PORIFERA/SPONS/KINDOM ANIMALIA/DUNIA HEWAN/INVERTEBRATA/VERTEBRATA/ANIMAL KINGDOM/SMA KELAS 10
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the fascinating world of Porifera (sponges), covering their key characteristics, structures, classification, and ecological importance. Porifera are simple, multicellular animals with porous bodies and lack organs, making them unique in the animal kingdom. The video explains their modes of reproduction, including both asexual and sexual methods, and the roles they play in filtering water, maintaining marine ecosystems, and offering industrial and medicinal benefits. It also highlights the three main classes of sponges and the various canal systems they possess. A comprehensive overview, perfect for those interested in marine biology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Porifera have a porous body that allows water to flow through, enabling filtration feeding.
- 😀 They are multicellular organisms, meaning they are made up of many cells, unlike unicellular species.
- 😀 Porifera are diploblastic, meaning they have two body layers, the ectoderm and endoderm, during embryonic development.
- 😀 They are considered parazoans, meaning they lack specialized organs and a nervous system.
- 😀 Porifera have a high regeneration ability, allowing them to regrow lost parts of their bodies.
- 😀 They are suspension feeders, capturing food particles suspended in water using structures like cilia or seta.
- 😀 Porifera live in both freshwater and marine environments, and they generally have limited movement, being mostly sessile.
- 😀 Asexual reproduction in porifera occurs via budding or gemmules, while sexual reproduction involves fertilization between male and female cells.
- 😀 Porifera can exhibit radial symmetry or be asymmetrical, depending on the species.
- 😀 Porifera are classified into three main classes based on skeletal composition: Calcarea (calcium carbonate spicules), Hexactinellida (silica spicules), and Demospongiae (silica and spongin spicules).
Q & A
What is the primary characteristic of Porifera?
-The primary characteristic of Porifera is their porous body structure, which is essential for their water filtration system.
How is the body of Porifera structured?
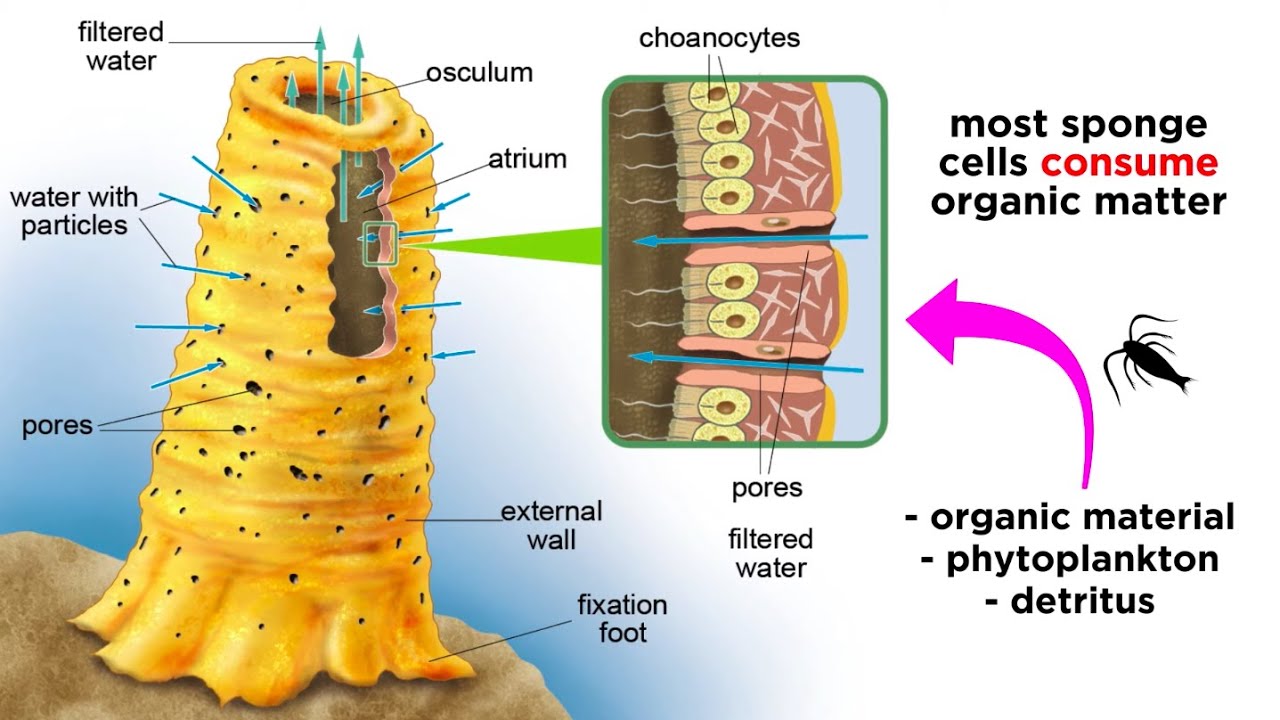
-Porifera have a simple body structure with multiple pores (ostia) for water intake, a central cavity called the spongocoel, and an opening called the osculum where water exits.
What does it mean that Porifera are diploblastic?
-Being diploblastic means that Porifera have two embryonic layers: the ectoderm (outer layer) and the endoderm (inner layer).
Why are Porifera classified as parazoans?
-Porifera are classified as parazoans because they lack true organs and have a simpler body organization compared to more complex animals.
What is the role of choanocytes in Porifera?
-Choanocytes, or collar cells, play a critical role in capturing food particles from the water, as they have flagella that create water currents and microvilli that trap food.
What are the three main classes of Porifera and their key differences?
-The three main classes of Porifera are: Calcarea (spicules made of calcium carbonate, marine habitat), Hexactinellida (glass sponges with silica spicules, live in deep waters), and Demospongiae (sponges with silica and spongin spicules, diverse in habitat and form).
What is the significance of the regeneration ability of Porifera?
-The high regeneration ability of Porifera allows them to recover from damage and reproduce through processes like budding or gemulation, making them resilient in their environments.
How do Porifera reproduce sexually?
-Porifera reproduce sexually through a process involving the fertilization of sperm and eggs, producing a larvae that eventually settles and grows into a new sponge.
What are the different water flow systems in Porifera and how do they differ?
-Porifera have three types of water flow systems: Asconoid (simple, with a central cavity), Syconoid (more complex, with radial canals), and Leuconoid (most complex, with many chambers for filtration).
What are some ecological and industrial roles of Porifera?
-Ecologically, Porifera provide habitats for various marine organisms and contribute to water filtration. Industrially, they are used in cosmetics, as building materials in some cultures, and have potential pharmaceutical uses.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Penjelasan PORIFERA ( Zoologi Invertebrata)

VIDEOAULA | Ciências | 8º ANO | Animais invertebrados I

MENGENAL FILUM PORIFERA BAGIAN DARI ANIMALIA

Biologi sma materi Invertebrata (9 filum hewan tidak bertulang belakang) bab animalia kelas 10
Phylum Porifera: Sponges

Learn Biology: Kingdom Animalia: Phylum Porifera |iKen | iKen Edu | iKen App
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)