How are Nutrients Transported Around the Body
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how the body processes and transports nutrients from the food we eat. It covers the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in the digestive system into their usable forms, such as glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids. Once digested, these nutrients enter the bloodstream through the small intestine and are transported to various parts of the body via capillaries. The circulatory and lymphatic systems play key roles in nutrient distribution, ensuring muscles receive the nourishment needed for recovery and growth. The process also involves storing excess nutrients in the liver for future use.
Takeaways
- 😀 Nutrients like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are essential for the body to perform daily activities.
- 😀 Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, proteins into amino acids, and fats into fatty acids during digestion.
- 😀 The digestive system, including the mouth, stomach, small intestine, and others, breaks down food into transportable nutrients.
- 😀 Enzymes in the digestive system play a key role in breaking down food into smaller, usable forms.
- 😀 Once food is broken down, nutrients are absorbed in the small intestine and transported via the circulatory system.
- 😀 The circulatory system, consisting of the heart, blood, and blood vessels, transports nutrients to body cells.
- 😀 Capillaries, small blood vessels, are the main transporters of nutrients, oxygen, and waste through the bloodstream.
- 😀 After a workout, the bloodstream carries amino acids to muscle cells to aid in muscle growth and repair.
- 😀 Excess nutrients like glucose and amino acids are stored in the liver for later use.
- 😀 Fatty acids are transported through both the bloodstream and lymphatic system for storage and distribution.
- 😀 Efficient nutrient transportation is crucial to ensure your body gets all the nourishment it needs to function properly.
Q & A
What are the major nutrients the body needs to function day to day?
-The major nutrients the body needs are carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
What is the role of enzymes in the digestive system?
-Enzymes in the digestive system break down food into smaller, transportable nutrients, making it easier for the body to use them.
How does the body break down carbohydrates?
-Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose during the digestion process.
What happens to proteins during digestion?
-Proteins are broken down into amino acids during digestion, which are then used by the body for various functions.
How are fats broken down in the digestive system?
-Fats are broken down into fatty acids during digestion.
What role does the small intestine play in nutrient absorption?
-The small intestine absorbs nutrients from digested food into the bloodstream, allowing them to be transported to different parts of the body.
How are nutrients transported throughout the body?
-Nutrients are transported throughout the body via the circulatory system, which includes the heart, blood, and blood vessels, with capillaries being the key vessels for nutrient transfer.
What are capillaries, and why are they important?
-Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that connect arteries to veins, allowing nutrients, oxygen, and waste to pass in and out of the bloodstream to reach cells.
How does the bloodstream help with muscle repair after exercise?
-After a hard workout, the bloodstream carries amino acids from digested proteins to the muscles to help with muscle growth and repair.
What happens to excess nutrients in the body?
-Excess nutrients are stored in the liver for future use. Specifically, glucose and amino acids are stored there, while fatty acids are stored in different body parts or transported through the lymphatic system.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

3D Digestive System of Human Body | Gastrointestinal Tract Animation

You are What You Eat

mekanisme indera pengecap (lidah) - biologi sma kelas 11 bab sistem indera

Food Chains for Kids: Food Webs, the Circle of Life, and the Flow of Energy - FreeSchool
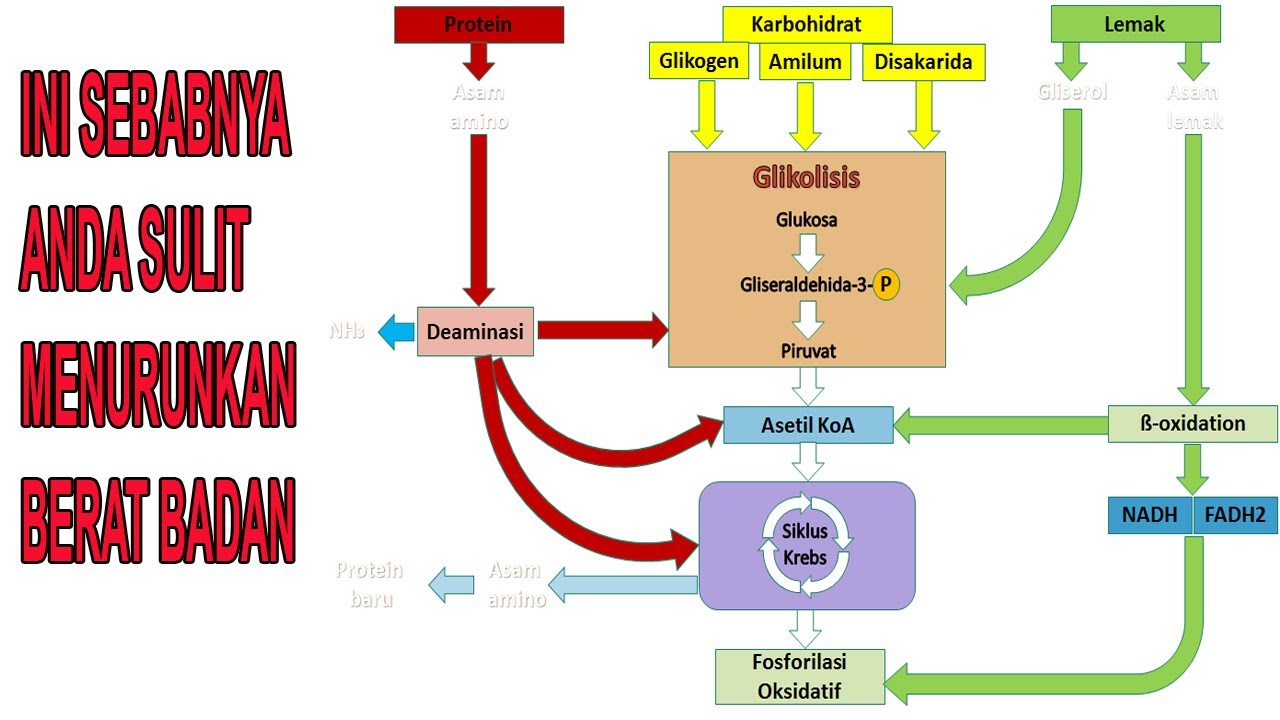
CARBOHYDRATE, FAT AND PROTEIN METABOLISM PATHWAYS

The digestive system and digestion | Educational Video for Kids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)