HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM | DIGESTIVE ORGANS AND THEIR FUNCTIONS
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the human digestive system, focusing on the key organs involved in digestion. It covers the main digestive organs, including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus, and describes how they work together to break down and absorb nutrients. Additionally, it highlights the role of accessory organs like the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder in supporting digestion by producing enzymes, bile, and regulating blood sugar. Through this detailed explanation, viewers gain a deeper understanding of how the body processes food and eliminates waste.
Takeaways
- 😀 The human digestive system consists of two main types of organs: primary digestive organs and accessory organs.
- 😀 Primary digestive organs include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
- 😀 The mouth plays a crucial role in breaking down food with teeth, tongue, and saliva, which contains the enzyme amylase to break down carbohydrates.
- 😀 The esophagus connects the mouth to the stomach and uses peristalsis to move food.
- 😀 The stomach is a muscular organ that stores food temporarily and breaks it down using stomach acids and enzymes like pepsin for protein digestion.
- 😀 The small intestine has three parts: the duodenum (chemical digestion), jejunum (nutrient absorption), and ileum (final nutrient absorption).
- 😀 The large intestine absorbs water and salts from waste and processes remaining undigested food.
- 😀 The rectum stores waste before it is expelled through the anus, where muscle and nerve coordination control the movement of feces.
- 😀 Accessory digestive organs, such as the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder, support digestion but do not directly carry food.
- 😀 The pancreas produces digestive enzymes (amylase, lipase, protease) and hormones like insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar levels.
- 😀 The liver produces bile to help digest fats, processes toxins, and regulates blood sugar. The gallbladder stores bile until it's needed for digestion.
Q & A
What are the two main categories of digestive organs?
-The two main categories of digestive organs are main digestive organs and supporting digestive organs. Main digestive organs are directly involved in the passage of food, while supporting digestive organs assist in the digestion process.
What are the main digestive organs involved in the food passage?
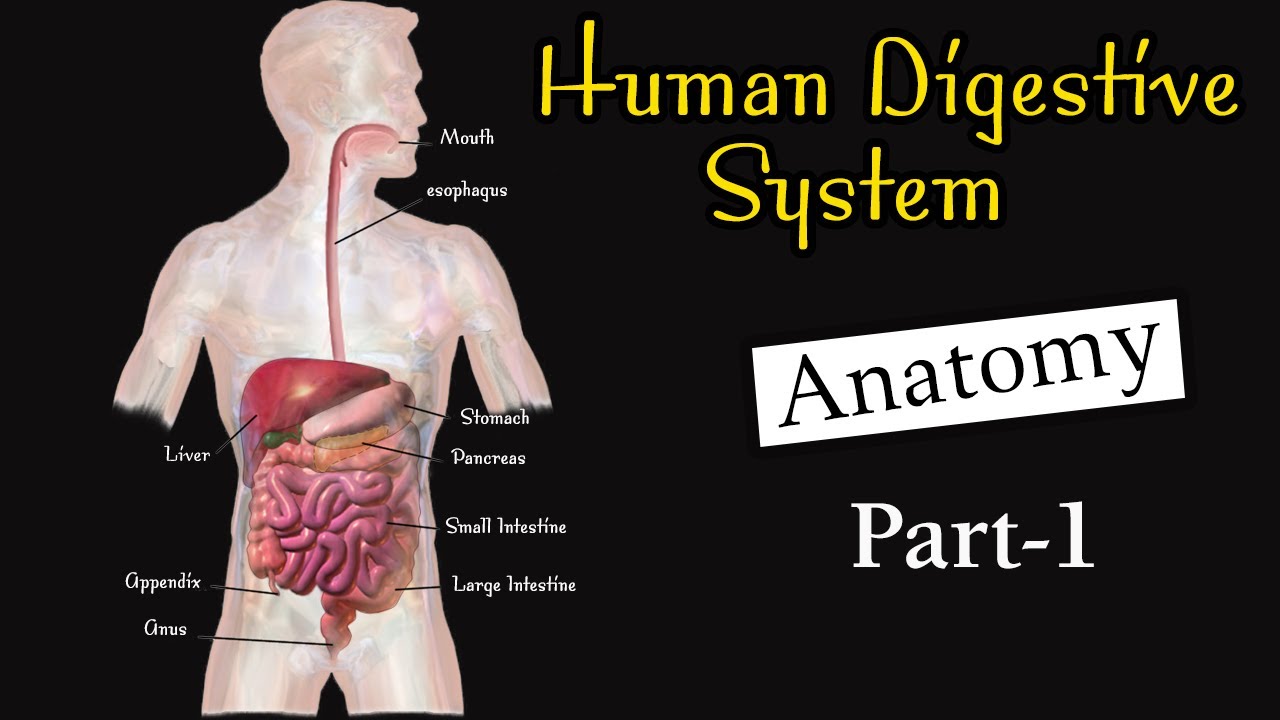
-The main digestive organs involved in the food passage are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
What role do the teeth and tongue play in digestion?
-Teeth help chew food into smaller pieces, while the tongue mixes food and forms a bolus to be swallowed, aiding in the mechanical breakdown of food.
What is the function of salivary glands in the mouth?
-Salivary glands produce saliva, which contains the enzyme amylase. This enzyme starts breaking down carbohydrates into simpler sugars.
How does the esophagus help in digestion?
-The esophagus connects the mouth to the stomach and uses peristalsis, a series of wave-like muscle contractions, to push food toward the stomach.
What happens in the stomach during digestion?
-In the stomach, food is mixed with gastric acid and enzymes. The acid activates pepsin, which breaks down proteins, while the food is mechanically digested through peristalsis, turning into a liquid called chyme.
What are the three parts of the small intestine, and what do they do?
-The three parts of the small intestine are the duodenum (where most chemical digestion occurs), the jejunum (where absorption of nutrients takes place), and the ileum (which further absorbs nutrients before the food moves to the large intestine).
What is the function of the large intestine in digestion?
-The large intestine absorbs water and salts from undigested food and processes waste, preparing it for elimination. It also houses bacteria that assist in digestion.
What role does the pancreas play in digestion?
-The pancreas produces digestive enzymes like amylase, lipase, and protease, which help break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, respectively. It also produces insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar levels.
How does the liver contribute to digestion?
-The liver produces bile, which helps digest fats, and processes toxins in the blood. It also helps regulate blood sugar levels and produces substances necessary for blood clotting.
What is the function of the gallbladder in digestion?
-The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile produced by the liver. It releases bile into the small intestine to aid in the digestion of fats when food enters the intestine.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Anatomy of human digestive system I Digestive system I Digestive system class 11

Digestive System

Sistem pencernaan Manusia : Struktur dan fungsi sistem pencernaan makanan pada manusia
SISTEM PENCERNAAN MANUSIA PART 2: IPA KELAS 8 SMP
HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Made Easy- Gastrointestinal System

SISTEMA DIGESTÓRIO APRENDA DE VEZ
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)