Working of Synchronous Motor
Summary
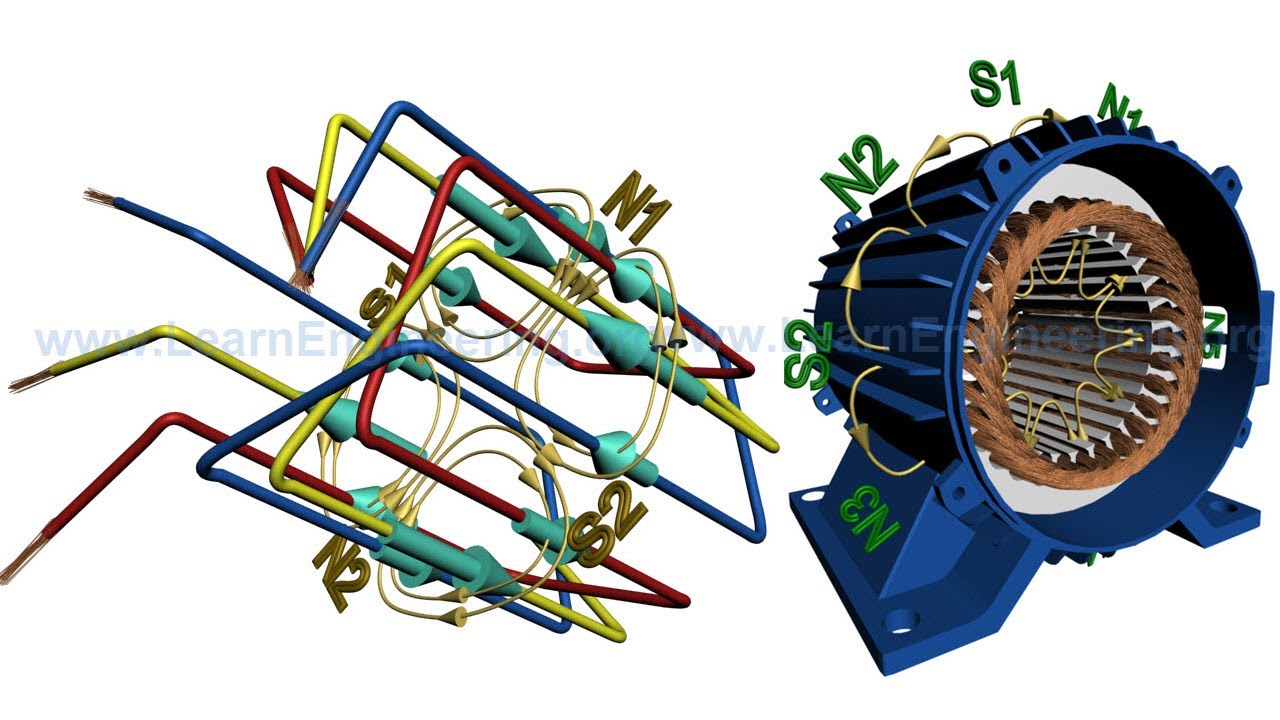
TLDRSynchronous motors are efficient machines that run at a constant speed, regardless of load. They work through the interaction of a rotating magnetic field (RMF) and a rotor that behaves like a permanent magnet. Though inherently not self-starting, they use a squirrel cage arrangement to initiate rotation like an induction motor before reaching synchronous speed. Once at this speed, the rotor is locked with the RMF, ensuring constant operation. Synchronous motors are used in high-precision applications and help improve power factor. However, they can slip out of synchronism if overloaded or faced with insufficient voltage.
Takeaways
- 😀 Synchronous motors run at constant speed, regardless of the load.
- 😀 They are highly efficient machines, typically used in precision applications.
- 😀 The constant speed of synchronous motors is achieved through the interaction of the rotor's magnetic field and the rotating magnetic field (RMF) generated by the stator.
- 😀 The rotor of a synchronous motor is either excited by DC power or made of a permanent magnet.
- 😀 When the rotor receives an initial rotation in the direction of the RMF, the poles attract each other, and the rotor locks in sync with the RMF, thus rotating at synchronous speed.
- 😀 The synchronous speed of the motor depends on the frequency of the AC supply, which allows for precise control of motor speed.
- 😀 If the rotor has no initial rotation, it struggles to start due to inertia, as the RMF keeps changing polarity, leading to a repulsive force.
- 😀 To make synchronous motors self-starting, a squirrel cage is added to the rotor, allowing it to behave like an induction motor during startup.
- 😀 Once the rotor reaches its maximum speed, its field coils are energized, and it locks in sync with the RMF, achieving synchronous speed.
- 😀 If the motor's load exceeds its torque capability, it will slip out of synchronism and come to a stop.
- 😀 Synchronous motors share similar construction features with alternators and help improve the overall power factor of the system.
Q & A
What is a synchronous motor?
-A synchronous motor is a type of motor that runs at a constant speed regardless of the load acting on it, due to the interaction between a constant and rotating magnetic field.
How is the constant speed of a synchronous motor achieved?
-The constant speed is achieved by the interaction between the rotor's constant magnetic field and the stator's revolving magnetic field. The rotor and stator fields lock together to maintain synchronous speed.
How is the stator of a synchronous motor powered?
-The stator of a synchronous motor is powered by a three-phase AC supply, which generates a revolving magnetic field.
What role does the rotor play in a synchronous motor?
-The rotor produces a constant magnetic field and is excited by a DC power supply, making it act like a permanent magnet. It interacts with the revolving magnetic field from the stator to maintain synchronous speed.
What happens if the rotor does not have an initial rotation in a synchronous motor?
-Without initial rotation, the rotor struggles to start because its inertia causes it to move slowly, and it may fail to achieve synchronous speed, resulting in the motor not starting.
How does the squirrel cage arrangement help a synchronous motor start?
-A squirrel cage arrangement is fitted to the rotor. When the motor starts, the rotor coils are not energized, and the squirrel cage bars are induced with electricity by the revolving magnetic field, allowing the rotor to start like an induction motor.
What happens once the rotor reaches its maximum speed in a synchronous motor?
-Once the rotor reaches its maximum speed, the rotor's field coils are energized, locking the rotor poles with the revolving magnetic field poles, and the motor starts running at synchronous speed.
What happens when the rotor reaches synchronous speed in a synchronous motor?
-When the rotor reaches synchronous speed, there is no relative motion between the rotor and the revolving magnetic field. This results in zero current and force on the squirrel cage bars, which do not affect the motor's synchronized operation.
Can synchronous motors run at a constant speed regardless of the load?
-Yes, synchronous motors will run at a constant speed, provided the load is within the motor's capability. If the load torque exceeds the motor's output, the motor will slip out of synchronism and stop.
What factors can cause a synchronous motor to go out of synchronism?
-Low supply voltage, insufficient excitation voltage, or other issues can cause a synchronous motor to go out of synchronism and stop running.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Synchronous Motor vs Asynchronous Motor | Synchronous vs Induction Motor | Come4Concepts
Rotating Magnetic Field & Synchronous Speed

Drehmoment Drehzahl Kennlinie - Kurzschlussläufermotor - einfach und anschaulich erklärt

What is a SYNCHRONOUS MOTOR and how does it work? - Rotating magnetic field - Synchronism speed

Reluctance motors explained

Explained: Droop vs Isochronous Governing
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)