19. Miniaula Astronomia GRAVITAÇÃO
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into Einstein's General Theory of Relativity, explaining how it uses tensor calculus to describe the curvature of spacetime. It covers the key components of the theory, including the Einstein tensor and the stress-energy tensor, and how they relate to matter and energy distribution. The video highlights several experimental confirmations, such as the deflection of light during the 1919 solar eclipse and the precession of Mercury's orbit. It also touches on modern discoveries like gravitational waves, providing an insightful overview of gravity's crucial role in our universe.
Takeaways
- 😀 General relativity, formulated by Albert Einstein, explains how gravity is the result of the curvature of space-time caused by mass and energy.
- 😀 In classical physics, gravity was considered a force acting at a distance, but Einstein’s theory shows it as the effect of curved space-time.
- 😀 Einstein's use of tensor calculus allows for a more sophisticated and accurate description of curved space-time and its interaction with matter.
- 😀 The **Einstein tensor** describes how space-time curves, while the **energy-momentum tensor** represents the distribution of matter and energy in space.
- 😀 The theory predicts that objects move through curved space-time differently, with their trajectories affected by the mass of surrounding objects.
- 😀 Gravitational lensing occurs when the light from distant objects bends around massive objects, distorting their appearance and providing evidence for space-time curvature.
- 😀 The orbit of Mercury exhibits a shift in its perihelion, which was an unexplained anomaly in classical physics but was predicted and explained by general relativity.
- 😀 Gravitational waves are ripples in space-time caused by massive objects, such as colliding black holes. They were first detected in 2015, confirming a key prediction of Einstein's theory.
- 😀 The **perihelion of Mercury** shifts by an observed 43 seconds per century, an anomaly not predicted by Newtonian mechanics but explained by general relativity.
- 😀 The bending of light near massive objects (like the Sun) can be observed as a displacement of stars, which was experimentally confirmed during a 1919 solar eclipse.
- 😀 Einstein’s theory has been confirmed over 200 times, with gravitational waves, gravitational lensing, and Mercury's perihelion advance being among the most notable examples.
Q & A
What is the central idea behind Einstein's theory of general relativity?
-The central idea is that gravity is not a force in the traditional sense, but rather a result of the curvature of space-time caused by mass and energy. The more mass and energy there is, the greater the curvature of space-time.
What role do tensors play in general relativity?
-Tensors are mathematical objects that generalize scalars and vectors. In general relativity, Einstein used tensors to describe the curvature of space-time and how matter and energy influence it. They provide a framework for expressing complex relationships in four-dimensional space-time.
What are Einstein's field equations?
-Einstein's field equations describe the relationship between the geometry of space-time (represented by the Einstein tensor) and the distribution of matter and energy (represented by the energy-momentum tensor). These equations govern the gravitational effects in the universe.
How does the curvature of space-time affect the movement of objects?
-The curvature of space-time alters the paths that objects follow. For instance, near a massive object like Earth, the space-time is curved, which changes the distance and time experienced by objects moving through that region. This is why objects in free fall near Earth appear to experience gravity.
Why is gravity weaker on Earth compared to more massive objects like black holes?
-Earth's mass is relatively small, so the curvature of space-time it creates is also small and not easily noticeable. In contrast, more massive objects, such as black holes, create much more significant curvature, which can drastically affect the movement of nearby objects and even light.
What evidence confirmed the theory of general relativity?
-Several key observations confirmed general relativity, including the bending of light around the Sun during a solar eclipse in 1919, the shift in Mercury's perihelion, gravitational lensing by galaxies, and the detection of gravitational waves from black hole collisions.
How does gravitational lensing provide evidence for general relativity?
-Gravitational lensing occurs when the space-time around a massive object (like a galaxy) bends light from more distant objects. This bending magnifies the distant objects, providing direct evidence of the curvature of space-time predicted by general relativity.
What is the significance of the deflection of light observed during the 1919 solar eclipse?
-During the 1919 solar eclipse, astronomers observed that light from stars near the Sun was bent due to the curvature of space-time around the Sun. This observation was one of the first confirmations of Einstein's theory of general relativity.
What is the perihelion of Mercury and how does it support general relativity?
-The perihelion of Mercury is the point in its orbit closest to the Sun. It was observed that this point shifted over time more than predicted by Newtonian mechanics. General relativity explained this discrepancy by accounting for the curvature of space-time around the Sun.
What are gravitational waves and how were they detected?
-Gravitational waves are ripples in space-time caused by massive objects accelerating, such as the collision of black holes. These waves were first detected in 2016 using laser-based instruments, providing direct evidence of the vibrational nature of space-time predicted by general relativity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What is the General Theory of Relativity?

How Mass WARPS SpaceTime: Einstein's Field Equations in Gen. Relativity | Physics for Beginners
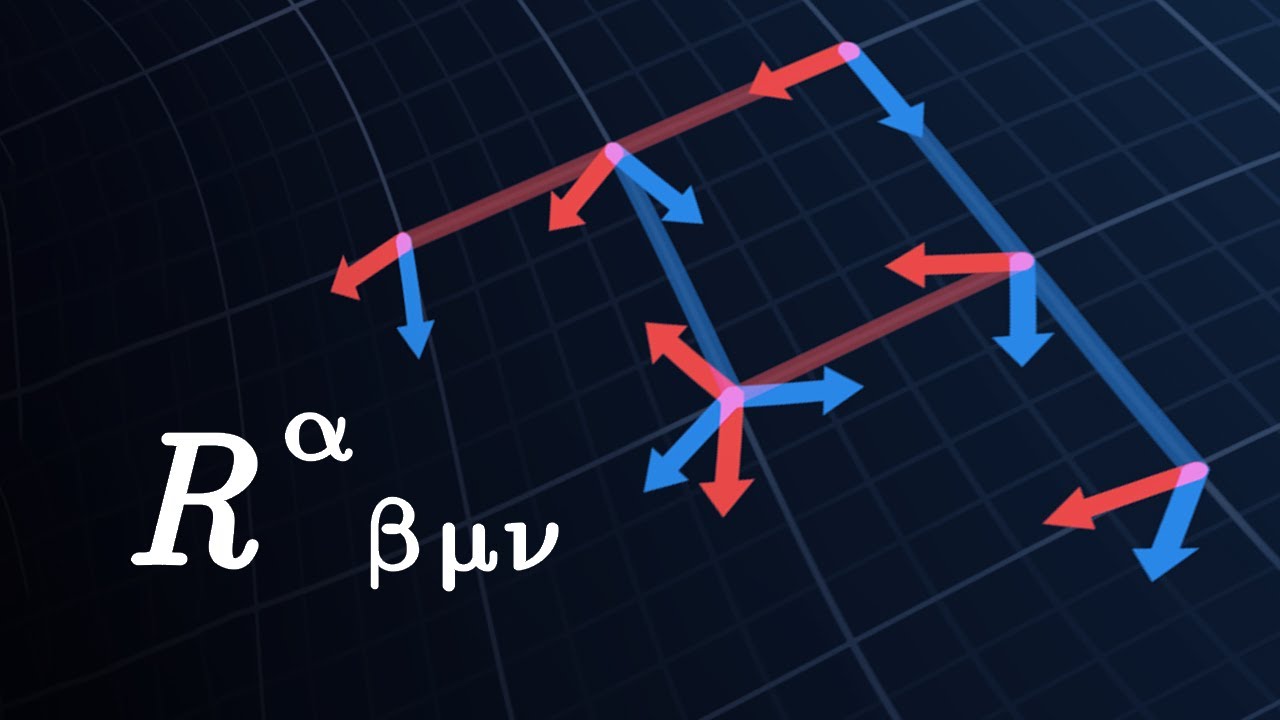
The Maths of General Relativity (5/8) - Curvature

#AghamUnite: Relativity and the Big Bang

Theory of relativity explained in 7 mins
General Relativity Explained in 7 Levels of Difficulty
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)