Food Chains for Kids: Food Webs, the Circle of Life, and the Flow of Energy - FreeSchool
Summary
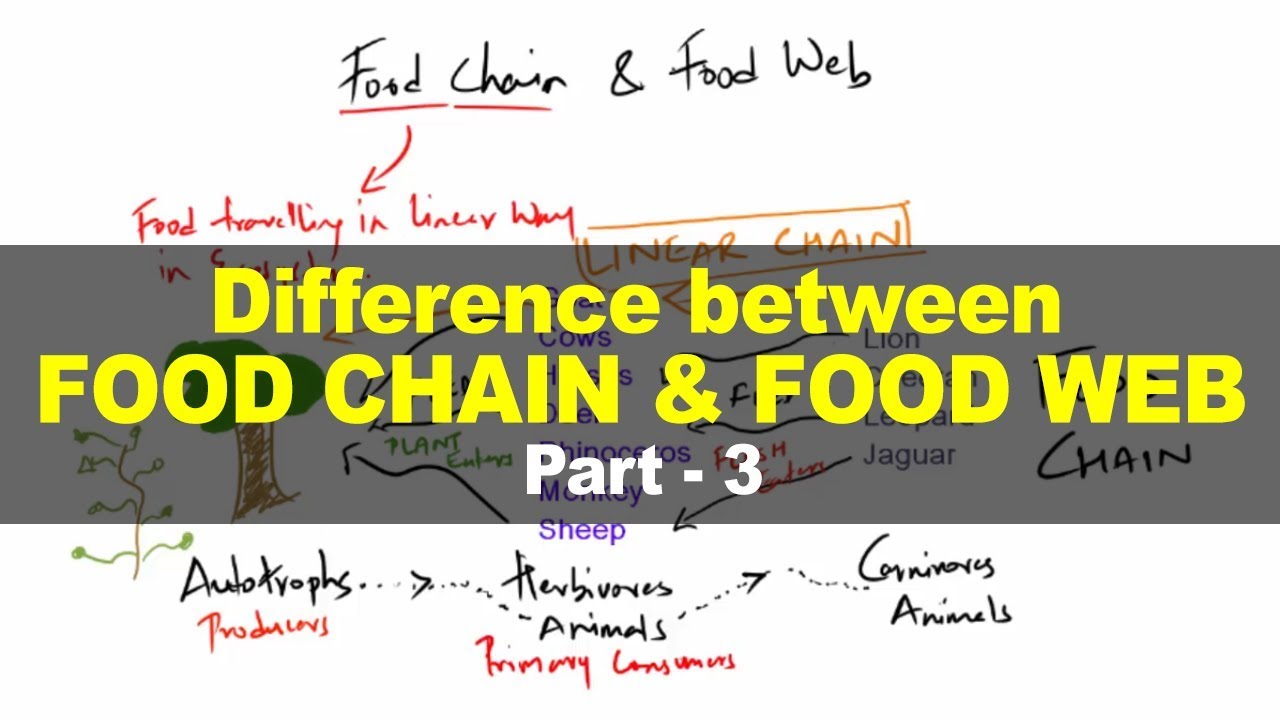
TLDRThis video explains the concept of food chains, showcasing how living things are interconnected through the transfer of energy. It starts with producers, like plants, which capture energy from the sun through photosynthesis. Herbivores, or primary consumers, eat the plants, followed by carnivores, or secondary consumers, that eat the herbivores. The video highlights the flow of energy through each link in the chain, apex predators at the top, and decomposers that break down dead organisms to recycle nutrients. It also introduces more complex ecosystems, where multiple food chains form a food web.
Takeaways
- 🌱 All living things are connected through food chains, which illustrate the flow of energy and matter between organisms.
- 🌞 The sun is the primary source of energy for all food chains on Earth, with plants capturing this energy through photosynthesis.
- 🌿 Producers, like plants, create their own food and are the starting point of every food chain.
- 🐰 Consumers, such as animals, cannot produce their own food and must consume other organisms to obtain energy.
- 🌿 Herbivores are primary consumers that eat plants, transferring the sun's energy into their bodies.
- 🦊 Secondary consumers, like carnivores, eat herbivores, further transferring energy up the food chain.
- 🐾 Tertiary consumers are higher up the food chain and eat secondary consumers, continuing the energy transfer.
- 🦉 Apex predators are at the top of the food chain and are not eaten by other animals.
- 🔄 Only about 10% of the energy consumed by an organism is passed on to the next level in the food chain.
- 🌿 Decomposers, like bacteria and fungi, break down dead organisms, returning nutrients to the soil and aiding plant growth.
- 🕸️ Food chains are interconnected in natural ecosystems, forming complex food webs that demonstrate the intricate relationships between living things.
Q & A
What is a food chain?
-A food chain is a way to describe the relationships between organisms and how matter and energy flow between living things, represented as a sequence starting from producers to consumers.
Where does the energy in a food chain originate?
-The energy in a food chain originates from the sun, which reaches the earth as light and heat and is captured by plants through photosynthesis.
What are producers in a food chain?
-Producers are organisms, such as plants, that can create or produce their own food from the sun's energy.
Why can't animals create their own food?
-Animals cannot create their own food because they lack the ability to perform photosynthesis, which is necessary to convert sunlight into food.
What is the role of consumers in a food chain?
-Consumers are animals that must eat or consume energy from other sources, as they cannot produce their own food.
What is an herbivore and what is its position in a food chain?
-An herbivore is a primary consumer that eats plants, and it is the second link in a food chain.
What is the term for a consumer that eats other animals?
-A consumer that eats other animals is called a carnivore.
Why can't food chains have too many links?
-Food chains can't have too many links because each animal uses up a lot of energy from the previous level, and only about 10% of the energy is passed on to the next level.
What is the role of decomposers in the food chain?
-Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, break down dead plants and animals into nutrients in the soil, which helps the plants at the beginning of the food chain to grow.
What is an apex predator in a food chain?
-An apex predator is a consumer that is not hunted and eaten by any other animals and is considered to be at the top of the food chain.
What is a food web?
-A food web is a network of interconnected food chains that illustrates the complex relationships and energy flows between different organisms in an ecosystem.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)