Perhitungan Metode Tsukamoto, Mamdani, Sugeno (Video Kampus) - Kuliah Soft Computing
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the fuzzy logic Tsukamoto method for solving production problems, using step-by-step calculations and case examples. It begins by illustrating the key concepts, such as membership degrees, alpha predicates, and the role of rules for 'AND' or 'OR' conditions. It then walks through a case where demand, inventory, and production capacity determine production output using the Tsukamoto method. The video also compares this with methods by Hamdani and Sugiono, highlighting differences in rule-based calculations and defuzzification techniques, including centroid and Sugiono linear equations, to finalize the production result.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Tsukamoto fuzzy logic method involves using membership functions based on the coordinates X and Y to calculate production values in fuzzy systems.
- 😀 The script explains how to set up the problem using a scenario involving demand, inventory, and production capacity.
- 😀 A key point of the Tsukamoto method is the use of membership functions to calculate values for each variable (e.g., demand, inventory, production).
- 😀 The transcript covers the four key rules for determining production based on demand and inventory (e.g., 'if demand decreases and inventory is high, then production decreases').
- 😀 The fuzzy logic method applies specific formulas like MIN and MAX to calculate the membership values for each rule.
- 😀 For each rule, the script details how to calculate the alpha-predicate (membership value), which is essential for finding the final result.
- 😀 A crucial concept discussed is the calculation of the defuzzified output, which combines the alpha-predicates with the corresponding production values to determine the final production output.
- 😀 The Mamdani method differs from Tsukamoto by calculating the maximum values for the production output from all rules rather than individual membership functions.
- 😀 The Sugeno method uses linear equations for each rule to calculate production, differentiating it from the Mamdani and Tsukamoto methods which rely on fuzzy rules with membership functions.
- 😀 The transcript provides practical examples of each method, showing how to apply them step-by-step to solve a given problem.
- 😀 Defuzzification in Mamdani and Sugeno involves different techniques, with Mamdani using centroid and Sugeno using a weighted average approach to determine the final production value.
Q & A
What is the focus of the video regarding the fuzzy logic method?
-The video focuses on explaining the technical calculation steps of fuzzy logic methods, particularly the Tsukamoto method, and the use of membership functions and defuzzification in decision-making processes.
What are the default coordinates used in the Tsukamoto method for the calculation?
-The default coordinates in the Tsukamoto method are set with the x-axis representing demand (ranging from the minimum to maximum values) and the y-axis representing the membership degree of the demand.
How is the value of 'mu' (membership degree) calculated for the demand in the Tsukamoto method?
-The 'mu' value for demand is calculated using a formula based on the minimum and maximum values of demand and the specific case value. The formula for the 'mu' value is used to determine the intersection points between the lines of 'increase' and 'decrease' for demand.
What are the four rules provided in the case study for demand, inventory, and production?
-The four rules are: 1) If demand decreases and inventory is high, then production decreases. 2) If demand decreases and inventory is low, then production decreases. 3) If demand increases and inventory is high, then production increases. 4) If demand increases and inventory is low, then production increases.
What role does 'defuzzification' play in the fuzzy logic process?
-Defuzzification is used to convert fuzzy values or membership degrees into a crisp output. It involves calculating a final value by weighing the rules and membership degrees, thus providing a concrete answer to the problem.
How are the fuzzy sets represented in the case study, and how are they used to calculate the production output?
-The fuzzy sets are represented by the membership degrees (alpha predicates) for different rules. Each rule's output is calculated by applying the membership degrees to the respective fuzzy set coordinates, followed by defuzzification to determine the final production value.
What is the significance of the 'alpha predicate' in the fuzzy logic calculations?
-The 'alpha predicate' represents the degree of membership or certainty for each rule in the fuzzy logic system. It is used to determine the contribution of each rule to the final output during defuzzification.
How are the values for production calculated using the Mamdani method different from the Tsukamoto method?
-In the Mamdani method, the output of each rule is represented as a fuzzy set, and defuzzification is performed by taking the centroid or weighted average of the resulting fuzzy sets. In contrast, the Tsukamoto method uses a more direct approach by calculating crisp values from the membership functions.
What is the role of the 'min' and 'max' functions in the fuzzy logic rules?
-'Min' is used for 'AND' operations in fuzzy logic (intersection of conditions), while 'max' is used for 'OR' operations (union of conditions). These functions are critical in determining how different conditions combine to affect the output in fuzzy systems.
Can you explain the process of calculating the production output using the Sugeno method?
-In the Sugeno method, the rules are represented with linear equations (such as production = demand - inventory). After calculating the membership degrees for each rule using 'min', the output is obtained by applying these degrees to the linear equations and performing a weighted average of the results.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
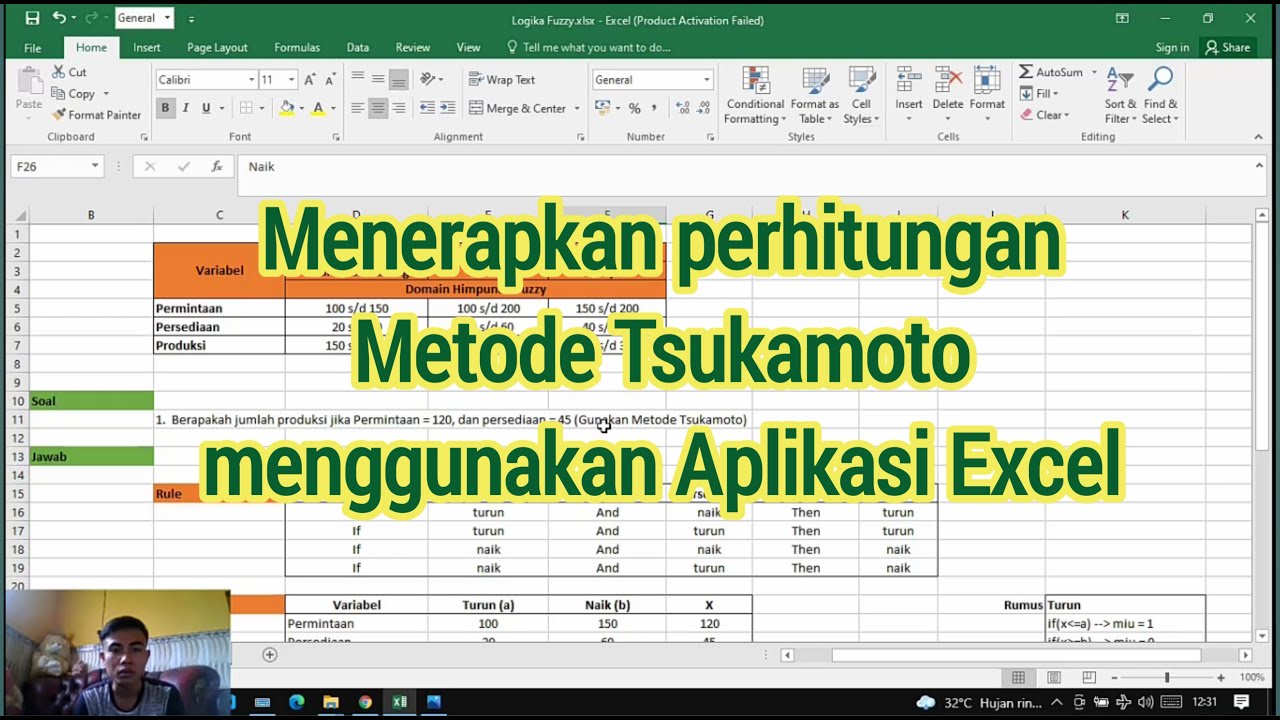
Perhitungan Metode Tsukamoto Menggunakan Aplikasi Microsoft Excel

Fuzzy TSUKAMOTO | Sistem Inferensi Fuzzy | Contoh Studi Kasus dan Langkah Penyelesaiannya

Fuzzy SUGENO alias TAKAGI-SUGENO-KANG | Sistem Inferensi Fuzzy | Studi Kasus Mesin Cuci Otomatis

Studi Kasus: Metode Fuzzy Mamdani

Materi 6 - Nilai Optimum fungsi Objektif

SPLDV (2) | Penyelesaian SPLDV Metode Substitusi | Metode Eliminasi | Metode Gabungan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)