Konsep mol , ringkasan dan latihan soal
Summary
TLDRThis educational video dives into the concept of 'mol' in chemistry, explaining its relationship to particles, mass, and volume. The instructor breaks down essential formulas, including how to calculate moles from the number of particles, the mass of substances, and gas volume under various conditions. Through clear explanations and practical examples, such as determining the number of carbon atoms in a given mol and calculating the volume of hydrogen gas under non-STP conditions, viewers gain a solid understanding of mol calculations and the ideal gas law. The video is ideal for chemistry students looking to grasp core concepts in molar calculations.
Takeaways
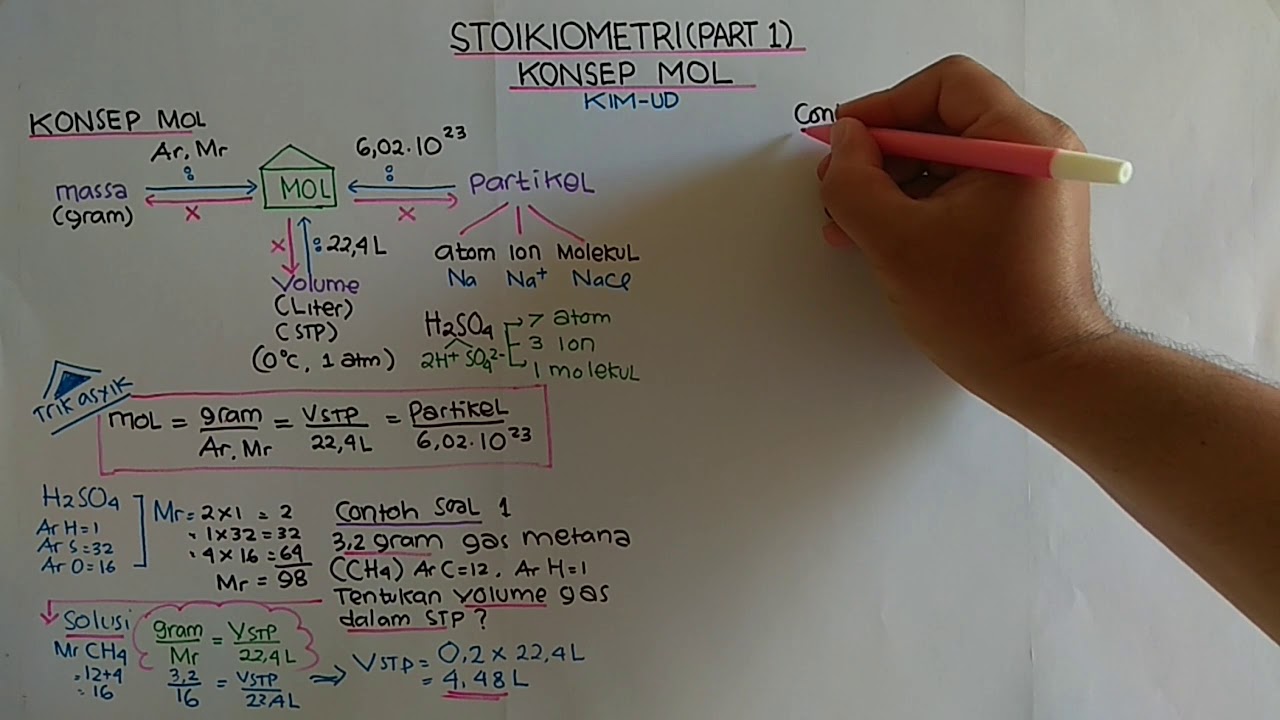
- 😀 Mol is a unit of measurement in chemistry that represents the quantity of a substance.
- 😀 To calculate mol, it can be related to three variables: particle count, mass, and volume (for gases).
- 😀 Avogadro's number (6.02 × 10^23) is used to connect mol to the number of particles (atoms or molecules).
- 😀 The formula for mol in relation to mass is mol = mass/Ar (for elements) or mol = mass/Mr (for compounds).
- 😀 For gases at STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure: 0°C, 1 ATM), the mol-volume relationship is mol = volume/22.4 L.
- 😀 When not at STP, the ideal gas law (PV = nRT) is used to find the mol of a gas, where R = 0.082 L·ATM/mol·K.
- 😀 Temperature must be in Kelvin when using the ideal gas law, so Celsius should be converted to Kelvin by adding 273.
- 😀 In the example, to find the number of atoms in 0.05 mol of carbon, the formula n = number of particles/Avogadro’s number is used.
- 😀 The mass of a substance can be used to calculate the number of moles using the formula mol = mass/Ar (for elements).
- 😀 To calculate the volume of a gas under non-STP conditions, the ideal gas law is applied by determining n first, then solving for V.
Q & A
What is the definition of a mole in chemistry?
-A mole is a unit used to measure the amount of substance in terms of the number of particles, such as atoms or molecules, contained in that substance.
How is the mole related to the number of particles in a substance?
-The number of moles is directly related to the number of particles through Avogadro's number, which is 6.02 × 10^23. The formula is: Mole = Number of Particles / Avogadro's Number.
What is Avogadro's number and why is it important?
-Avogadro's number is 6.02 × 10^23, and it represents the number of particles (atoms or molecules) in one mole of a substance. It is a fundamental constant in chemistry for converting between the number of moles and the number of particles.
How is the mole related to the mass of a substance?
-The mole is related to mass through the formula: Mole = Mass / Molar Mass (Ar for elements, Mr for compounds). The mass is measured in grams, and the molar mass is the atomic or molecular weight of the substance.
What is the formula used when calculating moles from the mass of a substance?
-The formula is Mole = Mass / Molar Mass, where Mass is in grams and Molar Mass is the atomic mass for elements (Ar) or molecular mass for compounds (Mr).
What are the two conditions for calculating the volume of gas using the mole?
-The two conditions for calculating gas volume using the mole are Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) and non-STP conditions. STP is defined as 0°C and 1 atm, while non-STP conditions require the use of the Ideal Gas Law.
What is the relationship between the mole and the volume of a gas at STP?
-At STP, one mole of gas occupies a volume of 22.4 liters. The formula used is: Mole = Volume / 22.4 (where volume is in liters).
What is the Ideal Gas Law and how does it relate to the mole?
-The Ideal Gas Law is PV = nRT, where P is pressure (in atm), V is volume (in liters), n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant (0.0821 L·atm/mol·K), and T is temperature (in Kelvin). This law is used when the gas is not at STP to calculate the volume, moles, or other properties.
In the Ideal Gas Law, how is temperature converted from Celsius to Kelvin?
-To convert temperature from Celsius to Kelvin, you add 273. For example, 27°C becomes 300 K.
How do you calculate the number of atoms in a given number of moles of an element?
-To calculate the number of atoms in a given number of moles, multiply the number of moles by Avogadro's number. For example, for 0.05 moles of carbon, the number of atoms is 0.05 × 6.02 × 10^23.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Konsep Mol • Part 1: Hubungan Mol & Massa, Jumlah Partikel, Volume Gas, Molaritas
KONSEP MOL - KIMIA - MATERI UTBK SBMPTN DAN SIMAK UI - UTBK 2022 | SIMAK UI 2022
STOIKIOMETRI (PART 1) KONSEP MOL

Konsep Mol - Stoikiometri - Perhitungan Kimia - Kimia Kelas 10

Konsep Mol | Kimia SMA | Tetty Afianti

OCR Gateway A (9-1) P1.2.1 - Density Summary
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)