VALORACION AUDITIVA
Summary
TLDRThe video script details the procedure for conducting Weber and Rinne tests to assess bone and air conduction in patients with suspected hearing loss. The use of a tuning fork is emphasized, highlighting the importance of correctly placing it for accurate vibration detection. The script outlines step-by-step instructions for evaluating both ears, measuring the duration of sound perception during bone and air conduction tests, and interpreting the results. Overall, the video serves as a practical guide for healthcare professionals performing hearing assessments.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Weber test assesses bone and air conduction to diagnose hearing loss.
- 🎶 A tuning fork is used to create vibrations for testing auditory responses.
- 🦻 Patients are asked to signal when they hear the sound during the test.
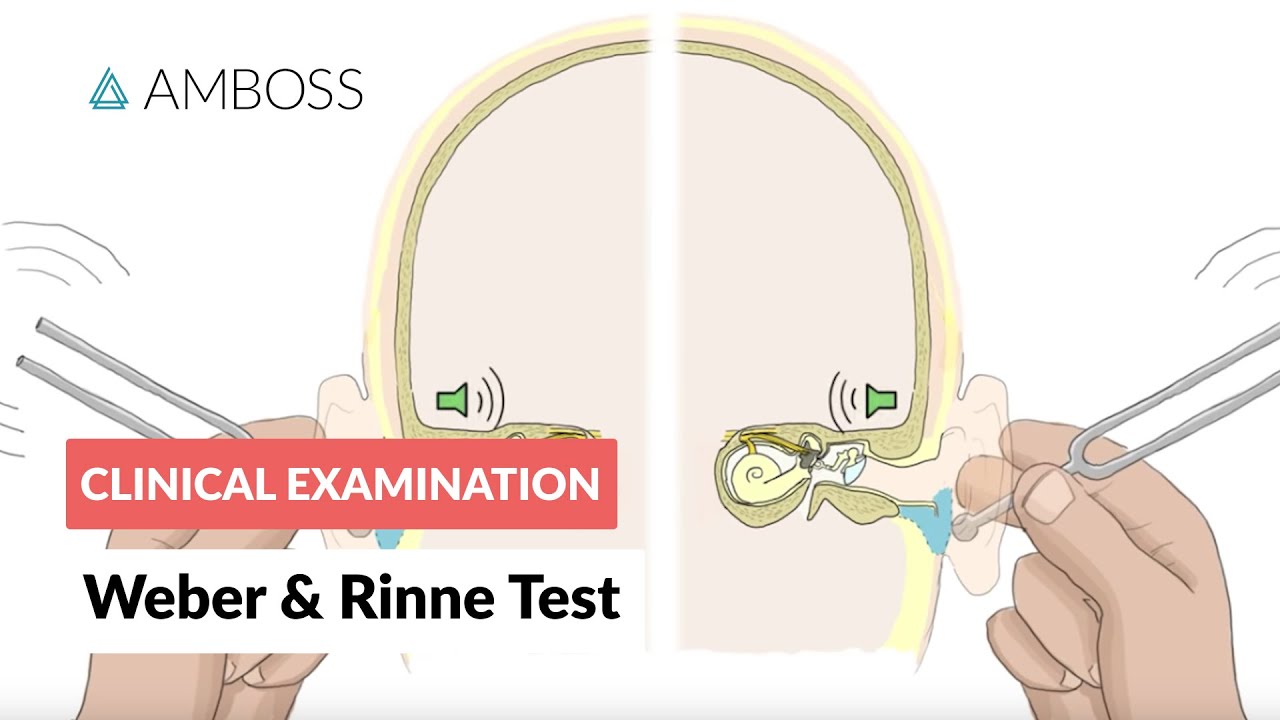
- 🔊 Air conduction is tested first by placing the tuning fork on the patient's head.
- 👂 The test evaluates each ear individually by covering one ear at a time.
- ⏱️ A stopwatch is necessary to measure the duration of sound perception during the tests.
- 🔄 Bone conduction is assessed by placing the tuning fork on the mastoid bone behind the ear.
- 📏 Air conduction should last about twice as long as bone conduction if hearing is normal.
- 📝 Results from both ears are compared to determine the type of hearing loss present.
- 📊 The procedure is repeated for the other ear to ensure accurate assessment.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the tuning fork test described in the script?
-The main purpose of the tuning fork test is to assess hearing loss by evaluating both air conduction and bone conduction in a patient.
How is air conduction tested using the tuning fork?
-Air conduction is tested by striking the tuning fork and placing it on the patient's head, asking them to indicate when they hear the sound. The test is repeated for each ear while the other ear is covered.
What indicates that air conduction is intact during the test?
-If the patient hears the sound when the tuning fork is placed on their head, it indicates that air conduction is intact.
What is the procedure for testing bone conduction?
-Bone conduction is tested by placing the tuning fork on the mastoid bone behind the ear and asking the patient to indicate when they hear the sound, while timing the duration of sound perception.
How does the examiner determine if there is normal hearing based on the timing of sound perception?
-Normal hearing is indicated if the duration of air conduction is approximately double that of bone conduction; for example, if bone conduction lasts 8 seconds, air conduction should last around 16 seconds.
What are the two key components being measured in this hearing assessment?
-The two key components being measured are bone conduction (via the mastoid bone) and air conduction (in front of the ear).
What is the significance of proper placement of the tuning fork during the test?
-Proper placement of the tuning fork is crucial because touching it incorrectly can stop its vibrations, affecting the test results.
What happens if a patient cannot hear the sound during the test?
-If the patient cannot hear the sound, it suggests there may be an issue with their air conduction, warranting further evaluation.
How does the examiner track the time during the testing?
-The examiner uses a stopwatch to track the duration of sound perception for both bone and air conduction tests.
Why is communication with the patient important during the hearing test?
-Effective communication is essential to ensure the patient understands the instructions and can accurately indicate when they hear the sound, leading to valid test results.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Hearing Test (Rinne and Weber Examinations) - ENT
Weber and Rinne Test - Clinical Examination

Cranial Nerve 8 | Vestibulocochlear Nerve Assessment for Physiotherapists

How to Perform the Weber & Rinne Hearing Tests | Clinical Examination Skills

Praktikum hearing 01: Bagaimana kita bisa mendengar suara?

Masking in Audiology (incl. the Rules of Masking) - An Overview
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)