Fisiologi Reproduksi Perempuan - Oogenesis dan Pembentukan Folikel Ovarium
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the process of oogenesis and ovarian follicle development in women. It starts with the formation of oogonium during fetal development and its progression to primary oocytes, which are surrounded by follicular cells. As women reach puberty, these primary oocytes begin meiosis but halt at prophase I. The follicles continue to mature, developing into secondary follicles and eventually Graafian follicles. The ovum completes its meiotic division during ovulation, but only if fertilization occurs. The video also touches on the roles of estrogen and progesterone produced by ovarian cells and how this process contributes to the menstrual cycle.
Takeaways
- 😀 Ovaries are essential reproductive organs in females that produce ova (eggs) necessary for fertilization.
- 😀 Oogenesis is the process by which ova are formed, starting during the fetal period and continuing after birth.
- 😀 The process of oogenesis begins with oogonia (diploid cells), which undergo mitosis to become primary oocytes.
- 😀 Primary oocytes are arrested in Prophase I of meiosis during fetal development and remain in this state until puberty.
- 😀 At puberty, primary oocytes resume meiosis and complete the first meiotic division, becoming secondary oocytes.
- 😀 Secondary oocytes undergo another meiotic division, but it is halted at Metaphase II unless fertilization occurs.
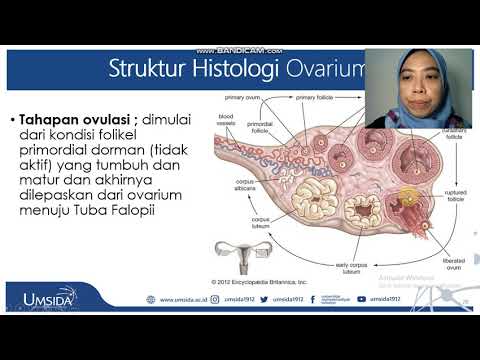
- 😀 Follicular development occurs in stages: from primordial follicles to primary follicles, secondary follicles, and finally mature (Graafian) follicles.
- 😀 In the primary follicle stage, the oocyte is surrounded by granulosa cells, which provide essential support for maturation.
- 😀 Ovulation occurs when a mature follicle releases the secondary oocyte, triggered by a surge in luteinizing hormone (LH).
- 😀 If fertilization occurs, the secondary oocyte completes meiosis, forming a mature ovum and another polar body; otherwise, it degenerates, leading to menstruation.
Q & A
What are the primary functions of the ovaries?
-The ovaries have two main functions: producing eggs (ova) and secreting hormones, primarily estrogen and progesterone.
What is oogenesis, and at what stage does it begin?
-Oogenesis is the process of egg formation. It begins during fetal development with the formation of oogonium cells.
At what stage does oogenesis halt during fetal development?
-Oogenesis halts at prophase I of meiosis during fetal development, and the primary oocytes remain in this arrested state until puberty.
What happens to the primary oocytes at puberty?
-At puberty, primary oocytes resume meiosis, completing the first meiotic division and moving on to the secondary oocyte stage.
What is the significance of follicular development in oogenesis?
-Follicular development is crucial as it surrounds and supports the oocyte, helping it mature. The process includes the development from primordial follicles to primary, secondary, and mature (Graafian) follicles.
What is the difference between primary and secondary follicles?
-Primary follicles consist of the oocyte surrounded by a layer of granulosa cells, while secondary follicles have an antrum (fluid-filled space) forming around the oocyte.
What happens during ovulation?
-During ovulation, the mature follicle (Graafian follicle) releases the secondary oocyte, which is arrested in metaphase II of meiosis.
What happens if the secondary oocyte is not fertilized?
-If the secondary oocyte is not fertilized, it will not complete meiosis and will degenerate, leading to menstruation.
How does fertilization affect the oocyte?
-If the secondary oocyte is fertilized by sperm, it will complete meiosis II and form a mature ovum.
What role do theca and granulosa cells play in the menstrual cycle?
-Theca cells secrete estrogen, and granulosa cells secrete progesterone, both of which are essential in regulating the menstrual cycle and supporting follicular development.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

✅ FOLICULOGÉNESIS ¿Qué son los FOLÍCULOS OVÁRICOS? | EMBRIOLOGÍA HUMANA 📚

Oogenesis

The ovarian cycle | Reproductive system physiology | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy
VIDEO SERI #2 ; GENETALIA INTERNA OVARIUM

Oogenesis, Struktur Ovum, dan Hormon Wanita (Reproduksi Manusia)

[eSVT] Schéma fonctionnel de la production d'hormones chez la femme
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)