What is Homeostasis?
Summary
TLDRThis lesson on homeostasis explores the critical processes that maintain stable internal conditions in the body. It begins by defining homeostasis and explaining its importance for optimal body function, particularly in maintaining enzyme efficiency. The script details how the body regulates conditions like temperature, blood glucose, and water content through automatic control systems involving receptors, coordination centers, and effectors. Key examples, such as temperature regulation during exercise and blood sugar control after eating, are provided to demonstrate these processes. Understanding these concepts is essential for further studies in biology and health sciences.
Takeaways
- 😀 Homeostasis is the regulation of internal conditions in the body to maintain optimum conditions for function.
- 😀 Homeostasis is vital for the body to function effectively despite changes in both internal and external environments.
- 😀 Enzymes in the body work best at specific temperatures and pH levels, and maintaining these conditions is crucial for proper cellular function.
- 😀 The body regulates several internal conditions, such as body temperature, blood glucose levels, and water balance, to maintain homeostasis.
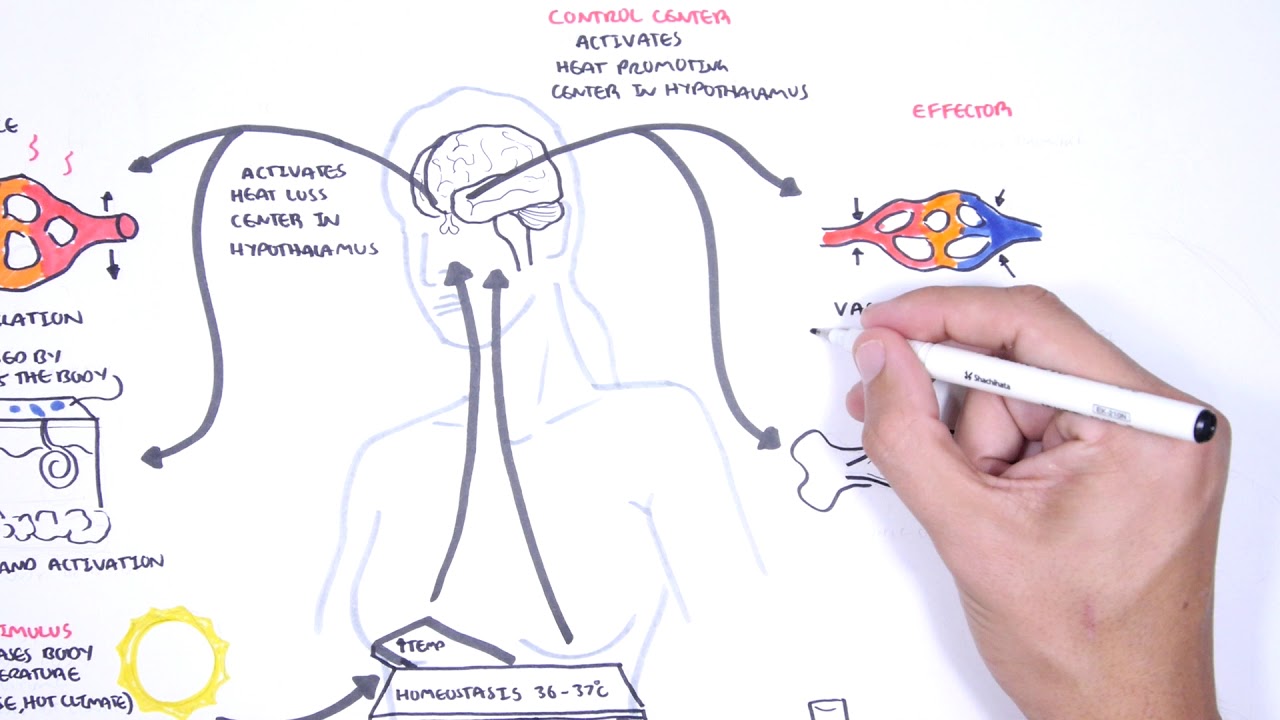
- 😀 Body temperature is regulated through mechanisms like sweating and increasing blood flow to the skin to prevent overheating.
- 😀 Blood glucose concentration is controlled by hormones like insulin and glucagon to ensure a steady supply of energy to cells.
- 😀 The body maintains water balance through the intake and excretion of fluids to ensure cells are neither dehydrated nor swollen.
- 😀 Automatic control systems in the body include both nervous and hormonal responses to maintain homeostasis.
- 😀 Receptors detect changes in the environment (stimuli) and send signals to coordination centers like the brain or spinal cord.
- 😀 Effectors, such as muscles or glands, carry out the responses to restore internal conditions to optimal levels.
- 😀 Examples of automatic control systems include temperature regulation through sweating and blood glucose regulation after eating.
Q & A
What is homeostasis?
-Homeostasis is the regulation of internal conditions in a cell or organism to maintain optimal conditions for its function, despite changes in the external environment.
Why is homeostasis important for the body?
-Homeostasis is crucial because it ensures that conditions within the body, such as temperature, pH, and glucose levels, remain within optimal ranges. This stability is necessary for enzymes and cells to function properly, supporting overall health.
What are enzymes, and why do they need optimal conditions?
-Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in cells. They work best under specific temperature and pH conditions, and if these conditions are not maintained, enzymes can become denatured and lose their function, disrupting cellular activities.
What are the primary internal conditions that the body regulates for homeostasis?
-The body regulates several internal conditions to maintain homeostasis, including body temperature, blood glucose concentration, and water content.
How does the body regulate temperature during exercise?
-When the body temperature rises due to exercise, thermoreceptors detect the change and send signals to the brain. The brain then activates effectors, such as sweat glands, to produce sweat, which cools the body down through evaporation.
How does the body regulate blood glucose levels after eating?
-After eating, blood glucose levels rise. The pancreas detects this increase and releases insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose and lower blood sugar levels back to an optimal range.
What are receptors in the body, and what role do they play in homeostasis?
-Receptors are specialized cells that detect changes in the internal or external environment, known as stimuli. They play a key role in homeostasis by sending signals to the brain or coordination centers, initiating appropriate responses to maintain balance.
What are coordination centers, and where are they located?
-Coordination centers are areas in the body that process information from receptors and organize responses. These centers include the brain and spinal cord, which integrate signals and send out instructions to effectors.
What are effectors, and how do they help maintain homeostasis?
-Effectors are muscles or glands that carry out the body's responses to restore internal conditions to optimal levels. For example, sweat glands act as effectors to cool the body down when temperature rises.
Why is maintaining a stable internal environment crucial for overall health?
-A stable internal environment ensures that the body's cells function optimally. Disruptions in conditions like temperature, pH, or glucose levels can impair enzyme activity and cellular processes, leading to health issues. Homeostasis ensures that these conditions remain stable for efficient biological processes.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

How Does Your Body Maintain its Balance?

Lesson 5: Nervous System Working Together with the Endocrine System to Maintain Homeostasis
Homeostasis - negative and positive feedback (thermoregulation and lactation)

GCSE Biology Revision "Homeostasis"

APA ITU HOMEOSTASIS ?? - KELOMPOK 3 BIOMEDIS

Homeostatic Loops
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)