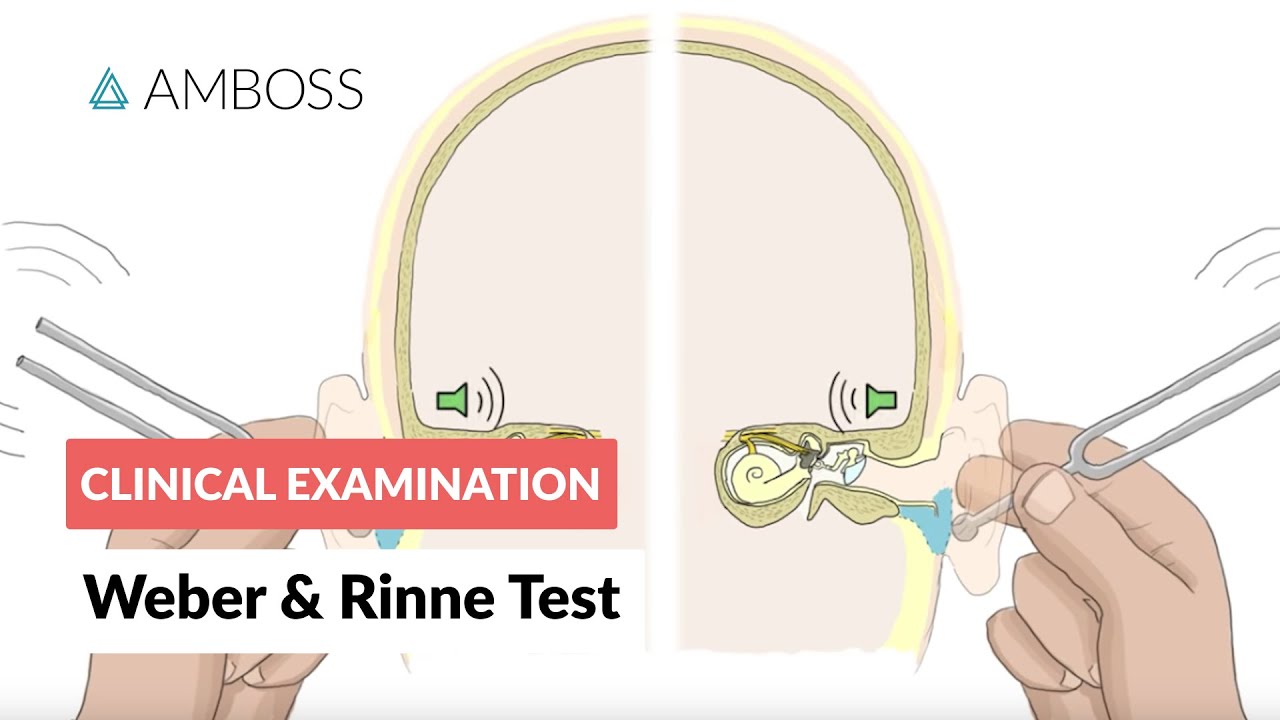
How to Perform the Weber & Rinne Hearing Tests | Clinical Examination Skills
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Sandra, a nurse practitioner, demonstrates how to perform the Rinne and Weber hearing tests, essential for screening hearing loss in primary care settings. The video explains how the 512 Hz tuning fork is used to assess unilateral hearing loss with the Weber test and conductive hearing loss with the Rinne test. Sandra provides a clear step-by-step guide on how to properly conduct these tests, interpret results, and the importance of referral to an ENT for formal evaluation if necessary. The video serves as an informative resource for healthcare professionals and students interested in auditory assessments.
Takeaways
- 😀 Sandra is a nurse practitioner and demonstrates how to perform the Rinne and Weber hearing tests.
- 😀 The Rinne and Weber tests are screening tools used in primary care to assess hearing loss, but they are not diagnostic.
- 😀 After performing the tests, if there is concern for hearing loss, patients should be referred to an ENT specialist for a formal hearing evaluation.
- 😀 A 512 Hz tuning fork is ideal for performing both the Rinne and Weber tests, although 128 Hz and 256 Hz tuning forks exist.
- 😀 There are three main types of hearing loss: sensory neural, conductive, and mixed hearing loss.
- 😀 The Weber test evaluates unilateral hearing loss (hearing loss in one ear) by determining if the sound is heard equally or louder in one ear.
- 😀 In sensory neural hearing loss, the sound will lateralize to the unaffected ear, meaning the tone is louder in the 'good' ear.
- 😀 In conductive hearing loss, the sound lateralizes to the affected ear, meaning the tone is louder in the ear with the hearing loss.
- 😀 The Rinne test evaluates for conductive hearing loss by comparing air conduction and bone conduction in each ear.
- 😀 A normal Rinne test shows air conduction lasting approximately twice as long as bone conduction (positive Rinne test).
Q & A
What are the Renee and Weber tests used for?
-The Renee and Weber tests are used as screening tools for hearing loss in primary care. They help identify potential hearing loss, but are not diagnostic. If hearing loss is suspected, patients should be referred to an ENT for a formal evaluation.
What is the ideal tuning fork frequency for performing the Renee and Weber tests?
-The ideal tuning fork frequency for performing the Renee and Weber tests is 512 Hz. While other frequencies like 128 Hz or 256 Hz can be used, 512 Hz is considered the most effective for these tests.
What are the three main types of hearing loss?
-The three main types of hearing loss are: sensory neural hearing loss (issues with the auditory nerve or cochlea), conductive hearing loss (problems with sound transmission through the outer or middle ear), and mixed hearing loss (a combination of both sensory neural and conductive hearing loss).
What is the purpose of the Weber test?
-The Weber test evaluates unilateral hearing loss, meaning it helps identify hearing loss in one ear. The test helps determine whether sound is heard equally in both ears or if it's louder in one ear.
How do you perform the Weber test?
-To perform the Weber test, activate the 512 Hz tuning fork by striking it on the elbow or knee. Place the vibrating tuning fork in the midline of the patient's head or forehead and ask if the sound is heard equally in both ears or louder in one ear.
What does it mean if the sound in the Weber test is louder in one ear?
-If the sound is louder in one ear during the Weber test, it suggests either sensory neural hearing loss (louder in the unaffected ear) or conductive hearing loss (louder in the affected ear).
What is the purpose of the Renee test?
-The Renee test evaluates for conductive hearing loss in one ear. It helps determine whether air conduction is better than bone conduction in the ear being tested.
How is the Renee test performed?
-To perform the Renee test, activate the tuning fork and place it on the mastoid bone behind the ear. Ask the patient to indicate when they can no longer hear the sound. Then move the tuning fork about 1-2 cm from the outer ear and ask again when they can no longer hear it.
What does a normal result in the Renee test look like?
-In a normal (positive) Renee test, air conduction should be heard approximately twice as long as bone conduction. This means the patient can hear the sound longer through the air than through bone conduction.
What indicates an abnormal (negative) Renee test result?
-In an abnormal (negative) Renee test, bone conduction is heard longer than air conduction. This suggests conductive hearing loss, where sound conducted through the bone is perceived better than sound conducted through the air.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)