How to do Critical Path analysis?
Summary
TLDRThis lesson demonstrates how to determine the estimated project duration using forward and backward path techniques. By working through an example from the Air Control Company project, the instructor explains how to calculate early start, early finish, late start, and late finish. Emphasizing critical path analysis, the video shows how to identify the project’s critical path and calculate slack. Additionally, the lesson covers assessing project sensitivity based on the number of critical paths and slack in non-critical activities, offering insights into project management strategies and timeline optimization.
Takeaways
- 😀 Start with an early start of 0 when performing forward and backward path calculations in project management.
- 😀 During the forward pass, add the activity's duration to the early start to calculate the early finish for each activity.
- 😀 In merge activities, choose the larger early finish when determining the early start for subsequent tasks.
- 😀 The earliest a task can start is determined by the early finish of its preceding activities.
- 😀 The backward pass involves subtracting from the late finish to calculate the late start and late finish for each task.
- 😀 In merge activities during the backward pass, choose the smaller late finish when determining the late start for preceding tasks.
- 😀 Slack represents the amount of time an activity can be delayed without affecting the overall project timeline.
- 😀 Non-critical activities can have slack, meaning they can be delayed without delaying the entire project.
- 😀 Activities with a slack of zero are on the critical path and cannot be delayed without affecting project completion.
- 😀 The critical path is the sequence of activities that directly impacts the project's duration—delaying any critical path activity will delay the entire project.
Q & A
What is the first step in the process of determining the estimated duration of the project?
-The first step is to review the diagram's legend, which contains information such as early start, early finish, late start, late finish, duration, slack, and the ID. In the current exercise, only the ID and duration are provided, and the forward and backward pass will be used to calculate the early start and late finish times.
Why do we start with an early start of 0 in this method?
-We start with an early start of 0 because, according to the methodology used in this technique, it simplifies the process. It may seem counterintuitive, but it helps in systematically calculating the early and late start/finish times for all activities.
How do you determine the early start for an activity in the forward pass?
-In the forward pass, the early start for an activity is determined by adding the duration of the preceding activity to its early finish. For example, if Activity A takes 2 days, its early finish will be on the 2nd day, and the subsequent activities can start after it finishes.
What is the significance of merge activities in the forward pass?
-Merge activities are important because they require the completion of multiple preceding activities before they can start. When calculating their early start, you must select the later of the early finishes from the preceding activities. This ensures that the merge activity starts only when all required activities have been completed.
What is the critical path and how is it identified in this method?
-The critical path consists of activities that directly impact the project's overall duration. These activities have zero slack, meaning any delay in their completion will delay the entire project. The critical path is identified by tracing activities with zero slack, and in the given example, activities A, D, F, G, and H form the critical path.
How do you calculate slack in project scheduling?
-Slack is calculated by subtracting the early start from the late start or the early finish from the late finish. It represents how much an activity can be delayed without affecting the project's overall timeline.
Why do we subtract and choose the smallest number in the backward pass?
-In the backward pass, we subtract to calculate the late finish and late start times. When there is a choice between multiple options, we choose the smallest number to ensure that the project is completed on time without any delays.
What does it mean when an activity has zero slack?
-When an activity has zero slack, it is on the critical path. This means that any delay in the completion of this activity will directly affect the project's completion date, making it crucial to finish on schedule.
How does the slack in non-critical activities impact the overall project?
-Non-critical activities with slack can be delayed without affecting the project's overall duration. However, activities with very little slack, such as Activity C in this example, may eventually become critical if they are delayed further.
What does it mean if there is only one critical path in a project?
-If there is only one critical path, it suggests that the project is less sensitive to changes. The project will be delayed only if any of the activities on the critical path are delayed. If there are multiple critical paths, the project becomes more sensitive to changes, as delays in any of these paths can affect the completion date.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
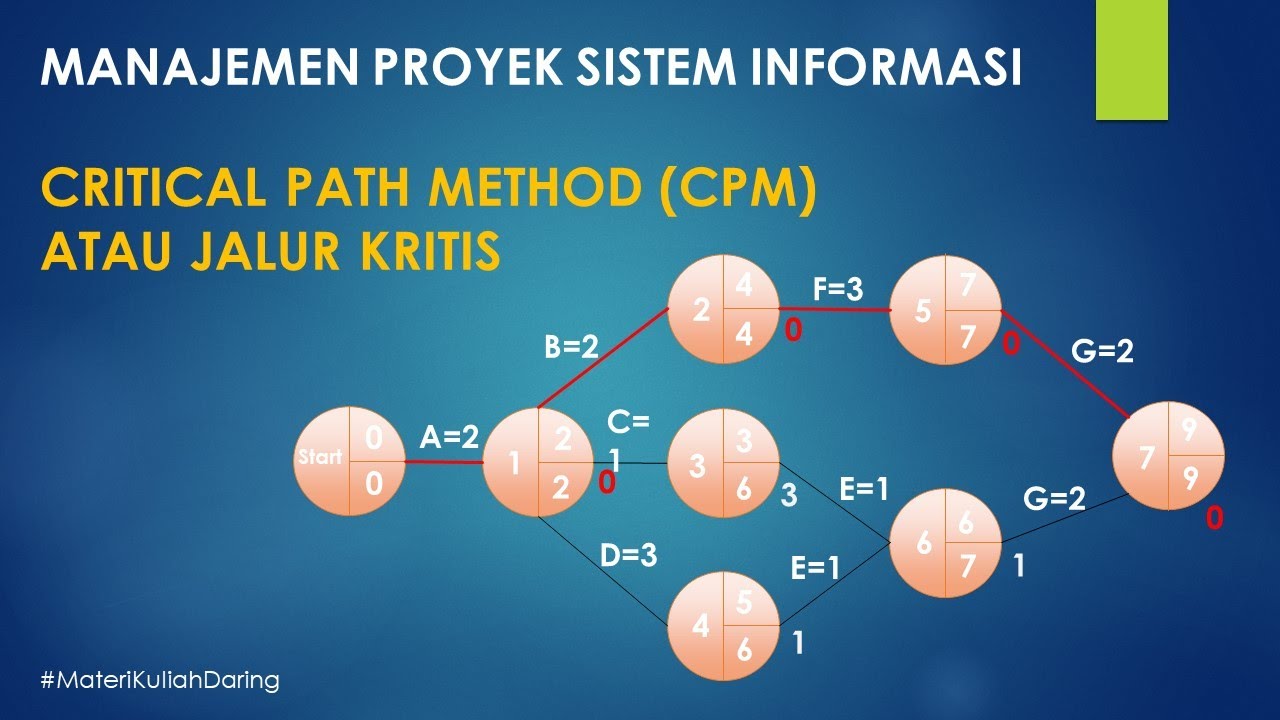
Critical Path Method (CPM) Atau Jalur Kritis Dalam Manajemen Proyek | Manajemen Proyek SI | GIS
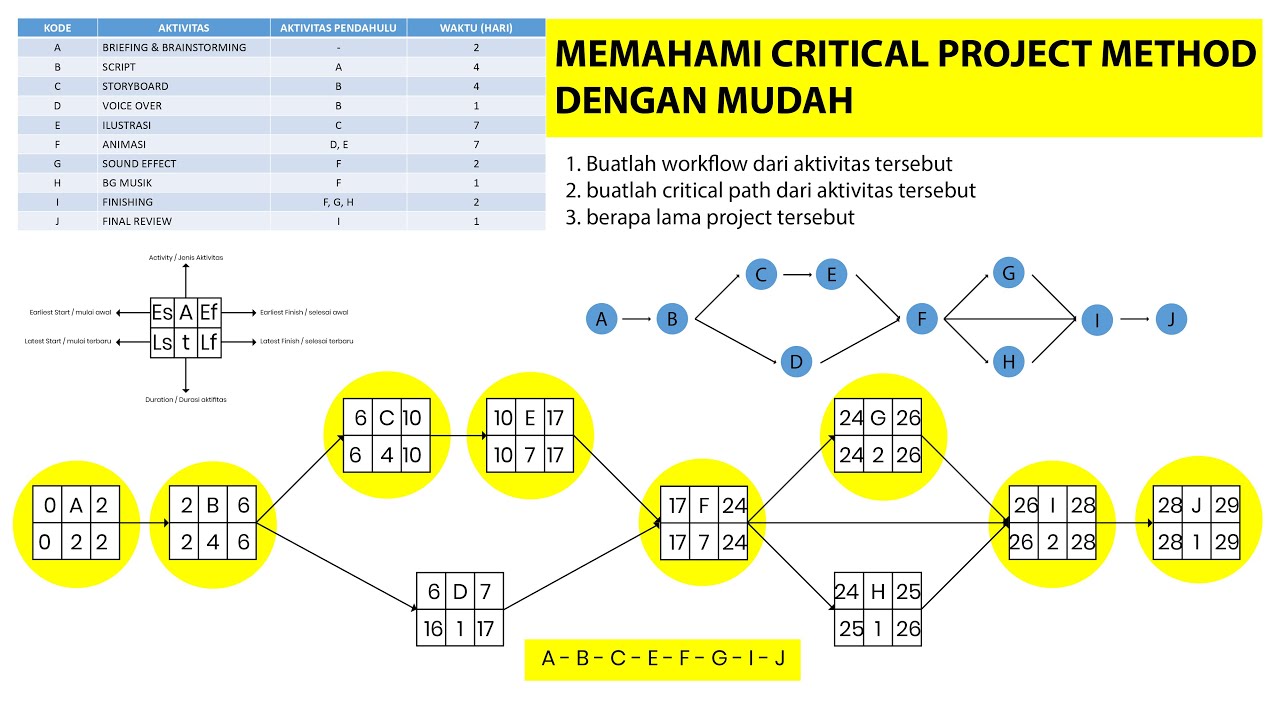
Cara memahami Critical Path Method (CPM) untuk mengetahui durasi proyek dan menentukan Critical Path

Use forward and backward pass to determine project duration and critical path

Diagram Jaringan Kerja, Contoh Kasus.

Akbar Adhi Utama: Project Management (Part 2)

Guling Depan & Belakang - Senam Lantai
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)