without sunlight.
- 😀 Lipid synthesis can occur from carbohydrates and proteins through processes that meet in the Krebs cycle, demonstrating the interconnectivity of metabolic pathways.
- 😀 Protein synthesis involves the use of DNA, RNA, and ribosomes to create proteins, which are polypeptides essential for cellular functions.
- 😀 Aerobic respiration requires oxygen and consists of four stages: glycolysis, oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain.
- 😀 Anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen and includes processes like lactate fermentation, fat catabolism, and protein catabolism, with energy production via these alternative pathways.
Q & A
What is metabolism in animals?
-Metabolism in animals refers to the biochemical process by which cells convert substances into energy, involving both the synthesis and breakdown of compounds. It includes anabolic processes like building complex molecules and catabolic processes like breaking down molecules for energy.
What are the main goals of metabolism?
-The main goals of metabolism include converting food into energy, converting food into building blocks for proteins, and eliminating metabolic waste products.
What is the difference between anabolism and catabolism?
-Anabolism is the process of building complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy. Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy.
How does the digestive system of cows relate to their metabolism?
-In cows, the digestive system is an example of animal metabolism where food is broken down into simpler molecules like proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. These molecules are then absorbed and used for energy or building tissues.
What is the process of kemosynthesis?
-Kemosynthesis is a type of anabolism where energy from chemical reactions, rather than sunlight, is used to assimilate carbon. It is typically performed by certain bacteria known as chemoautotrophs.
What role does the Krebs cycle play in metabolism?
-The Krebs cycle, or citric acid cycle, is crucial in aerobic respiration. It processes acetyl-CoA into carbon dioxide and transfers electrons to produce energy-rich molecules like ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
What are the key stages of aerobic respiration?
-Aerobic respiration consists of four main stages: glycolysis, oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. These processes convert glucose into ATP, the energy currency of cells.
What is the significance of fermentation in anaerobic respiration?
-Fermentation is a key part of anaerobic respiration, where glucose is partially broken down in the absence of oxygen to produce energy, typically generating byproducts like lactic acid or ethanol depending on the organism.
What happens during glycolysis?
-During glycolysis, one molecule of glucose (a six-carbon compound) is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate (three-carbon compounds). This process occurs in the cytoplasm and produces a small amount of ATP and NADH.
How does the body use proteins, fats, and carbohydrates in metabolism?
-Proteins, fats, and carbohydrates are used in metabolism as energy sources. Carbohydrates are first broken down into glucose, fats into fatty acids, and proteins into amino acids, all of which can enter various metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis or the Krebs cycle, to generate ATP.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

[BAKTERIOLOGI] Part 1 Metabolisme Bakteri

Transformasi Energi dan Metabolisme di dalam Sel - Energi dalam Sistem Kehidupan
Overview of metabolism: Anabolism and catabolism | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy

🌱 Anabolismo y catabolismo | Metabolismo celular | Papel de las enzimas y el ATP | Examen UNAM

DNA

Metabolisme (pengertian dan perbedaan Katabolisme dan Anabolisme)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)