Lei de Lavoisier | Leis Ponderais - Brasil Escola
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Professor Choven introduces the concept of the Law of Conservation of Mass, proposed by Antoine Lavoisier. The law states that in a closed system, the mass of the reactants is always equal to the mass of the products in any chemical reaction. The professor explains this with a practical example using the formation of water from hydrogen and oxygen, showcasing the mass balance before and after the reaction. The video encourages viewers to grasp the core idea that mass is neither created nor destroyed, only transformed in chemical processes.
Takeaways
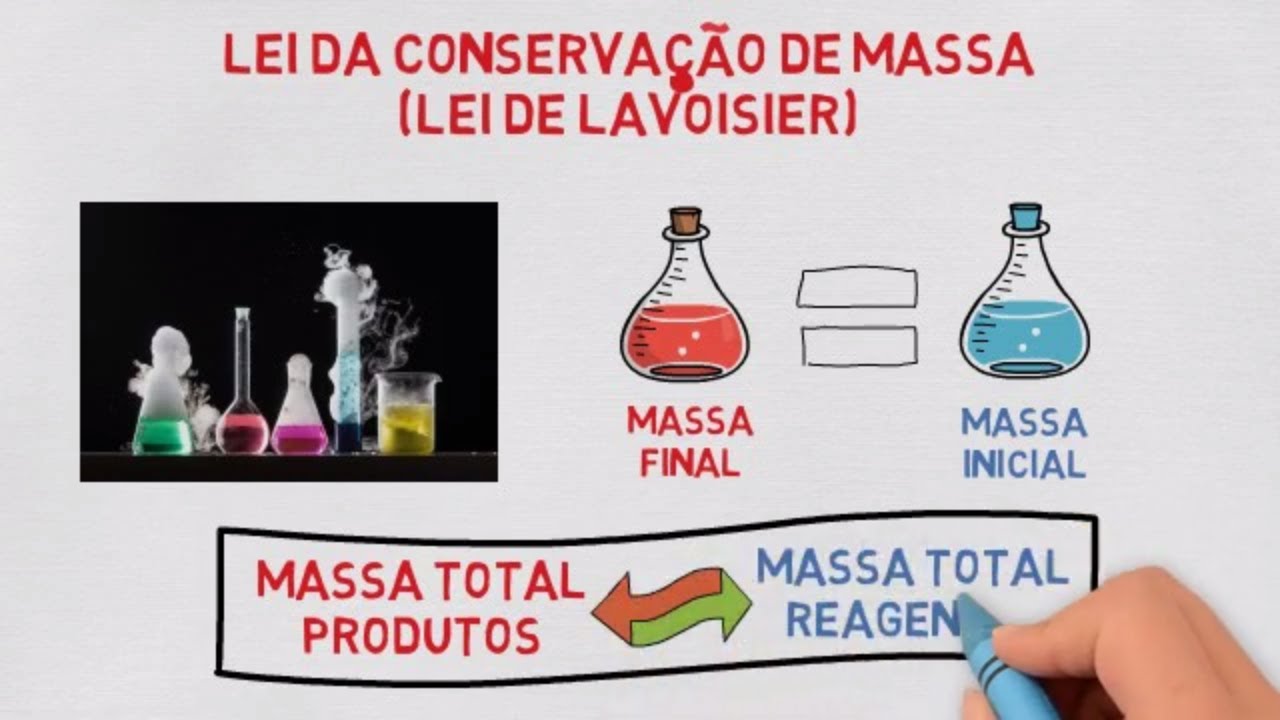
- 😀 The video explains the law of conservation of mass, also known as Lavoisier's law, which states that in a closed system, the total mass of the reactants is always equal to the total mass of the products in any chemical reaction.
- 😀 The law of conservation of mass was proposed by Antoine Lavoisier and applies to all chemical reactions in a closed system.
- 😀 The key idea is that nothing is lost or gained in a chemical reaction; matter only transforms. This is summarized by the phrase 'nothing is created, nothing is lost, everything transforms.'
- 😀 Reactants are the substances that undergo a chemical change, while products are the substances that are formed as a result of the reaction.
- 😀 The video provides a simple example: when hydrogen reacts with oxygen to form water, the mass of the hydrogen and oxygen before the reaction is equal to the mass of the water formed after the reaction.
- 😀 In the example, the mass of hydrogen is 4g and the mass of oxygen is 32g, resulting in a total mass of 36g for the products, proving the conservation of mass.
- 😀 The law only holds true in a closed system, where no matter is lost or added from the surroundings.
- 😀 The concept of balancing chemical reactions is highlighted, with an emphasis on ensuring that the mass on both sides of the equation is equal.
- 😀 The video encourages viewers to share the phrase 'nothing is created, nothing is lost, everything transforms' as a status on social media to spread awareness of the law of conservation of mass.
- 😀 The video ends by inviting viewers to leave comments, like the video, share it, and explore additional resources and exercises to deepen their understanding of the topic.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is the Law of Conservation of Mass, also known as Lavoisier's Law, which explains how the mass of reactants in a chemical reaction equals the mass of the products in a closed system.
Who proposed the Law of Conservation of Mass?
-The Law of Conservation of Mass was proposed by Antoine Lavoisier.
What does the Law of Conservation of Mass state?
-The law states that in a closed system, the sum of the masses of the reactants in a chemical reaction is always equal to the sum of the masses of the products.
What is meant by a 'closed system' in the context of this law?
-A 'closed system' refers to a situation where no mass is lost or gained during a chemical reaction, meaning that all the reactants and products remain within the system.
How is the Law of Conservation of Mass usually summarized?
-It is often summarized with the phrase, 'In nature, nothing is created or destroyed; everything is transformed.' This highlights the idea that mass is conserved in chemical reactions.
Can you explain the example given in the video using hydrogen and oxygen?
-The example demonstrates that when hydrogen gas (H2) reacts with oxygen gas (O2) to form water (H2O), the mass of the reactants (H2 and O2) equals the mass of the product (H2O). For instance, 4 grams of hydrogen react with 32 grams of oxygen, producing 36 grams of water.
What is the formula used to calculate the mass of the reactants and products in the water formation reaction?
-To calculate the mass, the video uses the molar masses of hydrogen (H2 = 2 g/mol) and oxygen (O2 = 32 g/mol). The reaction involves 2 moles of H2 and 1 mole of O2, which results in 2 moles of water (H2O), where the mass of water is 36 grams.
Why is the mass of the reactants equal to the mass of the products in this reaction?
-Because the Law of Conservation of Mass holds true in a closed system, the total mass remains unchanged. The total mass of hydrogen and oxygen before the reaction is equal to the total mass of water produced after the reaction.
How does the Law of Conservation of Mass apply to any chemical reaction?
-The law applies universally to all chemical reactions in closed systems, meaning that regardless of the type of reaction, the total mass of the reactants will always equal the total mass of the products.
What practical takeaway does the video suggest regarding the Law of Conservation of Mass?
-The video suggests using the principle 'nothing is created or destroyed; everything is transformed' as a practical takeaway, and encourages students to remember this concept when studying chemistry and chemical reactions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Hukum Lavoisier (Hukum Kekekalan Massa) | Kimia SMA | Tetty Afianti

Hukum Dasar Kimia (Hukum Kekekalan Massa/Hukum Lavoisier) – [Kimia X Semester 2]
Lei de Lavoisier: Lei de Conservação das Massas!

Praktikum Konsep Mol (Hukum Kekekalan Massa)

Law of Conservation of Mass

Law of Conservation of Mass Example
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)