Depolarization and Repolarization of Heart: Action Potential (Atrial & Ventricular) Animation
Summary
TLDRIn this tutorial, Sarah explains the concepts of atrial and ventricular depolarization and repolarization, which are fundamental for interpreting EKGs. The video covers how heart cells change from a negative resting state to a positive depolarized state, causing heart muscle contraction, followed by repolarization for relaxation. The electrical conduction system, including the SA node, AV node, and Purkinje fibers, coordinates the contraction and relaxation of the atria and ventricles. The tutorial breaks down the PQRST complex, helping viewers understand how depolarization and repolarization correspond to different phases of the heart's electrical activity.
Takeaways
- 😀 Depolarization leads to contraction, and repolarization leads to relaxation of the heart muscles.
- 😀 Heart cells are negatively charged at rest, a state called polarization, due to unequal ion concentrations across the cell membrane.
- 😀 Sodium ions play a key role in depolarization by entering the heart cell when the cell membrane becomes permeable.
- 😀 Atrial depolarization causes the atria to contract, while ventricular depolarization causes the ventricles to contract.
- 😀 Repolarization is the process where the heart cells return to their negative resting state, causing relaxation.
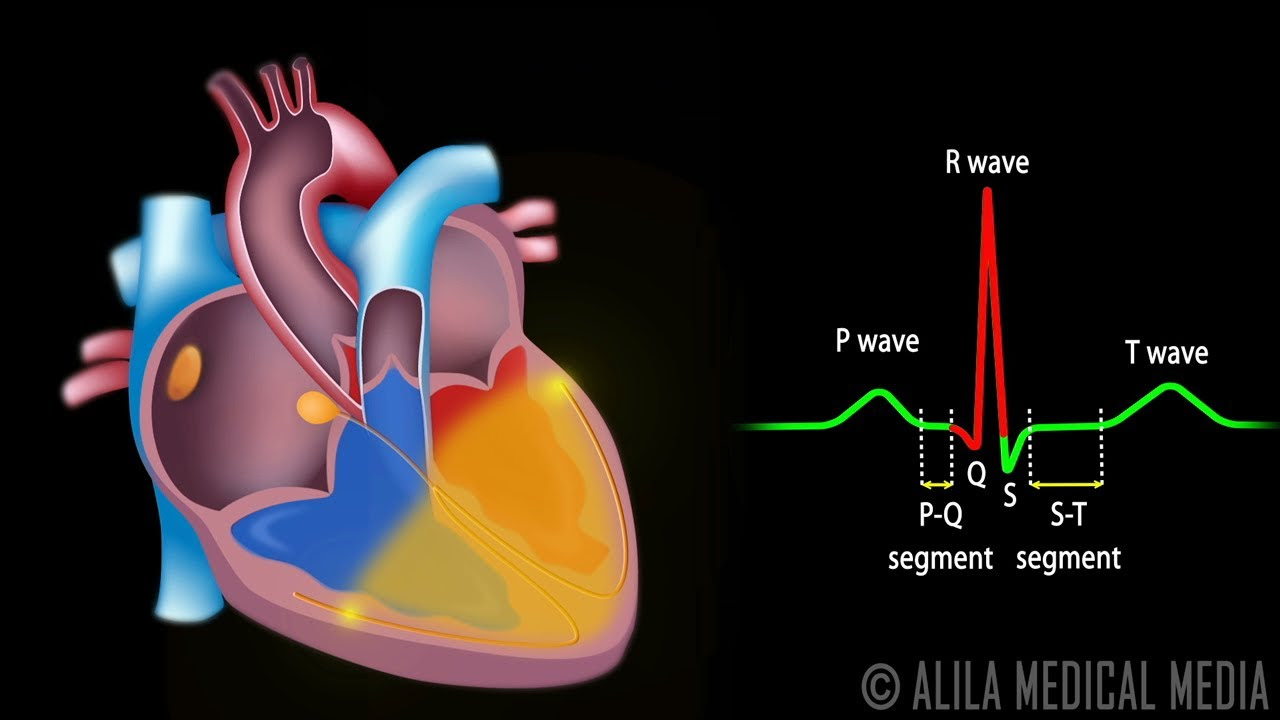
- 😀 In an ECG, the P wave represents atrial depolarization (atrial contraction).
- 😀 The PR segment marks the completion of atrial depolarization before ventricular depolarization begins.
- 😀 The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization, where the ventricles contract.
- 😀 Atrial repolarization occurs during the QRS complex but is not visible in the ECG.
- 😀 The T wave indicates ventricular repolarization, starting the relaxation of the ventricles.
- 😀 The isoelectric line in the ECG marks the completion of ventricular repolarization, indicating the heart is at rest again.
Q & A
What is the main function of the electrical conduction system in the heart?
-The electrical conduction system sends electrical signals that target the cells of the atria and ventricles, causing them to contract and relax, facilitating the heartbeat.
What does it mean for a heart cell to be 'polarized'?
-A heart cell is polarized when it is at rest and negatively charged inside. This occurs due to the unequal distribution of ions, with a higher concentration of sodium outside the cell.
How does sodium contribute to depolarization in heart cells?
-When a heart cell receives an electrical signal, its membrane becomes more permeable, allowing sodium to enter. As sodium is positive, this makes the inside of the cell less negative (more positive), initiating depolarization.
What happens during depolarization in a heart cell?
-During depolarization, the heart cell becomes more positively charged inside as sodium enters, causing the cell to contract.
What is the relationship between depolarization and contraction in the heart?
-Depolarization directly leads to the contraction of the heart muscle. When the heart cells depolarize, they contract to pump blood.
What is repolarization, and how is it related to relaxation in the heart?
-Repolarization is the process of the heart cell returning to its negative resting state after depolarization. This relaxation phase allows the heart muscle to rest between contractions.
What is the significance of the P wave in an ECG?
-The P wave represents atrial depolarization, which causes the atria to contract.
What does the QRS complex on an ECG represent?
-The QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization, which leads to the contraction of the ventricles. It also coincides with the relaxation of the atria.
How does the T wave on an ECG relate to the heart's electrical activity?
-The T wave represents ventricular repolarization, the process where the ventricles relax after contracting.
What happens during the ST segment on an ECG?
-The ST segment represents the completion of ventricular depolarization, marking the time between the end of ventricular contraction and the beginning of relaxation.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Cardiac Conduction System and Understanding ECG, Animation.

Guyton and Hall Medical Physiology (Chapter 11) REVIEW The Normal Electrocardiogram || Study This!

ELETROCARDIOGRAMA FÁCIL E RÁPIDO: ENTENDENDO OS PRIMEIROS PASSOS DO ECG

EKG/ECG Interpretation Basics Nursing NCLEX | QRS Complex, P Wave, T Wave, PR Interval

EC365 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING || LECT 4 || Sources of Bioelectric Potential

Ventricular Action Potential | Cardiac Action Potential | Part 1 | Phases | Cardiac Physiology
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)