🌱 Anabolismo y catabolismo | Metabolismo celular | Papel de las enzimas y el ATP | Examen UNAM
Summary
TLDRIn this biology lesson, Carlos explains cellular metabolism, emphasizing the roles of anabolism and catabolism. Anabolism builds complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy in the form of ATP, as seen in processes like protein synthesis and glycogenesis. On the other hand, catabolism breaks down complex molecules, releasing energy, such as in glycolysis and glycogenolysis. The importance of enzymes in speeding up metabolic reactions is highlighted, and the concept of ATP as the energy carrier is clarified. The video also contrasts heterotrophic organisms (like humans and animals) with autotrophic plants, which can synthesize their own organic matter using sunlight.
Takeaways
- 😀 Metabolism refers to the series of chemical reactions that allow organisms to obtain energy to grow, reproduce, move, and perform essential functions.
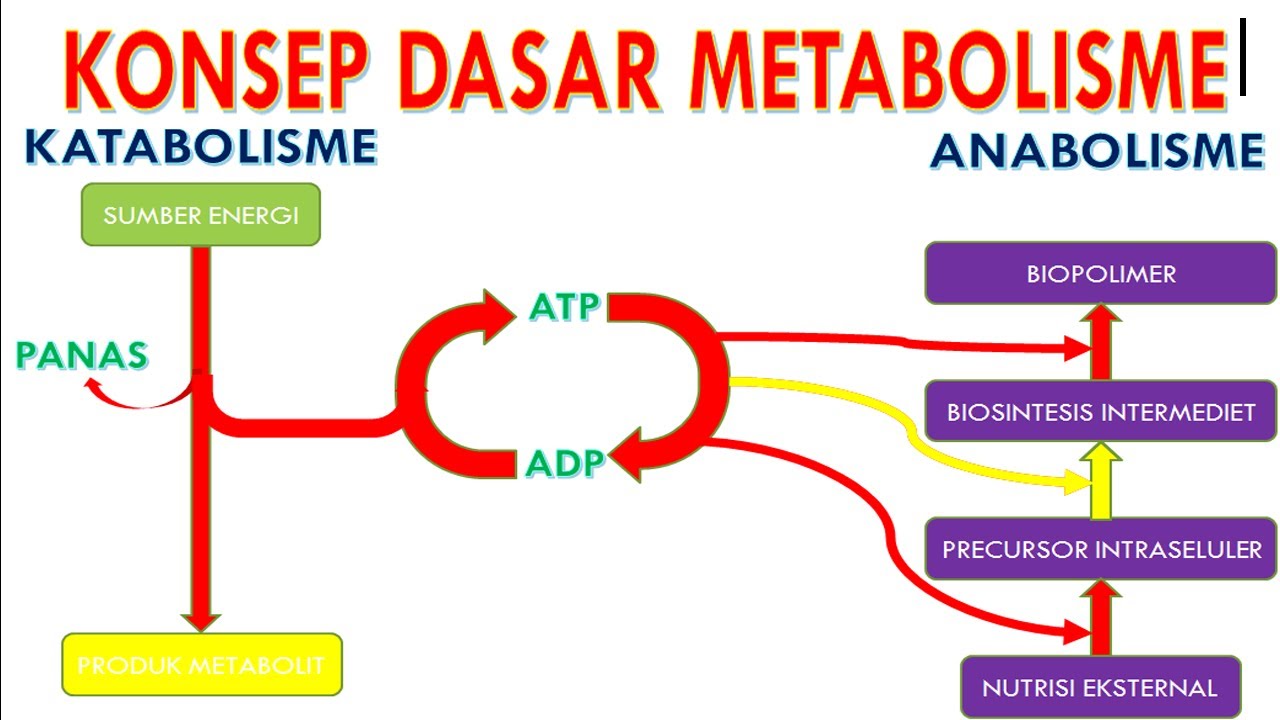
- 😀 Metabolism is divided into two main processes: Anabolism (building complex molecules from simpler ones) and Catabolism (breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones).
- 😀 Anabolism involves the creation of large, complex molecules from small, simple ones and requires energy in the form of ATP.
- 😀 Anabolic reactions are typically referred to as 'synthesis' or 'genesis' because they build molecules, like the synthesis of glycogen or proteins.
- 😀 An example of an anabolic process is glycogenesis, the creation of glycogen from glucose molecules in the liver.
- 😀 Another example of an anabolic process is protein synthesis, where amino acids (small molecules) combine to form proteins (complex molecules).
- 😀 Humans and animals are heterotrophic organisms, meaning they obtain organic matter (like carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins) from external sources.
- 😀 Plants are autotrophic, meaning they can synthesize their own organic matter (like carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins) from inorganic molecules using sunlight.
- 😀 Photosynthesis is an anabolic process in plants where simple molecules (water and carbon dioxide) are used to create complex molecules (like glucose and starch).
- 😀 Catabolism involves the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules, releasing energy (in the form of ATP) during the process.
- 😀 An example of a catabolic process is glycolysis, where glucose (a complex molecule) is broken down into smaller molecules, generating energy in the form of ATP.
Q & A
What is metabolism in biological terms?
-Metabolism refers to the series of chemical reactions that allow organisms to obtain the energy necessary for functions such as growth, reproduction, movement, and feeding.
What is the difference between anabolism and catabolism?
-Anabolism is the process of creating complex molecules from simpler ones, consuming energy in the form of ATP. Catabolism, on the other hand, is the process of breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy in the form of ATP.
Why is it important to understand enzymes before studying metabolism?
-Enzymes play a crucial role in metabolic reactions by accelerating the rate at which chemical reactions occur. Understanding enzymes helps clarify how metabolic processes like anabolism and catabolism function.
What is an example of an anabolic process in the human body?
-An example of an anabolic process is the synthesis of proteins from amino acids, where small molecules (amino acids) are combined to form a larger, more complex molecule (protein), consuming ATP in the process.
What role does ATP play in metabolism?
-ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the primary energy carrier in metabolic processes. It provides the energy necessary for both anabolic and catabolic reactions in the body.
Why do organisms like humans and animals rely on external food sources for energy?
-Humans and animals are heterotrophs, meaning they cannot synthesize their own organic material. Instead, they obtain energy and nutrients from consuming plants, fruits, vegetables, and other organisms.
What is the process of glucogenesis, and why is it considered anabolic?
-Glucogenesis is the creation of glycogen from glucose molecules, which is an anabolic process because small glucose molecules are linked together to form a larger, complex molecule, consuming energy in the form of ATP.
What makes photosynthesis an anabolic process?
-Photosynthesis is an anabolic process because it involves the creation of complex organic molecules, such as glucose, from simpler molecules like water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight.
How is catabolism related to the breakdown of glucose?
-Catabolism refers to the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones. For example, in the process of glycolysis, a glucose molecule is broken down into smaller molecules, releasing energy in the form of ATP.
What is the function of enzymes in metabolic reactions?
-Enzymes act as catalysts in metabolic reactions, speeding up the chemical processes by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. They are essential in both anabolic and catabolic reactions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Metabolismo Energético - Brasil Escola

Metabolism, Anabolism, & Catabolism - Anabolic vs Catabolic Reactions

[BAKTERIOLOGI] Part 1 Metabolisme Bakteri

Biologi part 4: Energi & Metabolisme

VIDA E CARACTERÍSTICAS GERAIS DOS SERES VIVOS (PROVA, VESTIBULAR, ENEM) - OLHAR QUÍMICO |PROF. ROMEU
KONSEP DASAR METABOLISME
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)