Critical Path Method (CPM) Atau Jalur Kritis Dalam Manajemen Proyek | Manajemen Proyek SI | GIS
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the host explains the Critical Path Method (CPM), a project management technique used to plan and schedule activities. CPM helps identify the sequence of tasks that directly affect the overall project duration. Key concepts covered include early start (ES), late finish (LF), float time, and the critical path itself. The video details both forward and backward pass techniques for calculating the earliest and latest times for tasks, along with methods for calculating slack, free float, and total float. Real-life examples are provided to illustrate these concepts, making it a comprehensive guide to mastering CPM in project management.
Takeaways
- 😀 CPM (Critical Path Method) is a project management technique used to plan, schedule, and analyze project activities to determine the longest sequence of dependent tasks, known as the critical path.
- 😀 The critical path consists of tasks that must be completed on time to ensure the project finishes as scheduled. Any delay in these tasks will delay the entire project.
- 😀 Non-critical tasks have slack time, meaning they can be delayed without affecting the overall project timeline.
- 😀 The key components in CPM are Early Start (ES), Late Finish (LF), and Slack, which help determine the scheduling and flexibility of project tasks.
- 😀 Early Start (ES) represents the earliest time a task can begin, while Late Finish (LF) is the latest time it can finish without delaying the project.
- 😀 Slack or float refers to the amount of time a task can be delayed without affecting the completion time of the entire project. Tasks on the critical path have zero slack.
- 😀 The network diagram visualizes the order of tasks and their relationships, showing dependencies between tasks using nodes (events) and arrows (activities).
- 😀 The Forward Pass technique calculates the earliest start and finish times for each activity by working from the project start to the finish.
- 😀 The Backward Pass technique works in reverse, from the project finish to the start, to calculate the latest possible start and finish times for each activity.
- 😀 The Critical Path is identified by tasks with zero slack, and it represents the longest path through the project that dictates the project’s duration.
- 😀 The Total Float (TF) is the maximum amount of time a task can be delayed without affecting the overall project completion, calculated using the formula LF - ES - duration.
- 😀 Free Float (FF) is the amount of time a task can be delayed without affecting the start of any dependent tasks in the project.
Q & A
What is the Critical Path Method (CPM)?
-The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique used to analyze and visualize the sequence of activities necessary to complete a project. It identifies the longest sequence of dependent activities and their durations, which determines the minimum time required to complete the project.
What is the significance of 'critical' activities in CPM?
-In CPM, an activity is considered 'critical' if any delay in its completion will result in a delay in the overall project completion. Critical activities have no flexibility in terms of time; any delay will directly affect the project deadline.
What is the difference between critical and non-critical activities in CPM?
-Critical activities have no slack time and must be completed on time to avoid delaying the entire project. Non-critical activities, on the other hand, have some slack time and can be delayed without affecting the overall project completion date.
What is the role of the network diagram in CPM?
-A network diagram in CPM visually represents the sequence of activities and their dependencies. It uses symbols like nodes (for events) and arrows (for activities) to depict the flow of tasks and their relationships within the project.
How are the terms 'Early Start' (ES), 'Late Start' (LS), 'Early Finish' (EF), and 'Late Finish' (LF) used in CPM?
-These terms are used to calculate the scheduling of project activities. 'Early Start' (ES) is the earliest time an activity can begin, while 'Late Start' (LS) is the latest time it can start without delaying the project. 'Early Finish' (EF) is the earliest an activity can be completed, and 'Late Finish' (LF) is the latest time an activity can finish without affecting the overall project timeline.
What is the Forward Pass technique in CPM?
-The Forward Pass technique calculates the earliest possible start and finish times for each activity. It starts from the initial event and moves towards the terminal event, determining the earliest times at which activities can begin and end.
What is the Backward Pass technique in CPM?
-The Backward Pass technique calculates the latest possible start and finish times for each activity. It starts from the terminal event and works backward to the initial event, identifying the latest time activities can begin and finish without delaying the project.
How is Slack or Float time calculated in CPM?
-Slack or Float time is the amount of time an activity can be delayed without affecting the overall project timeline. It is calculated by subtracting the Early Start time (ES) from the Late Finish time (LF) for an activity.
What is the significance of the Critical Path in a project?
-The Critical Path is the sequence of activities with zero slack time. It determines the minimum project duration. Any delay in an activity on the Critical Path will delay the entire project.
What is the difference between Total Float and Free Float?
-Total Float refers to the total time an activity can be delayed without affecting the overall project timeline, while Free Float is the time an activity can be delayed without impacting the subsequent activities in the project.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

KULIAH ONLINE PROJECT MANAGEMENT PERT CPM
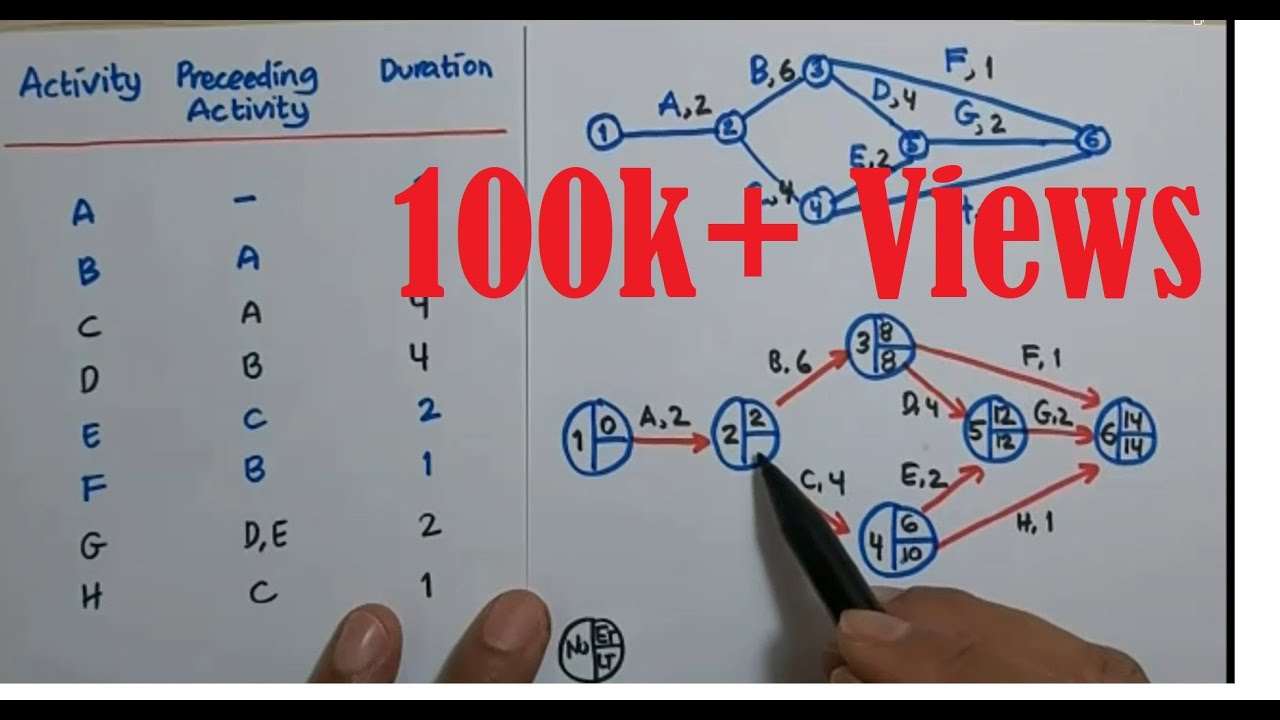
8.4 CPM (Critical Path Method): Contoh Soal

Akbar Adhi Utama: Project Management (Part 2)

MANAJEMEN PROYEK (SESI 1) - PENJADWALAN DENGAN SOFTWARE POM-QM VERSI 4
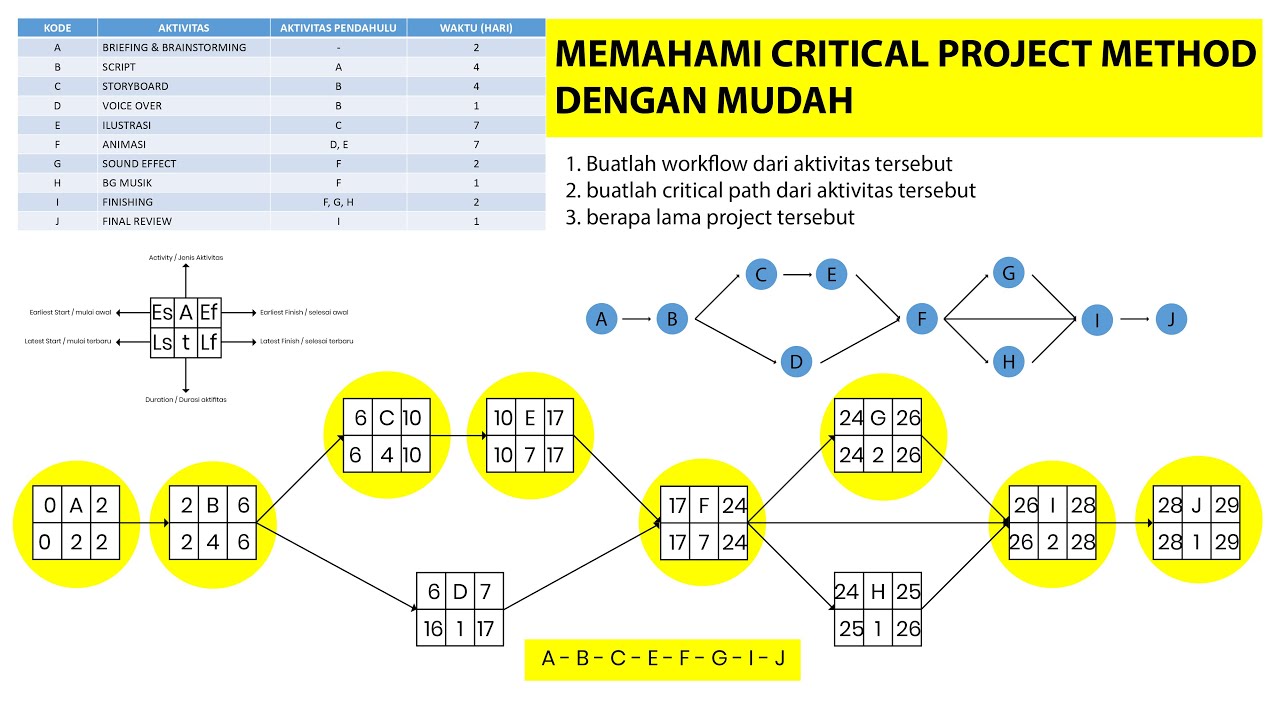
Cara memahami Critical Path Method (CPM) untuk mengetahui durasi proyek dan menentukan Critical Path
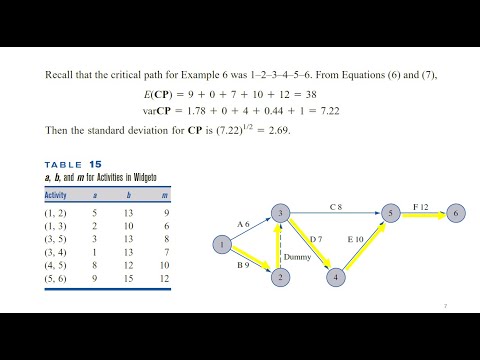
Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)