Oogenesis, Struktur Ovum, dan Hormon Wanita (Reproduksi Manusia)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Widyaningsih discusses human reproduction, focusing on oogenesis, the formation of ova in females. She explains the stages of oogenesis, including the development of primary and secondary oocytes, and the structure of the ovum. The video also covers the hormonal regulation of female reproduction, detailing hormones like FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone, and their roles in follicle development, ovulation, and the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. The session ends with a brief mention of the menstrual cycle, engaging viewers with a concise overview of the reproductive system.
Takeaways
- 😀 Oogenesis is the process of egg cell (ovum) formation in females, occurring in the ovaries.
- 😀 The formation of an ovum involves stages like the primary oocyte, secondary oocyte, and eventually the mature ovum.
- 😀 Oogenesis begins with oogonium, which undergoes mitosis during fetal development, producing primary oocytes.
- 😀 Meiosis I leads to the formation of secondary oocytes and polar bodies, while Meiosis II produces ootids and secondary polar bodies.
- 😀 The ovum has several structural components, including the corona radiata, zona pellucida, vitelline membrane, and the yolk (cytoplasm).
- 😀 The nucleus of the ovum contains haploid genetic material (n).
- 😀 Polar bodies are small cells resulting from oogenesis, containing little cytoplasm, and are eventually discarded.
- 😀 The process of oogenesis results in one mature ovum and several polar bodies that degenerate.
- 😀 Female reproductive hormones include FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone), LH (Luteinizing Hormone), estrogen, and progesterone, each playing a key role in reproduction.
- 😀 FSH stimulates the development of primary follicles into Graafian follicles in the ovaries, while LH triggers ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum.
- 😀 Estrogen is responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics in women and the thickening of the uterine lining (endometrium).
- 😀 Progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum and is crucial for maintaining the endometrium in preparation for pregnancy.
Q & A
What is oogenesis?
-Oogenesis is the process of formation of the ovum (female gamete) in the ovaries. It involves the development of oogonium into primary oocytes, secondary oocytes, and eventually the mature ovum.
What is the role of the Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) in the female reproductive system?
-FSH is produced by the anterior pituitary gland and is responsible for stimulating the development of primary follicles into Graafian follicles, which are mature and ready for ovulation.
What is the significance of the structure 'corona radiata' in the ovum?
-The corona radiata is the outermost protective layer of the ovum. It contains hyaluronidase, an enzyme that aids in fertilization by breaking down the barriers surrounding the egg.
How does the process of meiosis contribute to the formation of the ovum?
-Meiosis in oogenesis begins with the primary oocyte undergoing Meiosis I to form a secondary oocyte and a polar body. Meiosis II completes when the secondary oocyte forms an ootid, which then matures into an ovum.
What is the role of luteinizing hormone (LH) in female reproduction?
-LH is also produced by the anterior pituitary and plays a key role in transforming the Graafian follicle into the corpus luteum and triggering ovulation, which is the release of the ovum.
What function does estrogen perform in the female reproductive system?
-Estrogen is produced by the Graafian follicle and is essential for developing secondary sexual characteristics in women, as well as for thickening the endometrial lining to prepare the uterus for pregnancy.
What is the role of progesterone in pregnancy?
-Progesterone is secreted by the corpus luteum and is crucial for maintaining the endometrium, ensuring it remains suitable for the implantation of a fertilized egg, which is essential for pregnancy.
What are polar bodies and how are they formed during oogenesis?
-Polar bodies are small cells that are formed during meiosis in oogenesis. They are the result of unequal cell division and contain minimal cytoplasm. They do not develop into ova.
What is the function of the zona pellucida in the ovum?
-The zona pellucida is the middle protective layer of the ovum. It is thick and contains glycoproteins, playing a key role in the fertilization process by allowing sperm to bind to it.
What happens to the primary oocyte during the menstrual cycle?
-At the start of the menstrual cycle, primary oocytes undergo meiosis I, leading to the formation of secondary oocytes, which are released during ovulation, marking the progression from oogenesis to potential fertilization.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
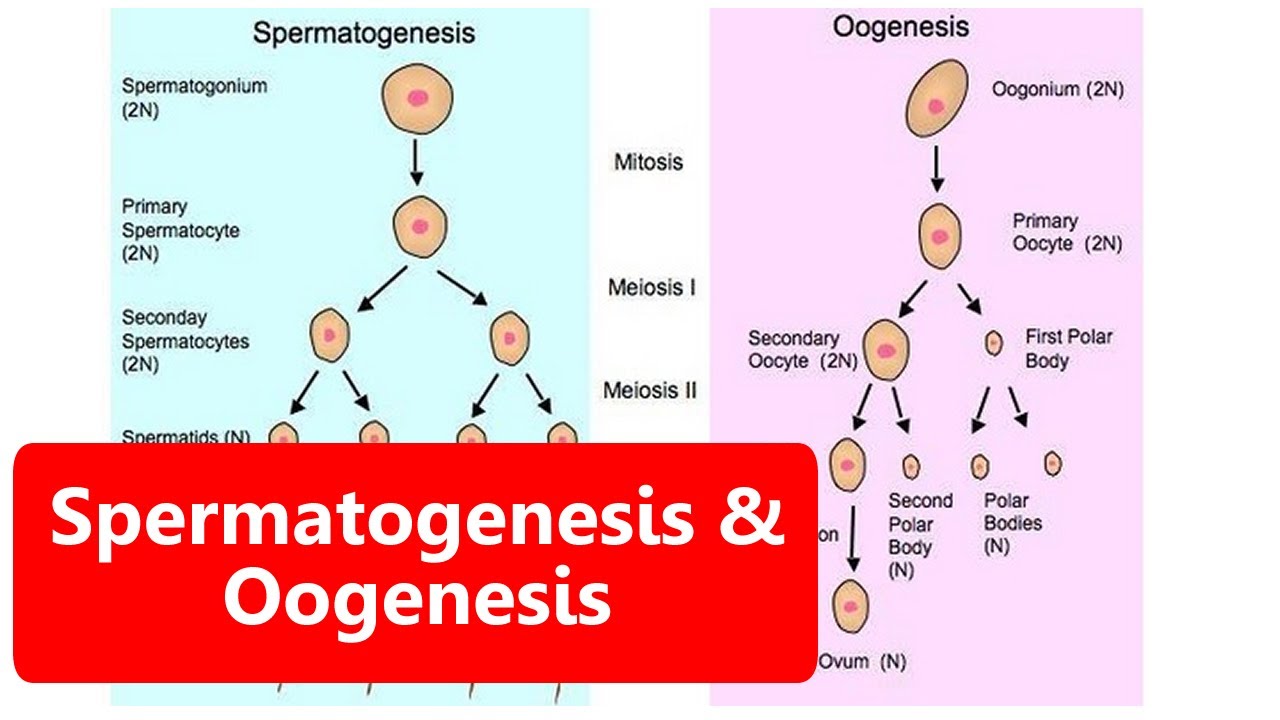
SPERMATOGENESIS DAN OOGENESIS - Sistem Reproduksi Pada Manusia | Belajar IPA Kelas 9 SMP/ MTS

GAMETOGENESIS #videopembelajaranipa @nova_scienceart9251

Mekanisme Hormon pada Genital Betina (Wanita) dan Jantan (Pria)

Gamet Structure part 1
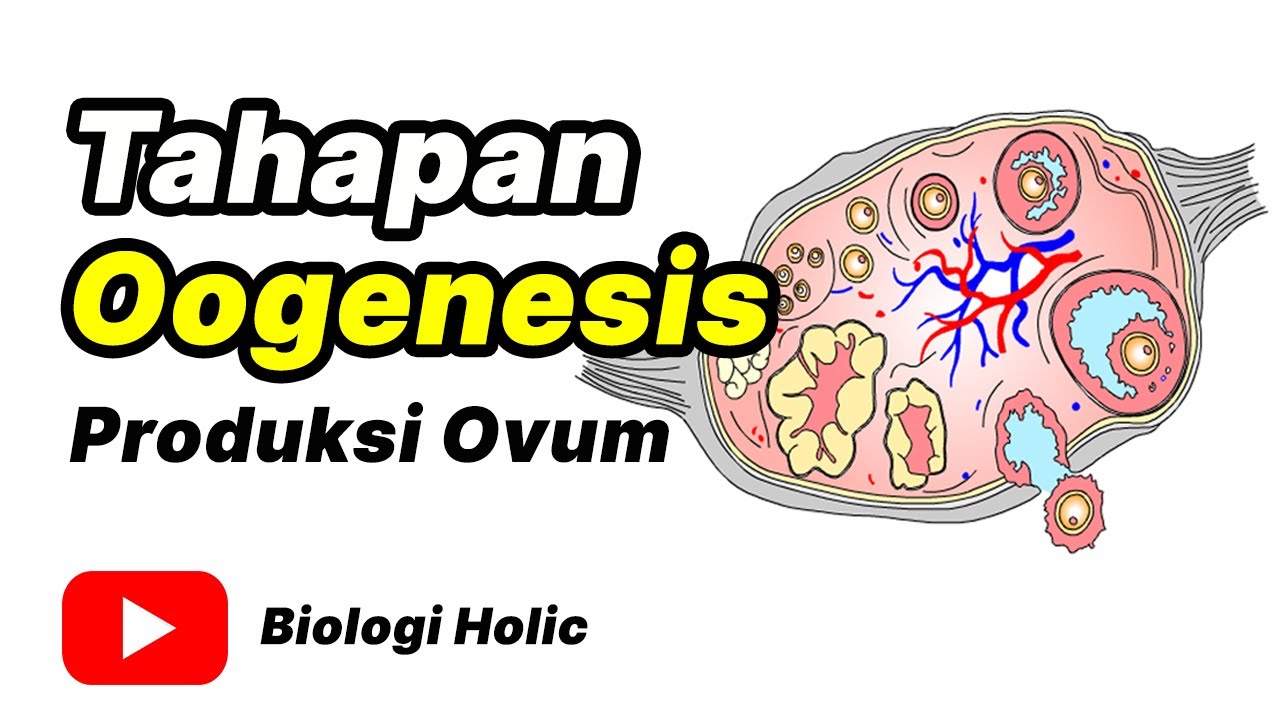
Tahap oogenesis | Produksi ovum (Animasi)

Oogenesis and Spermatogenesis | Reproductive
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)