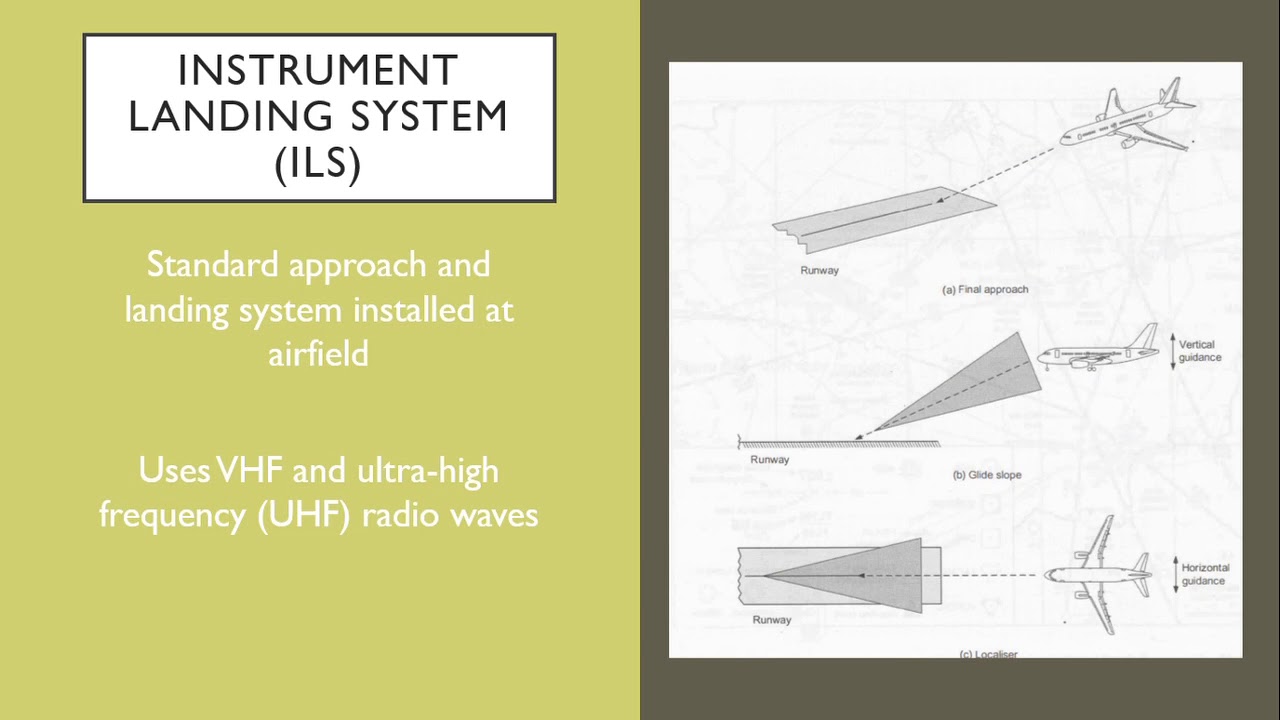
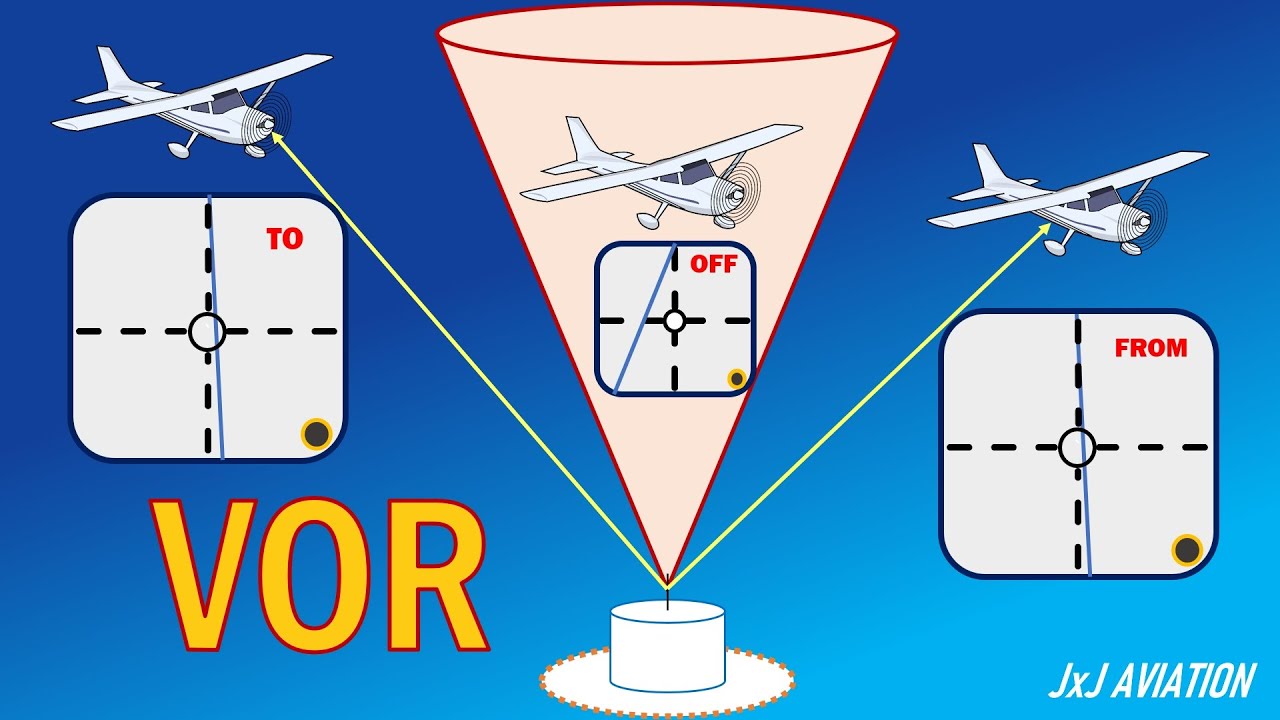
ATPL Radio Navigation - Class 5: VOR.
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the workings of Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range (VOR) beacons, an upgrade over NDB systems, used for aircraft navigation. VORs transmit signals in all directions, allowing aircraft to determine position and direction relative to the beacon. The video covers the two types of VOR systems: standard and Doppler, detailing how they function differently but achieve the same goal. It also discusses various display methods, including Radio Magnetic Indicator (RMI), Omni Bearing Indicator (OBI), and Horizontal Situation Indicator (HSI). Additionally, the video addresses common errors in VOR systems, such as the cone of confusion and signal reflection issues.
Takeaways
- 😀 VOR (Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range) beacons are an advanced version of NDBs (Non-Directional Beacons), providing more accurate and reliable navigation for aircraft.
- 😀 VOR operates on the VHF frequency range between 108 and 117.95 MHz, transmitting signals in all directions for position and direction determination, but not distance information.
- 😀 VOR signals are broadcast in two types: standard and Doppler. Both achieve the same goal but use different methods to detect aircraft position and heading.
- 😀 Standard VOR relies on two signals: a stationary reference FM signal and a rotating variable AM signal, with phase differences providing bearing information.
- 😀 Doppler VOR uses Doppler shifts, caused by the movement of the signal around the aircraft, to detect frequency differences and determine aircraft direction.
- 😀 The VOR beacon’s identifier is sent via a separate signal in Morse code at 1020 Hz every 10 seconds for identification purposes.
- 😀 VOR information can be displayed using Radio Magnetic Indicators (RMI), Omni Bearing Indicators (OBI), or Horizontal Situation Indicators (HSI), with each providing varying levels of detail.
- 😀 The OBI allows aircraft to follow specific radials and provides a course deviation indicator to show how far off course the aircraft is.
- 😀 The HSI combines heading and course information, offering a more advanced way of displaying VOR data compared to the OBI, and is common in modern aircraft.
- 😀 Common VOR system errors include the Cone of Confusion (no signal detected overhead), scalloping (signal interference from reflections), and line-of-sight issues (signal loss due to obstructions like mountains).
Q & A
What is a Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range (VOR) beacon?
-A VOR beacon is a short-range radio navigation system used by aircraft to determine their position and direction relative to the beacon. It operates on the VHF band between 108 and 117.95 MHz and transmits signals in all directions, allowing aircraft to navigate based on signal orientation.
How does a standard VOR system work?
-A standard VOR system uses two types of signals: a stationary reference signal (FM) that is transmitted in all directions, and a rotating variable signal (AM) that sweeps 360° around the beacon. The phase difference between these two signals is detected by the aircraft to determine its position and direction relative to the VOR.
What is the primary difference between standard and Doppler VOR systems?
-The primary difference lies in how the signals are produced. A standard VOR uses a rotating AM signal and a stationary FM reference signal, while a Doppler VOR uses a moving FM signal and a reference AM signal. The Doppler effect creates a frequency shift that allows the aircraft to determine its position.
Why do VOR systems have an identifier signal?
-The identifier signal is sent to help pilots verify the VOR beacon they are receiving. It is a three-letter Morse code that is transmitted every 10 seconds to confirm the specific VOR beacon the aircraft is tuned to.
What are the three primary ways to display VOR information in an aircraft?
-VOR information can be displayed using a Radio Magnetic Indicator (RMI), an Omni Bearing Indicator (OBI), or a Horizontal Situation Indicator (HSI). Each provides different levels of detail, from basic directional guidance (RMI) to more precise bearing and heading information (OBI and HSI).
How does an Omni Bearing Indicator (OBI) work?
-An OBI shows the aircraft's position relative to the VOR beacon by displaying a rotating compass rose with a course deviation indicator. The pilot can select a radial to follow, and the deviation bar will show how far the aircraft is from the selected course.
What is the difference between an OBI and an HSI?
-An OBI displays bearing information but lacks heading information, while an HSI shows both heading and bearing information. The HSI is linked to the aircraft's compass, providing more accurate navigation data compared to an OBI.
What is the 'Cone of Confusion' in VOR systems?
-The 'Cone of Confusion' refers to a region above the VOR beacon where no signal can be detected due to the line-of-sight nature of the signals. This occurs when an aircraft is directly overhead the VOR, causing a temporary degradation in signal reception.
What are some common errors associated with VOR systems?
-Common errors in VOR systems include the 'Cone of Confusion' (signal loss when overhead), scalloping (signal reflection causing interference), and line-of-sight issues (obstructions like mountains or the curvature of the Earth blocking the signal).
What is the typical range and accuracy of a VOR system?
-The range of a VOR system depends on factors like the power output of the beacon and the aircraft's equipment. VOR systems typically have a stated accuracy of ±5° 95% of the time when within range, which is crucial for precise navigation along airways and during airport approaches.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)