GCSE Biology Revision "Homeostasis"
Summary
TLDRThis video from Three Science explores the concept of homeostasis, the process by which the body maintains optimal internal conditions for cellular function despite changes. It explains that homeostasis involves automatic control systems using the nervous system or hormones to regulate factors like blood glucose, body temperature, and water levels. The video outlines the key components of these systems: receptor cells that detect environmental changes, a coordination center that processes information, and effectors that execute responses to maintain balance. Viewers are encouraged to practice with questions provided in the accompanying workbook.
Takeaways
- 🌡️ Homeostasis is the process of maintaining stable internal conditions in an organism to ensure optimal functioning of cells and enzymes.
- 🏃 Enzymes and cells require stable conditions to function properly, which is why the body has systems in place to maintain these conditions.
- 🔬 Homeostasis is defined as the regulation of internal conditions to maintain optimum conditions for function in response to changes.
- 💡 The concept of homeostasis is about keeping internal conditions as constant as possible, despite internal and external changes.
- 🏋️♂️ Examples of internal conditions that need to be maintained include blood glucose concentration, body temperature, and water levels.
- 🔑 Automatic control systems in the body involve the nervous system or hormones to detect and respond to changes in the body's environment.
- 👀 Receptor cells are crucial in detecting changes or stimuli in the body's internal and external conditions.
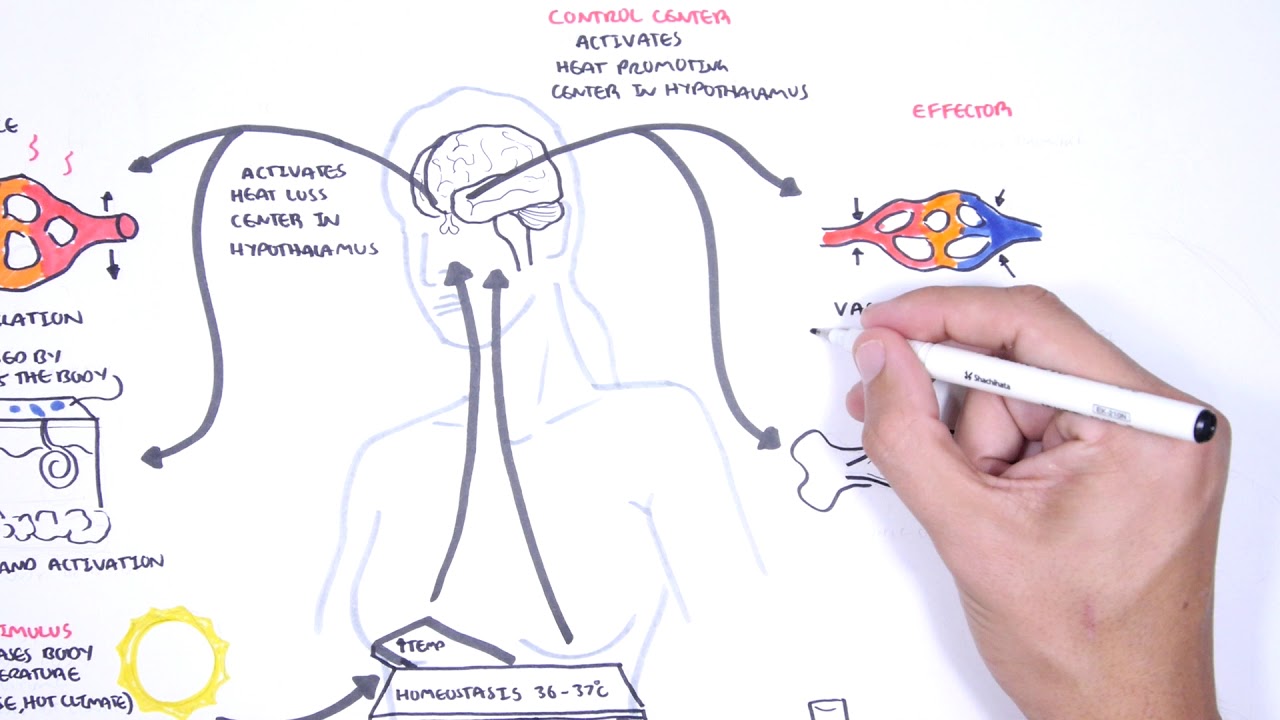
- 🧠 The Coordination Center, such as the brain or pancreas, processes the information received from receptor cells and sends instructions.
- 💪 Effectors, which can be muscles or glands, carry out the response to maintain the optimal level of internal conditions.
- 📚 Understanding the general features of an automatic control system is important for grasping the concept of homeostasis.
- 📘 The video script suggests that there are many questions on homeostasis in the accompanying workbook, indicating its significance in the curriculum.
Q & A
What is the term 'homeostasis' defined as in the context of this video?
-Homeostasis is defined as the regulation of the internal conditions of a cell or organism to maintain optimum conditions for function in response to internal and external changes.
Why is it important for enzymes and cells to have stable conditions?
-Enzymes and cells require stable conditions to work effectively. If the conditions around them change too much, enzymes cannot function properly, which is crucial for cellular processes like respiration.
What are the main internal conditions that the human body maintains through homeostasis?
-The main internal conditions maintained through homeostasis include blood glucose concentration, body temperature, and water levels.
How does exercise affect the internal conditions of the body that need to be maintained by homeostasis?
-Exercise can cause changes in the body such as a decrease in blood glucose concentration due to energy generation, an increase in body temperature, and water loss through sweating.
What are the components of an automatic control system in the context of homeostasis?
-The components of an automatic control system include receptor cells that detect changes, a Coordination Center that processes information, and effectors that carry out the response to maintain optimum conditions.
What is the role of receptor cells in the automatic control system of homeostasis?
-Receptor cells detect changes in the body's internal or external environment, such as glucose concentration or skin temperature, and pass this information to the Coordination Center.
What is meant by the term 'stimulus' in the context of homeostasis?
-A stimulus is a change to the environment that is detected by receptor cells. It could be a change in the body's internal conditions like blood glucose levels or external conditions like temperature.
What is the function of the Coordination Center in the automatic control system?
-The Coordination Center, which could be the brain, spinal cord, or pancreas, receives and processes information from receptor cells and sends instructions to the effectors.
What is an effector in the context of an automatic control system, and what does it do?
-An effector is a muscle or gland that carries out the response to a stimulus as instructed by the Coordination Center, helping to maintain the body's internal conditions at an optimum level.
How can students practice understanding homeostasis and related concepts?
-Students can practice by working through questions on homeostasis found in the provided vision workbook, accessible via the link mentioned in the video.
What is the significance of maintaining constant internal conditions for the body's cells and enzymes?
-Maintaining constant internal conditions is crucial for the optimal functioning of cells and enzymes, which in turn is essential for sustaining life processes and overall health.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Homeostasis - negative and positive feedback (thermoregulation and lactation)

Why is homeostasis important?

GCSE Biology - Homeostasis | Receptors, Coordination Centres, Effectors | Negative Feedback

Introduction to Homeostasis

Homeostasis: Fisiologi Pengatur Keseimbangan Tubuh (Suhu, pH, nutrisi, dsb...)

How Does Your Body Maintain its Balance?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)