Precio Unitario de Zapata Corrida
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script offers a detailed tutorial on analyzing a 60-centimeter wide reinforced concrete slab, 1 meter long and 20 centimeters thick, designed for a linear meter. It covers material calculations for concrete, rebar, and wire, including waste percentages, and provides a step-by-step guide on determining quantities and costs. The script also explains labor calculations for both the rebar and concrete pouring teams, considering efficiency and unit prices. Finally, it addresses equipment needs and indirect costs, concluding with the total cost per linear meter of the slab.
Takeaways
- 🏗️ The video is a tutorial for architects, engineers, and students on analyzing a 'zapata corrida' (a type of concrete slab), specifically one that is 60 centimeters wide.
- 📏 The analysis covers a linear meter of the slab, which is 60 centimeters wide, 1 meter long, and 20 centimeters thick, made with 250-grade concrete and reinforced with medium-sized rebar every 20 centimeters in both directions.
- 📋 The tutorial includes a list of materials needed, such as concrete, rebar, and wire, and provides a method to quantify the amount of each material required for the construction.
- 📘 The script references a book by engineer Suárez for concrete mix ratios and strength information, which is essential for calculating the amount of cement, sand, gravel, and water needed.
- 🛠️ The cost of materials is calculated by multiplying quantities by unit prices, including a basic price for on-site concrete production and a 5% waste factor for concrete.
- 🧵 The amount of rebar needed is determined by the spacing and the length of the slab, with a 3% waste factor for steel, and the weight of the rebar is converted from meters to tons.
- 🔢 The quantity of wire required is calculated based on the number of intersections and the average length of wire used for each tie, considering a 50% waste factor.
- 👷♂️ The labor cost is estimated by the number of workers needed for each task, such as rebar tying and concrete pouring, and their respective daily wages, including a real salary factor.
- 👷♀️ The tutorial explains how to calculate the productivity of the labor force, which is measured in terms of how many tons of rebar can be tied or how many cubic meters of concrete can be poured per workday.
- 🚜 Equipment costs are factored in, including the use of a concrete mixer and a vibrator, with their respective productivity rates considered in the calculation.
- 💰 The total direct cost is the sum of materials, labor, and equipment, and an indirect cost of 30% is added to this subtotal to determine the final cost per linear meter of the slab.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is to analyze a 60-centimeter wide flat slab, specifically a flat slab with a thickness of 20 centimeters, made of concrete with a resistance of 250, and reinforced with rebar at every 20 centimeters in both directions.
What is the purpose of the analysis in the video?
-The purpose of the analysis is to calculate the materials, manpower, equipment, and all the necessary elements for the execution of a flat slab construction project.
What are the dimensions of the flat slab being analyzed?
-The flat slab being analyzed is 60 centimeters wide, 1 meter long, and 20 centimeters thick.
What is the concrete strength used for the flat slab?
-The concrete strength used for the flat slab is 250.
What is the rebar spacing mentioned in the video?
-The rebar spacing mentioned in the video is every 20 centimeters in both directions.
What does the video cover regarding the calculation of materials needed?
-The video covers the calculation of concrete in cubic meters, rebar in tons, and wire in kilograms needed for the construction of the flat slab.
How does the video approach the calculation of concrete volume?
-The video approaches the calculation of concrete volume by using the dimensions of the slab (width, length, and thickness) and accounting for a 5% waste factor.
What is the role of the 'ingeniero Suárez al azar' mentioned in the video?
-The 'ingeniero Suárez al azar' is referred to for reference in his book on construction, which provides the proportions needed to produce concrete with a resistance of 250 and other relevant information for structural analysis.
How is the cost of materials calculated in the video?
-The cost of materials is calculated by multiplying the quantities of cement, sand, gravel, and water by their respective unit prices, and then summing these amounts to get the total material cost for one cubic meter of concrete.
What is the process for calculating the amount of rebar needed?
-The process for calculating the amount of rebar needed involves determining the number of rebar pieces required for both the longitudinal and transversal directions, converting the linear meters of rebar to kilograms, and then to tons, while also accounting for a 3% waste factor.
How is the amount of wire needed calculated in the video?
-The amount of wire needed is calculated by determining the number of ties to be made at each intersection of rebar, measuring the average length of wire used for each tie on-site, and then accounting for a 50% waste factor.
What is the approach to calculating labor costs in the video?
-Labor costs are calculated by determining the specialized workforce needed (such as rebar workers and bricklayers), calculating the daily cost of each worker, and then determining the productivity rate (how many tons of rebar or cubic meters of concrete they can process per day) and multiplying it by the unit price of the workforce.
What is the role of equipment in the cost calculation?
-Equipment such as the mixer and vibrator are considered in the cost calculation by determining their productivity (how many cubic meters they can process) and then applying a percentage to the total labor cost for equipment and safety gear.
How is the indirect cost calculated in the video?
-The indirect cost is calculated by multiplying the direct cost (which includes material, labor, and equipment) by a percentage that represents the overhead charges, in this case, 30%.
What is the final cost per linear meter of the flat slab construction?
-The final cost per linear meter of the flat slab construction, after accounting for material, labor, equipment, direct and indirect costs, is 130 and 1.48 pesos.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

How to Measure Using a Meter Stick
3 2 ANALIS DAN DESAIN LENTUR BALOK PERSEGI BERTULANGAN RANGKAP ANALISIS LENTUR

Desain Pelat 2 Arah Beton Bertulang - Part 1 Konsep SNI 2847-2019

How to Read Reinforced Concrete Drawings for Beginners

Section through a Brick Veneer, Slab on ground Building Part 1
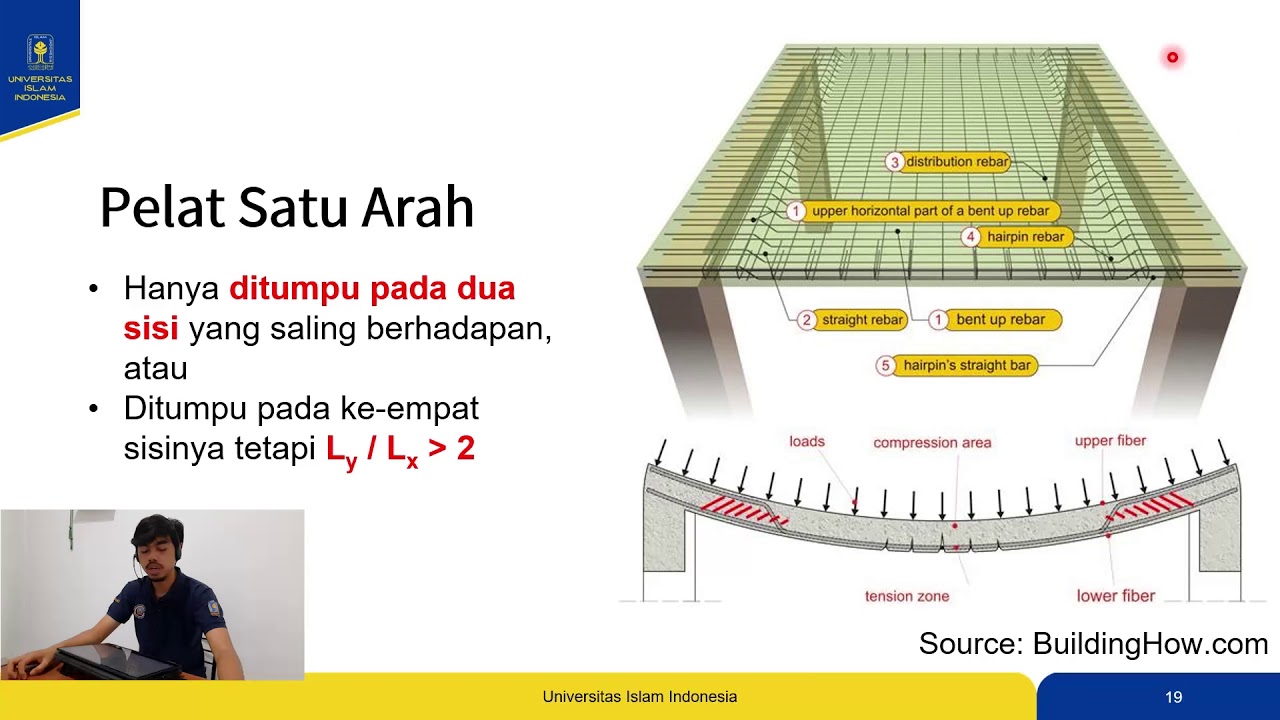
Desain Pelat Satu Arah SNI 2847-2019
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)