QUE ES UN TORQUE O MOMENTO DE UNA FUERZA - QUE ES EL BRAZO DE PALANCA DE UNA FUERZA (EJEMPLO)
Summary
TLDRThis script provides a detailed explanation of torque, also known as the moment of force, and its application in various scenarios. It covers how torque is generated when force is applied to an object, the concept of the lever arm, and the direction of rotation, which determines whether the torque is positive or negative. The video explains calculations involving torque, such as using the force-distance formula and considering angles, with examples like tightening bolts and applying forces in different directions. The script helps viewers understand both the theoretical and practical aspects of torque in physics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Torque, or moment of force, is the rotational effect produced when a force is applied to an object at a distance from the point of rotation.
- 😀 Torque is calculated by multiplying the applied force by the distance from the rotation point, specifically when the force is perpendicular to the distance (90 degrees).
- 😀 When calculating torque, if the rotation is clockwise, the result is considered negative, and if it's counterclockwise, the result is positive.
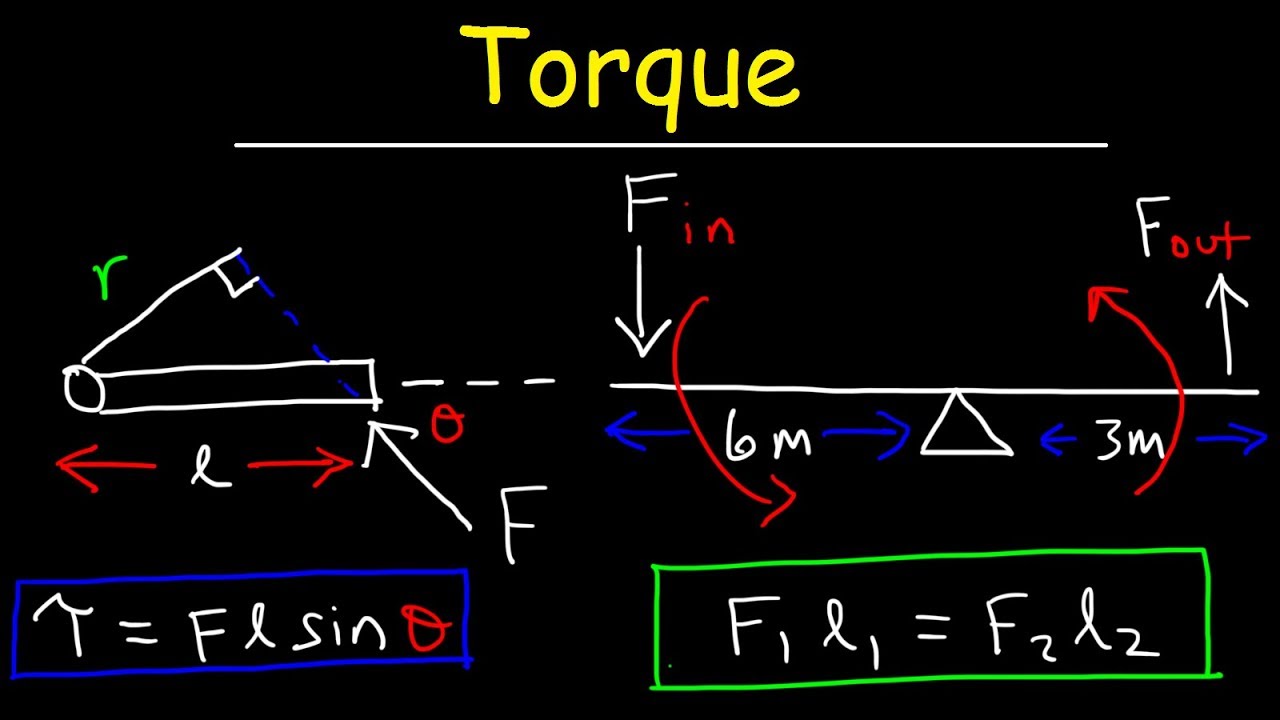
- 😀 The torque formula is expressed as τ = F * d, where τ is the torque, F is the force applied, and d is the distance from the rotation point.
- 😀 When the force is not perpendicular to the distance, the torque calculation involves finding the 'lever arm' or 'brazo de palanca', which is the perpendicular distance from the line of action of the force to the point of rotation.
- 😀 To calculate torque in non-perpendicular situations, the 'lever arm' can be calculated by using the sine or cosine of the angle between the applied force and the distance vector.
- 😀 The torque direction is significant: clockwise rotations are considered negative, while counterclockwise rotations are positive.
- 😀 In practical scenarios, like using a wrench to loosen a bolt, torque is created by applying a force at a distance from the rotation point, which causes the bolt to rotate.
- 😀 In a scenario with multiple forces acting simultaneously, the resulting torque is the algebraic sum of the individual torques, considering both their magnitude and direction.
- 😀 The example of calculating torque with multiple forces (like a 60 N vertical force and an 80 N horizontal force) shows how to combine torques and determine the resulting rotational direction and magnitude.
- 😀 To calculate the torque from forces applied at angles, one needs to use trigonometric functions to resolve the force components and find the effective lever arm for each force.
Q & A
What is torque and how is it related to force?
-Torque, also known as the moment of force, is the rotational effect produced when a force is applied to an object at a certain distance from the rotation point. The torque is calculated as the force multiplied by the distance from the pivot point, assuming the force is applied perpendicular to the object.
Why is torque considered negative when the rotation is clockwise?
-Torque is considered negative when the rotation is clockwise because the convention for angular motion is to consider counterclockwise rotations as positive and clockwise rotations as negative.
How does the length of the lever arm affect the torque?
-The length of the lever arm directly influences the torque. The longer the distance (lever arm) from the point of rotation, the greater the torque produced by the same amount of force.
How does the angle between the force and the lever arm affect the torque?
-The torque is maximized when the force is applied perpendicular (90 degrees) to the lever arm. If the force is applied at an angle other than 90 degrees, the effective torque is reduced and must be calculated using the component of the force that is perpendicular to the lever arm.
What is the significance of the line of action of the force in calculating torque?
-The line of action of the force is important because it helps to determine the direction and the perpendicular distance from the point of rotation to where the force is applied. This distance is crucial in calculating the torque, especially when the force is not applied at a 90-degree angle.
What does it mean for torque to be positive or negative?
-Torque is positive when the object rotates counterclockwise (antihorically), and negative when the object rotates clockwise (horologically). The sign indicates the direction of rotation, which is important in determining the net torque when multiple forces are applied.
How do you calculate the torque when the force is applied at an angle other than 90 degrees?
-When the force is applied at an angle other than 90 degrees, you need to calculate the torque by finding the perpendicular distance (the arm of leverage) from the rotation point to the line of action of the force. This can be done by using trigonometric functions like sine or cosine depending on the situation.
What is the difference between the torque calculation for a force applied at 90 degrees versus an angle?
-For a force applied at 90 degrees to the lever arm, the torque is simply the product of the force and the lever arm distance. For forces applied at other angles, you must calculate the perpendicular component of the force and multiply that by the distance from the pivot point.
What is the role of the pivot point in torque calculations?
-The pivot point (or the center of rotation) is the point around which the object rotates. The torque is determined by how far the force is applied from this pivot point, which influences the lever arm's length and thus the amount of torque generated.
In the example with two forces of 60 N and 80 N, how do you calculate the resulting rotation?
-In the example, the torques produced by each force are calculated separately, considering their respective lever arms and angles. The resulting rotation is determined by adding the torques algebraically. If one torque is negative (clockwise) and the other is positive (counterclockwise), their sum gives the net torque, which indicates the direction of the overall rotation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

MOMEN GAYA - FISIKA - MATERI UTBK SBMPTN DAN SIMAK UI

TORQUE OU MOMENTO DE UMA FORÇA | RESUMO DE FÍSICA PARA O ENCCEJA
Torque, Basic Introduction, Lever Arm, Moment of Force, Simple Machines & Mechanical Advantage

FISIKA KELAS XI || Momen Gaya dan Momen Inersia || DINAMIKA ROTASI DAN KESETIMBANGAN BENDA TEGAR

Torque Introduction

Fisika Kelas XI: Dinamika Benda Tegar
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)