Sistem Eksitasi Ritmis pada Jantung | Proses Sistem Konduksi - SA Node, AV Node, AV Bundle, Purkinje
Summary
TLDRThe transcript explains the role of the sinoatrial (SA) node in the heart's conduction system. Located in the right atrium, the SA node generates electrical impulses that regulate the heart's rhythm. These impulses travel through various pathways, including the internodal pathways, the AV node, and the bundle of His, before reaching the Purkinje fibers in the ventricles. The transmission of electrical signals ensures proper contraction and blood flow from the atria to the ventricles. The entire process takes approximately 0.24 seconds, ensuring the heart functions efficiently and in sync.
Takeaways
- 😀 The sinoatrial (SA) node is located in the right atrium and acts as the heart's natural pacemaker, generating electrical impulses.
- 😀 These electrical impulses travel through the atrial muscles, causing the atria to contract.
- 😀 The electrical signals pass through specific pathways such as Bachmann’s bundle, Wenckebach, and posterior internodal pathways to the atrioventricular (AV) node.
- 😀 The AV node creates a slight delay to allow the atria to fully contract and fill the ventricles with blood before they contract.
- 😀 After the AV node, the electrical signal travels through the bundle of His and its right and left branches at a faster rate (about 2 m/s).
- 😀 The Purkinje fibers allow the impulse to spread rapidly through the ventricles at about 4 m/s to ensure efficient ventricular contraction.
- 😀 The SA node generates the electrical impulse at the beginning of the heartbeat, starting the process of contraction in the heart.
- 😀 The total time for an impulse to travel from the SA node to ventricular contraction is approximately 0.24 seconds.
- 😀 The AV node's delay ensures that the ventricles have enough time to fill with blood before contracting.
- 😀 The conduction system of the heart is designed to ensure coordinated and efficient heart function, maintaining a proper rhythm.
Q & A
What is the sinoatrial (SA) node, and where is it located?
-The sinoatrial (SA) node is a nodal tissue in the heart located in the right atrium, near the opening of the superior vena cava.
What is the primary function of the SA node?
-The primary function of the SA node is to generate electrical impulses that regulate the heart's rhythm, acting as the natural pacemaker of the heart.
How does the electrical impulse from the SA node spread to the atrium?
-The electrical impulse from the SA node is transmitted through specialized fibers that connect directly to the atrial muscle fibers, triggering atrial contraction.
What is the conduction speed in the atrial fibers?
-The conduction speed in most atrial muscle fibers is around 0.5 meters per second, though certain fibers can conduct impulses faster, up to 1 meter per second.
What are the different pathways for conducting the electrical impulse in the atria?
-The electrical impulse travels through different internodal pathways such as the Bachmann's bundle, which directs the impulse to the left atrium, and the Wenckebach and posterior internodal pathways.
Why is there a delay in conduction at the AV node?
-The delay at the AV node is necessary to allow blood from the atria to flow into the ventricles before the ventricles contract.
What is the role of the His bundle in the conduction system?
-The His bundle conducts the electrical impulse from the AV node to the ventricles, splitting into the right and left branches that further distribute the impulse.
How fast is the conduction speed through the His bundle and Purkinje fibers?
-The conduction speed through the His bundle and its branches is around 2 meters per second, and through the Purkinje fibers, it speeds up to about 4 meters per second.
Why is the conduction in the Purkinje fibers faster than in other parts of the heart?
-The conduction in Purkinje fibers is faster due to their larger size and higher permeability, allowing ions to flow more easily between cells.
What is the total time it takes for an electrical impulse to travel from the SA node to the ventricles?
-The total time for the electrical impulse to travel from the SA node to the ventricles, including all delays and conduction times, is approximately 0.24 seconds.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
(2/2) Anatomi Sistem Konduksi & Vaskular Jantung dan Topografi : #1 BASIC CARDIOVASKULAR

Cardiovascular | Electrophysiology | Intrinsic Cardiac Conduction System
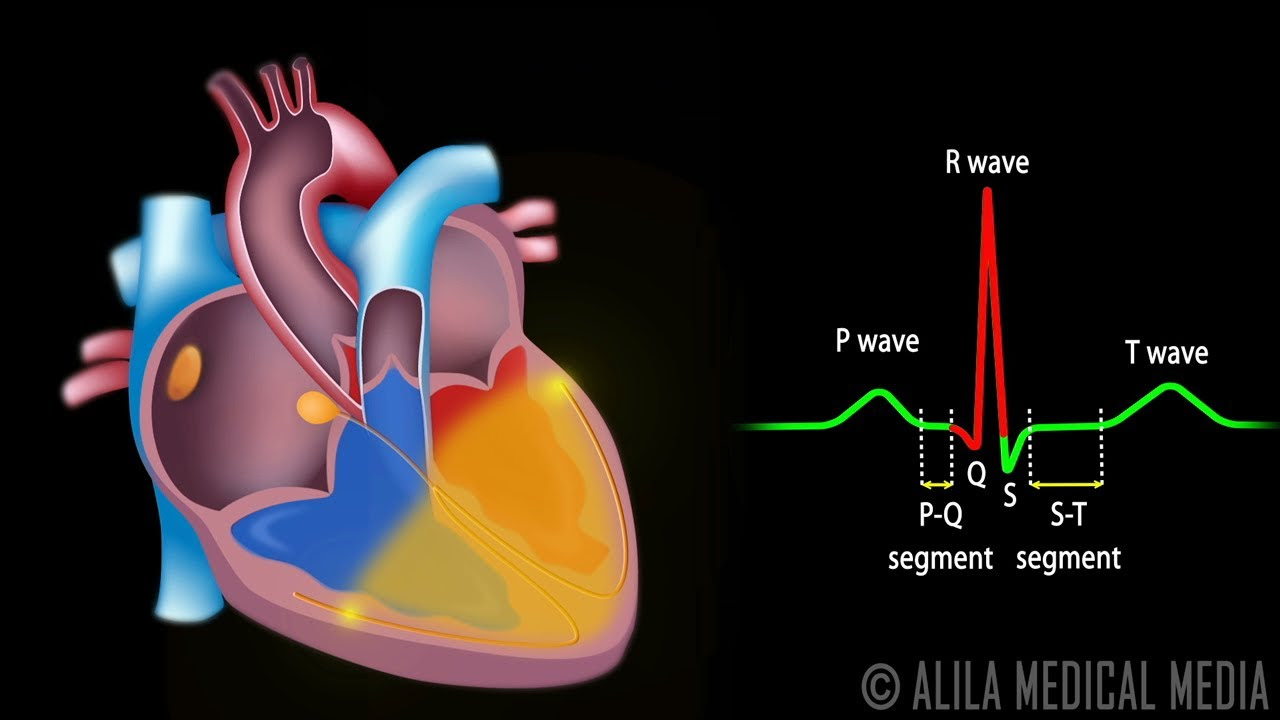
Cardiac Conduction System and Understanding ECG, Animation.

Anatomi Systema Cardiovasculare : Systema conducente cordis

Heart Conduction System & ECG (EKG)

Cardiac Conduction System
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)